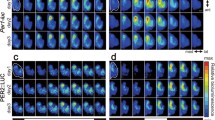
Using an immunohistochemical technique and densitometric analysis in experiments on rats, we examined the expression of an early-response protein, c-Fos, in the medial parvicellular subnucleus of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (mpcPVN). During 7 days, the animals were kept under conditions of (i) normal photoperiod (group LD), (ii) continuous illumination (group LL), and (iii) continuous darkness (light deprivation, group DD). It was found that both normal photoperiodicity and artificial modifications of the latter result in significant changes of c-Fos immunopositivity in the nuclei of mpcPVN neurons (cells that synthesize corticotropin-releasing factor). Changes in the indices of concentration and amount of c-Fos in mpcPVN neurons were, from some aspects, similar to those observed under analogous experimental conditions in neurons of a leading pacemaker of the circadian periodicity, the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SChNs) of the hypothalamus [10], but, at the same time, demonstrated noticeable specificity from other aspects. In all experimental groups, the concentration and amount of c-Fos in mpcPVN neurons were greater during daytime than at night. Dramatic increases in the above parameters observed at daytime in rats subjected to light deprivation were the most significant effect of modifications of the photoperiod. Both continuous illumination and light deprivation resulted in some increase of the number (density) of c-Fos-immunopositive units in the mpcPVN. The nuclei of neurons of this structure demonstrated the phenomenon found earlier in SChN neuron; geometrical dimensions of the cell nuclei of these structures depended noticeably on both illumination conditions and periodicity. Probable mechanisms of the dependence of c-Fos expression in the hypothalamic nuclei on the photoperiod and its modifications, interdependence of such changes observed in the circadian pacemaker (SChN) and an important component of the system controlling the stress reactions (mpcPVN), and the relation of the above phenomena to the level of melatonin produced by the epiphysis cerebri (main neuroendocrine intermediator organizing the above-mentioned periodicity) are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. A. Golombek, G. A. Ferreyra, M. E. Katz, et al., “Neurochemistry of mammalian entrainment: Signal transduction pathways in the suprachiasmatic nuclei,” Biol. Rhythm Res., 31, No. 1, 56–70 (2000).
C. Green and M. Menaker, “Circadian rhythms. Clocks of the brain,” Science, 301, No. 5631, 319–320 (2003).
I. I. Zamorskii and V. P. Pishak, “Functional organization of the cerebral photoperiodic system,” Usp. Fiziol. Nauk, 34, No. 4, 37–53 (2003).
R. J. Reiter, “Melatonin: clinical relevance,” Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 17, No. 2, 273–285 (2003).
P. Witt-Enderby, J. Bennett, M. Jarzynka, et al., “Melatonin receptors and their regulation: biochemical and structural mechanisms,” Life Sci., 72, No. 2, 2183–2198 (2003).
J. Arendt, “Melatonin: characteristics, concerns, and prospects,” J. Biol. Rhythms, 20, 291–303 (2005).
L. A. Bondarenko, G. I. Goubina-Vakulik, N. N. Sotnik, and A. R. Gevorkyan, “Effects of continuous illumination on the circadian rhythm of melatonin and structure of the pineal gland in rabbits,” Probl. Endokrinol. Patol., No. 4, 38–45 (2005).
J. Hannibal, N. Vrang, J. Card, and J. Fahrenkrug, “Lightdependent induction of c-Fos during subjective day and night in PACAP-containing ganglion cells of the retinohypothalamic tract,” J. Biol. Rhythms, 16, No. 5, 457–470 (2001).
M. T. Barakat, B. F. O’Hara, V. H. Cao, et al., “Light induces c-fos and per1 expression in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of arrhythmic hamsters,” Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol., 289, No. 5, R1381–R1386 (2005).
V. P. Pishak, R. E. Bulyk, and D. A. Vasilenko, “State of the gene of early functional activity c-fos in neurons of the suprachiasmatic hypothalamic nuclei in rats under conditions of modifications of the photoperiod,” Neurophysiology, 40, No. 2, 112–119 (2008).
G. D. Paxinos and C. C. Watson, The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Acad. Press, New York (1985).
J. M. Polak and S. Van Norden, An Introduction to Immunocytochemistry: Current Techniques and Problems [in Russian], Mir, Moscow (1987).
R. Dauchy, L. Sauer, D. Blask, and G. Vaughan, “Light contamination during the dark phase in “photoperiodically controlled” animal rooms: effect on tumor growth and metabolism in rats,” Lab. Anim. Sci., 47, No. 5, 511–518 (1997).
D. A. Vasilenko, I. E. Kuznetsov, and N. I. Bondarenko, “Morphological rearrangements in the preoptic/anterior hypothalamus in hyper- and hyponatremia,” Arkh. Klin. Eksp. Med., 12, No. 1, Suppl., 6 (2003).
G. Z. Mikhailova, N. V. Tiras, V. D. Pavlik, et al., “Morphological characteristics of Mauthner neurons in goldfishes with modified asymmetry of motor behavior,” Neurophysiology, 38, No. 1, 18–31 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bulyk, R.E., Vasilenko, D.A., Pishak, V.P. et al. Neurons of the Paraventricular Hypothalamic Nucleus Under Normal and Modified Illumination Conditions: Immunohistochemical and Morphometric Parallels. Neurophysiology 44, 26–32 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-012-9263-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-012-9263-3