Abstract
Introduction
Various treatment options exist to salvage stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) failures for brain metastases, including repeat SRS and hypofractionated SRS (HSRS). Our objective was to report outcomes specific to salvage HSRS for brain metastases that failed prior HSRS/SRS.
Methods
Patients treated with HSRS to salvage local failures (LF) following initial HSRS/SRS, between July 2010 and April 2020, were retrospectively reviewed. The primary outcomes were the rates of LF, radiation necrosis (RN), and symptomatic radiation necrosis (SRN). Univariable (UVA) and multivariable (MVA) analyses using competing risk regression were performed to identify predictive factors for each endpoint.
Results
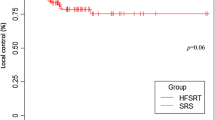
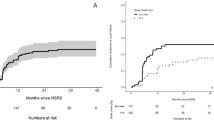
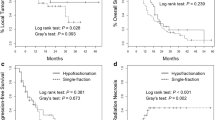
120 Metastases in 91 patients were identified. The median clinical follow up was 13.4 months (range 1.1–111.1), and the median interval between SRS courses was 13.1 months (range 3.0–56.5). 115 metastases were salvaged with 20–35 Gy in 5 fractions and the remaining five with a total dose ranging from 20 to 24 Gy in 3-fractions. 67 targets (56%) were postoperative cavities. The median re-treatment target volume and biological effective dose (BED10) was 9.5 cc and 37.5 Gy, respectively. The 6- and 12- month LF rates were 18.9% and 27.7%, for RN 13% and 15.6%, and for SRN were 6.1% and 7.0%, respectively. MVA identified larger re-irradiation volume (hazard ratio [HR] 1.02, p = 0.04) and shorter interval between radiosurgery courses (HR 0.93, p < 0.001) as predictors of LF. Treatment of an intact target was associated with a higher risk of RN (HR 2.29, p = 0.04).
Conclusion
Salvage HSRS results in high local control rates and toxicity rates that compare favorably to those single fraction SRS re-irradiation experiences reported in the literature.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gondi V, Bauman G, Bradfield L, Burri SH, Cabrera AR, Cunningham DA et al (2022) Radiation therapy for brain metastases: an ASTRO clinical practice guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2022.02.003
Suh JH, Kotecha R, Chao ST, Ahluwalia MS, Sahgal A, Chang EL (2020) Current approaches to the management of brain metastases. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 17(5):279–299. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-019-0320-3
Sahgal A, Aoyama H, Kocher M, Neupane B, Collette S, Tago M et al (2015) Phase 3 trials of stereotactic radiosurgery with or without whole-brain radiation therapy for 1 to 4 brain metastases: individual patient data meta-analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 91(4):710–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.10.024
Vogelbaum MA, Brown PD, Messersmith H, Brastianos PK, Burri S, Cahill D et al (2022) Treatment for brain metastases: ASCO-SNO-ASTRO guideline. J Clin Oncol 40(5):492–516. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.21.02314
Sahgal A, Ruschin M, Ma L, Verbakel W, Larson D, Brown PD (2017) Stereotactic radiosurgery alone for multiple brain metastases? A review of clinical and technical issues. Neurooncology 19(suppl2):ii2–ii15. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nox001
Vogelbaum MA, Angelov L, Lee S-Y, Li L, Barnett GH, Suh JH (2006) Local control of brain metastases by stereotactic radiosurgery in relation to dose to the tumor margin. J Neurosurg 104(6):907–912. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2006.104.6.907
Sneed PK, Mendez J, Vemer-Van Den Hoek JGM, Seymour ZA, Ma L, Molinaro AM et al (2015) Adverse radiation effect after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: incidence, time course, and risk factors. J Neurosurg 123(2):373–386. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.10.jns141610
Singh R, Didwania P, Lehrer EJ, Palmer JD, Trifiletti DM, Sheehan JP (2022) Repeat stereotactic radiosurgery for locally recurrent brain metastases previously treated with stereotactic radiosurgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy and safety. J Radiosurg SBRT 8(1):1–10
Heßler N, Jünger ST, Meissner A-K, Kocher M, Goldbrunner R, Grau S (2022) Recurrent brain metastases: the role of resection of in a comprehensive multidisciplinary treatment setting. BMC Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-022-09317-6
Vogelbaum MA, Suh JH (2006) Resectable brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 24(8):1289–1294. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.04.6235
