Abstract
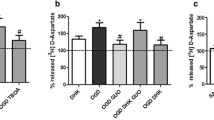
Glutathione (γ-glutamylcysteinylglycine, GSH and oxidized glutathione, GSSG), may function as a neuromodulator at the glutamate receptors and as a neurotransmitter at its own receptors. We studied now the effects of GSH, GSSG, glutathione derivatives and thiol redox agents on the spontaneous, K+- and glutamate-agonist-evoked releases of [3H]dopamine from mouse striatal slices. The release evoked by 25 mM K+ was inhibited by GSH, S-ethyl-, -propyl-, -butyl- and pentylglutathione and glutathione sulfonate. 5,5′-Dithio-bis-2-nitrobenzoate (DTNB) and l-cystine were also inhibitory, while dithiothreitol (DTT) and l-cysteine enhanced the K+-evoked release. Ten min preperfusion with 50 μM ZnCl2 enhanced the basal unstimulated release but prevented the activation of K+-evoked release by DTT.
Kainate and 2-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate (AMPA) evoked dopamine release but the other glutamate receptor agonists N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA), glycine (1 mM) and trans-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylate (t-ACPD, 0.5 mM), and the modulators GSH, GSSG, glutathione sulfonate, S-alkyl-derivatives of glutathione, DTNB, cystine, cysteine and DTT (all 1 mM) were without effect. The release evoked by 1 mM glutamate was enhanced by 1 mM GSH, while GSSG, glutathionesulfonate and S-alkyl derivatives of glutathione were generally without effect or inhibitory. NMDA (1 mM) evoked release only in the presence of 1 mM GSH but not with GSSG, other peptides or thiol modulators. l-Cysteine (1 mM) enhanced the glutamate-evoked release similarly to GSH. The activation by 1 mM kainate was inhibited by S-ethyl-, -propyl-, and -butylglutathione and the activation by 0.5 mM AMPA was inhibited by S-ethylglutathione but enhanced by GSSG.
Glutathione alone does not directly evoke dopamine release but may inhibit the depolarization-evoked release by preventing the toxic effects of high glutamate, and by modulating the cysteine–cystine redox state in Ca2+ channels. GSH also seems to enhance the glutamate-agonist-evoked release via both non-NMDA and NMDA receptors. In this action, the γ-glutamyl and cysteinyl moieties of glutathione are involved.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lenhoff HM (1998) The discovery of the GSH receptor in hydra and its evolutionary significance. In: Shaw CA (ed) Glutathione in the nervous system. Taylor & Francis, Washington, DC, pp 25–43
Shaw CA (1998) Multiple roles of glutathione in the nervous system. In: Shaw CA (ed) Glutathione in the nervous system. Taylor & Francis, Washington, DC, pp 3–23
Janáky R, Shaw CA, Varga V, Hermann A, Dohovics R, Saransaari P, Oja SS (2000) Specific glutathione binding sites in pig cerebral cortical synaptic membranes. Neuroscience 95:617–624
Shaw CA, Pasqualotto BA, Curry K (1996) Glutathione-induced sodium currents in neocortex. Neuroreport 7:1149–1152
Zängerle L, Cuénod M, Winterhalter KH, Do KQ (1992) Screening of thiol compounds: depolarization-induced release of glutathione and cysteine from rat brain slices. J Neurochem 59:181–189
Ogita K, Kitago T, Nakamuta H, Fukuda Y, Koida M, Ogawa Y, Yoneda Y (1986) Glutathione-induced inhibition of Na+-independent and -dependent bindings of L-[3H]glutamate in rat brain. Life Sci 39:2411–2418
Oja SS, Varga V, Janáky R, Kontro P, Aarnio T, Marnela K-M (1988) Glutathione and glutamatergic neurotransmission in the brain. In: Cavalheiro EA, Lehmann J, Turski L (eds) Frontiers in excitatory amino acid research. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 75–78
Varga V, Janáky R, Marnela K-M, Gulyás J, Kontro P, Oja SS (1989) Displacement of excitatory amino acid receptor ligands by acidic oligopeptides. Neurochem Res 14:1223–1227
Janáky R, Varga V, Oja SS, Saransaari P (1994) Release of [3H]GABA evoked by glutamate agonists from hippocampal slices: effects of dithiothreitol and glutathione. Neurochem Int 24:575–582
