Abstract
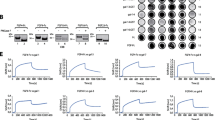
We investigated interaction of GM3 with N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) termini of N-linked glycans of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), as the underlying mechanism for inhibitory effect of GM3 on EGFR activation, using ldlD cells transfected with EGFR gene. These cells, defective in UDP-Gal/UDP-GalNAc 4-epimerase, are incapable of synthesizing galactose (Gal)-containing glycans, unless Gal is provided in culture (+Gal). Key observations: (1) Expression of GlcNAc termini was high in −Gal cells, and strongly reduced in +Gal cells. (2) Comparative study of inhibitory effect of exogenously-added GM3 on EGFR activation in +Gal versus −Gal cells indicated that higher level of GlcNAc termini on EGFR is correlated with greater inhibitory effect of GM3. (3) GM3-, but not GM1-, coated beads bound to EGFR in lysate of −Gal cells, which have highly exposed GlcNAc termini. Such binding was inhibited in the presence of EDTA, similarly to other carbohydrate-carbohydrate interactions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- Gal:
-
Galactose
- GlcNAc:
-
N-acetylglucosamine
- ITS:
-
Insulin/transferrin/selenium
- ldlD/EGFR:
-
ldlD cells transfected with EGFR gene
- SDS–PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
References
Cohen S, Carpenter G, King L (1980) Epidermal growth factor receptor-protein kinase interactions: co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem 255:4834–4842
Ushiro H, Cohen S (1980) Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem 255:8363–8365
Hakomori S, Murakami WT (1968) Glycolipids of hamster fibroblasts and derived malignant-transformed cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 59:254–261
Sakiyama H, Gross SK, Robbins PW (1972) Glycolipid synthesis in normal and virus-transformed hamster cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 69:872–876
Chandrabose KA, Graham JM, Macpherson IA (1976) Glycolipid glycosyl transferases of a hamster cell line in culture. II. Subcellular distribution and the effect of culture age and density. Biochim Biophys Acta 429:112–122
Langenbach R, Kennedy S (1978) Gangliosides and their cell density-dependent changes in control and chemically transformed C3H/10T1/2 cells. Exp Cell Res 112:361–372
Bremer EG, Schlessinger J, Hakomori S (1986) Ganglioside-mediated modulation of cell growth: specific effects of GM3 on tyrosine phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem 261:2434–2440
Bremer EG, Hakomori S, Bowen-Pope DF et al (1984) Ganglioside-mediated modulation of cell growth, growth factor binding, and receptor phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 259:6818–6825
Toledo MS, Suzuki E, Handa K et al (2004) Cell growth regulation through GM3-enriched microdomain (glycosynapse) in human lung embryonal fibroblast WI38 and its oncogenic transformant VA13. J Biol Chem 279:34655–34664
Mutoh T, Tokuda A, Miyada T et al (1995) Ganglioside GM1 binds to the Trk protein and regulates receptor function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5087–5091
Nojiri H, Stroud MR, Hakomori S (1991) A specific type of ganglioside as a modulator of insulin-dependent cell growth and insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity: possible association of ganglioside-induced inhibition of insulin receptor function and monocytic differentiation induction in HL60 cells. J Biol Chem 266:4531–4537
Weis FMB, Davis RJ (1990) Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signal transduction: role of gangliosides. J Biol Chem 265:12059–12066
Kingsley DM, Kozarsky KF, Hobbie L et al (1986) Reversible defects in O-linked glycosylation and LDL receptor expression in a UDP-Gal/UDP-GalNAc 4-epimerase deficient mutant. Cell 44:749–759
Yoon S, Nakayama K, Hikita T et al (2006) Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase is modulated by GM3 interaction with N-linked GlcNAc termini of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18987–18991
Kawashima N, Yoon SJ, Itoh K et al (2009) Tyrosine kinase activity of epidermal growth factor receptor is regulated by GM3 binding through carbohydrate to carbohydrate interactions. J Biol Chem 284:6147–6155
Symington FW, Fenderson BA, Hakomori S (1984) Fine specificity of a monoclonal anti-testicular cell antibody for glycolipids with terminal N-acetyl-D-glucosamine structure. Mol Immunol 21:877–882
Guan F, Handa K, Hakomori S (2009) Specific glycosphingolipids mediate epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human and mouse epithelial cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:7461–7466
Mitsuzuka K, Handa K, Satoh M et al (2005) A specific microdomain (“glycosynapse 3”) controls phenotypic conversion and reversion of bladder cancer cells through GM3-mediated interaction of alpha3beta1 integrin with CD9. J Biol Chem 280:35545–35553
Krieger M (1983) Complementation of mutations in the LDL pathway of receptor-mediated endocytosis by cocultivation of LDL receptor-defective hamster cell mutants. Cell 33:413–422
Ono M, Handa K, Withers DA et al (1999) Motility inhibition and apoptosis are induced by metastasis-suppressing gene product CD82 and its analogue CD9, with concurrent glycosylation. Cancer Res 59:2335–2339
Ono M, Handa K, Sonnino S et al (2001) GM3 ganglioside inhibits CD9-facilitated haptotactic cell motility: co-expression of GM3 and CD9 is essential in down-regulation of tumor cell motility and malignancy. Biochemistry 40:6414–6421
Kawakami Y, Kawakami K, Steelant WFA et al (2002) Tetraspanin CD9 is a “proteolipid”, and its interaction with a3 integrin in microdomain is promoted by GM3 ganglioside, leading to inhibition of laminin-5-dependent cell motility. J Biol Chem 277:34349–34358
Kobata A (1996) Cancer cells and metastasis: the Warren-Glick phenomenon: basis of tumorigenesis and metastasis. In: Montreuil J, Vliegenthart JFG, Schachter H (eds) Glycoproteins and disease. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 211–227
Yamashita K, Kamerling JP, Kobata A (1982) Structural study of the carbohydrate moiety of hen ovomucoid: occurrence of a series of pentaantennary complex-type asparagine-linked sugar chains. J Biol Chem 257:12809–12814
Shankar Iyer PN, Wilkinson KD, Goldstein IJ (1976) An N-acetyl-D-glycosamine binding lectin from Bandeiraea simplicifolia seeds. Arch Biochem Biophys 177:330–333
Eggens I, Fenderson BA, Toyokuni T et al (1989) Specific interaction between Lex and Lex determinants: a possible basis for cell recognition in preimplantation embryos and in embryonal carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 264:9476–9484
Kojima N, Fenderson BA, Stroud MR et al (1994) Further studies on cell adhesion based on Lex-Lex interaction, with new approaches: embryoglycan aggregation of F9 teratocarcinoma cells, and adhesion of various tumour cells based on Lex expression. Glycoconj J 11:238–248
Handa K, Kojima N, Hakomori S (2000) Analysis of glycolipid-dependent cell adhesion based on carbohydrate-carbohydrate interaction. Meth Enzymol 312:447–458
Yoon S, Nakayama K, Takahashi N et al (2006) Interaction of N-linked glycans, having multivalent GlcNAc termini, with GM3 ganglioside. Glycoconj J 23:639–649
Schlessinger J (1988) Signal transduction by allosteric receptor oligomerization. Trends Biochem Sci (TIBS) 13:443–447
Ullrich A, Schlessinger J (1990) Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell 61:203–212
Zhou Q, Hakomori S, Kitamura K et al (1994) GM3 directly inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation and de-N-acetyl-GM3 directly enhances serine phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor, independently of receptor-receptor interaction. J Biol Chem 269:1959–1965
Lee L, Abe A, Shayman JA (1999) Improved inhibitors of glucosylceramide synthase. J Biol Chem 274:14662–14669
Park S-Y, Yoon S-J, Freire-de-Lima L et al (2009) Control of cell motility by interaction of gangliosides, tetraspanins, and epidermal growth factor receptor in A431 vs. Kb epidermoid tumor cells. Carbohydr Res 344:1479–1486
Rebbaa A, Yamamoto H, Moskal JR et al (1996) Binding of erythroagglutinating phytohemagglutinin lectin from Phaseolus vulgaris to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibits receptor function in the human glioma cell line, U373 MG. J Neurochem 67:2265–2272
Rebbaa A, Yamamoto H, Saito T et al (1997) Gene transfection-mediated overexpression of b1,4 GlcNAc bisecting oligosaccharide structure in a glioma cell line, U373MG, inhibits EGF receptor function. J Biol Chem 272:9275–9280
Schachter H (1986) Biosynthetic controls that determine the branching and microheterogeneity of protein-bound oligosaccharides. Biochem Cell Biol 64:163–181
Kang R, Saito H, Ihara Y et al (1996) Transcriptional regulation of the N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V gene in human bile duct carcinoma cells (HuCC-T1) is mediated by Ets-1. J Biol Chem 271:26706–26712
Buckhaults P, Chen L, Freigen N et al (1997) Transcriptional regulation of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V by the src oncogene. J Biol Chem 272:19575–19581
Yoshimura M, Nishikawa A, Ihara Y et al (1995) Suppression of lung metastasis of B16 mouse melanoma by N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase III gene transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8754–8758
Yoshimura M, Ihara Y, Matsuzawa Y et al (1996) Aberrant glycosylation of E-cadherin enhances cell-cell binding to suppress metastasis. J Biol Chem 271:13811–13815
Cummings RD, Kornfeld S (1982) Characterization of structural determinants required for the high-affinity interaction of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides with immobilized Phaseolus vulgaris leukoagglutinating and erythroagglutinating lectins. J Biol Chem 257:11230–11234
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by NIH National Cancer Institute grant 2 R01 CA080054. The authors thank Monty Krieger for donation of ldlD14 cells, Roger Davis for donation of plasmid pXER, and Steve Anderson for help in preparing the manuscript and figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue: In Honor of Dr. Robert K. Yu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, F., Handa, K. & Hakomori, Si. Regulation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Through Interaction of Ganglioside GM3 with GlcNAc of N-Linked Glycan of the Receptor: Demonstration in ldlD Cells. Neurochem Res 36, 1645–1653 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0379-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0379-9