Oja SS, Janáky R, Saransaari P, Jenei Zs, Varga V (1995) Interaction of glutathione derivatives with brain 2-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate (AMPA) receptors. Proc West Pharmacol Soc 38:9–11
Janáky R, Varga V, Jenei Zs, Saransaari P, Oja SS (1998) Glutathione and glutathione derivatives: possible modulators of ionotropic glutamate receptors. In: Shaw CA (ed) Glutathione in the nervous system. Taylor & Francis, Washington, DC, pp 163–196
Terramani T, Kessler M, Lynch G, Baudry M (1988) Effects of thiol-reagents on [3H]α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid binding to rat telencephalic membranes. Mol Pharmacol 34:117–123
Aizenman E., Lipton SA, Loring RH (1989) Selective modulation of NMDA responses by reduction and oxidation. Neuron 2:1257–1263
Janáky R, Ogita K, Pasqualotto BA, Bains JS, Oja SS, Yoneda Y, Shaw CA (1999) Glutathione and signal transduction in the mammalian CNS. J Neurochem 73:889–902
Perry TL, Godin DV, Hansen S (1982) Parkinson’s disease: a disorder due to nigral glutathione deficiency? Neurosci Lett 33:305–310
Bannon MJ, Goedert M, Williams B (1984) The possible relationship of glutathione, melanin, and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) to Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Pharmacol 33:2697–2698
Perry TL, Yong VW (1986) Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy and glutathione metabolism in the substantia nigra of patients. Neurosci Lett 67:269–274
Riederer P, Sofic E, Rausch W-D, Schmidt B, Reynolds GP, Jellinger K, Yudim MB (1989) Transition metals, ferritin, glutathione, and ascorbic acid in parkinsonian brains. J Neurochem 52:515–520
Yong VW, Perry TL, Krisman AA (1986) Depletion of glutathione in brainstem of mice by N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine is prevented by antioxidant treatment. Neurosci Lett 63:56–60
Andersen JK, Mo JQ, Hom DG, Lee FY, Harnish P, Hamill RW, McNeill TH (1996) Effect of buthionine sulfoximine, a synthesis inhibitor of the antioxidant glutathione, on the murine nigrostriatal neurons. J Neurochem 67:2164–2171
Masuoka DT, Jonsson G, Finch CE (1979) Aging and unusual catecholamine-containing structures in the mouse brain. Brain Res 169:335–341
McNeill TH, Koek LL, Haycock JW (1984) Age-correlated changes in dopaminergic nigrostriatal perikarya of the C57BL/6Nni mouse. Mech Ageing Dev 24:293–307
Felten DL, Felten SY, Fuller RW, Romano DT, Smalstig EB, Wong DT, Clemens JA (1992) Chronic dietary pergolide preserves nigrostriatal neuronal integrity in aged F344 rats. Neurobiol Aging 13:339–351
Pileblad E, Magnusson T (1990) Effective depletion of glutathione in rat striatum and substantia nigra by L-buthionine sulfoximine in combination with 2-cyclohexen-1-one. Life Sci 47:2333–2342
Paxinos G, Franklin WBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
DiChiara G, Morelli M (1993) Dopamine-acetylcholine-glutamate interactions in the striatum: a working hypothesis. Adv Neurol 60:102–106
Chéramy A, Desce JM, Godeheu, Glowinski J (1994) Presynaptic control of dopamine synthesis and release by excitatory amino acids in rat striatal synaptosomes. Neurochem Int 25:145–154
Morari M, O’Connor WT, Darvelid M, Ungerstedt U, Bianchi C, Fuxe K (1996) Functional neuroanatomy of the nigrostriatal and striatonigral pathways as studied with dual probe microdialysis in the awake rat. I. Effects of perfusion with tetrodotoxin and low-calcium medium. Neuroscience 72:79–87
Janáky R, Varga V, Hermann A, Saransaari P, Oja SS (2000) Mechanisms of L-cysteine neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res 25:1397–1405
Cho Y, Bannai S (1990) Uptake of glutamate and cystine in C-6 glioma cells and in cultured astrocytes. J Neurochem 55:2091–2097
Gilbert KR, Aizenman E, Reynolds IJ (1991) Oxidized glutathione modulates N-methyl-D-aspartate- and depolarization-induced increases in intracellular Ca2+ in cultured rat forebrain neurons. Neurosci Lett 133:11–14
Ruppersberg JP, Stocker M, Pongs O, Heinemann SH, Frank K, Koenen M (1991) Regulation of fast inactivation of cloned mammalian Ik(A) channels by cysteine oxidation. Nature 352:711–714
Maret W (1998) The glutathione redox state and zinc mobilization from metallothionein and other proteins with zinc-sulfur coordination sites. In: Shaw CA (ed) Glutathione in the nervous system. Taylor & Francis, Washington, DC, pp 257–273
Hermann A, Varga V, Janáky R, Dohovics R, Saransaari P, Oja SS (2000) Interference of S-nitrosoglutathione with the binding of ligands to ionotropic glutamate receptors in pig cerebral cortical synaptic membranes. Neurochem Res 25:1119–1124
Chinta SJ, Andersen JK (2006) Reversible inhibition of mitochondrial complex I activity following chronic dopaminergic glutathione depletion in vitro: implications for Parkinson’s disease. Free Rad Biol Med 41:1442–1448
Hsu M, Srinivas B, Kumar J, Subramanian R, Andersen J (2005) Glutathione depletion resulting in selective mitochondrial complex I inhibition in dopaminergic cells via an NO-mediated mitochondrial pathway not involving peroxynitrite: implications for Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 92:1091–1103
Li Y-J, Scott WK, Zhang L, Lin P-I, Oliveira SA, Skelly T, Doraiswamy MP, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Martin ER, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Vance JM (2006) Revealing the role of glutathione S-transferase omega in age-at-onset of Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. Neurobiol Aging 27:1087–1093
Duncan MW, Marini AM, Watters R, Kopin IJ, Markey SP (1992) Zinc, a neurotoxin to cultured neurons, contaminates Cycad flour prepared by traditional Guamanian methods. J Neurosci 12:1523–1537
Leviel V, Gobert A, Guibert B (1990) The glutamate-mediated release of dopamine in the rat striatum: further characterization of the dual excitatory-inhibitory function. Neuroscience 39:305–312
Krebs MO, Desce JM, Kemel ML, Gauchy C, Godehey G, Chéramy A, Glowinski J (1991) Glutamatergic control of dopamine release in the rat striatum: evidence for presynaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on dopaminergic nerve terminals. J Neurochem 56:81–85
O’Connor WT, Drew KL, Ungerstedt U (1995) Differential cholinergic regulation of dopamine release in the dorsal and ventral neostriatum of the rat: an in vivo microdialysis study. J Neurosci 15:8353–8361
Varga V, Jenei Zs, Janáky R, Saransaari P, Oja SS (1997) Glutathione is an endogenous ligand of rat brain N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and 2-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate (AMPA) receptors. Neurochem Res 22:1165–1171
Sucher NJ, Lipton SA (1991) Redox modulatory site of the NMDA receptor-channel complex: regulation by oxidized glutathione. J Neurosci Res 30: 582–591
Ogita K, Enomoto R, Nakahara F, Ishitsubo N, Yoneda Y (1995) A possible role of glutathione as an endogenous agonist in the N-methyl-D-asparate recognition domain in rat brain. J Neurochem 64:1088–1096
Clow DW, Jhamandas K (1989) Characterization of L-glutamate action on the release of endogenous dopamine from the rat caudate-putamen. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248:722–728
Borkowska HD, Oja SS, Saransaari P, Albrecht J (1997) Release of [3H]dopamine from striatal and cerebral cortical slices from rats with thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy: different responses to stimulation by potassium ion and agonists of ionotrophic glutamate receptors. Neurochem Res 22:101–106
Acknowledgments
The skilful technical assistance of Ms Oili Pääkkönen, Ms. Irma Rantamaa and Ms Sari Luokkala is gratefully acknowledged. The study was financially supported by the competitive research funding of Pirkanmaa Hospital District.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janáky, R., Dohovics, R., Saransaari, P. et al. Modulation of [3H]Dopamine Release by Glutathione in Mouse Striatal Slices. Neurochem Res 32, 1357–1364 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9315-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9315-z