Nguyen TK, Sahgal A, Detsky J, Atenafu EG, Myrehaug S, Tseng C-L et al (2020) Predictors of leptomeningeal disease following hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for intact and resected brain metastases. Neurooncology 22(1):84–93. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noz144
Cagney DN, Lamba N, Sinha S, Catalano PJ, Bi WL, Alexander BM et al (2019) Association of neurosurgical resection with development of pachymeningeal seeding in patients with brain metastases. JAMA Oncol 5(5):703. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.7204
Soliman H, Ruschin M, Angelov L, Brown PD, Chiang VLS, Kirkpatrick JP et al (2018) Consensus contouring guidelines for postoperative completely resected cavity stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 100(2):436–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.09.047
Luther E, Mansour S, Echeverry N, McCarthy D, Eichberg DG, Shah A et al (2020) Laser ablation for cerebral metastases. Neurosurg Clin N Am 31(4):537–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nec.2020.06.004
Srinivasan ES, Grabowski MM, Nahed BV, Barnett GH, Fecci PE (2021) Laser interstitial thermal therapy for brain metastases. Neuro-Oncol Adv 3(Supplement5):v16–v25. https://doi.org/10.1093/noajnl/vdab128
Shao J, Radakovich NR, Grabowski M, Borghei-Razavi H, Knusel K, Joshi KC et al (2020) Lessons learned in using laser interstitial thermal therapy for treatment of brain tumors: a case series of 238 patients from a single Institution. World Neurosurg 139:e345–e54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2020.03.213
Bartsch R, Berghoff AS, Furtner J, Marhold M, Bergen ES, Roider-Schur S et al (2022) Trastuzumab deruxtecan in HER2-positive breast cancer with brain metastases: a single-arm, phase 2 trial. Nat Med 28(9):1840–1847. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-01935-8
Alvarez-Breckenridge C, Remon J, Piña Y, Nieblas-Bedolla E, Forsyth P, Hendriks L et al (2022) Emerging systemic treatment perspectives on brain metastases: moving toward a better outlook for patients. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educational Book. https://doi.org/10.1200/edbk_352320
Franchino F, Ruda R, Soffietti R (2018) Mechanisms and therapy for Cancer metastasis to the brain. Front Oncol 8:161. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00161
Kowalchuk RO, Niranjan A, Lee CC, Yang HC, Liscak R, Guseynova K et al (2022) Reirradiation with stereotactic radiosurgery after local or marginal recurrence of brain metastases from previous radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 112(3):726–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.10.008
Minniti G, Scaringi C, Paolini S, Clarke E, Cicone F, Esposito V et al (2016) Repeated stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with progressive brain metastases. J Neurooncol 126(1):91–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1937-4
Mckay WH, Mctyre ER, Okoukoni C, Alphonse-Sullivan NK, Ruiz J, Munley MT et al (2017) Repeat stereotactic radiosurgery as salvage therapy for locally recurrent brain metastases previously treated with radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 127(1):148–156. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.5.jns153051
Sneed PK, Chan JW, Ma L, Braunstein SE, Theodosopoulos PV, Fogh SE et al (2022) Adverse radiation effect and freedom from progression following repeat stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2022.4.jns212597
Yan M, Holden L, Wang M, Soliman H, Myrehaug S, Tseng C-L et al (2022) Gamma knife icon based hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery (GKI-HSRS) for brain metastases: impact of dose and volume. J Neurooncol 159(3):705–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04115-3
Gutschenritter T, Venur VA, Combs SE, Vellayappan B, Patel AP, Foote M et al (2020) The judicious use of stereotactic radiosurgery and hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in the management of large brain metastases. Cancers 13(1):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13010070
Lehrer EJ, Peterson JL, Zaorsky NG, Brown PD, Sahgal A, Chiang VL et al (2019) Single versus multifraction stereotactic radiosurgery for large brain metastases: an international meta-analysis of 24 trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 103(3):618–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.10.038
Mehrabian H, Desmond KL, Soliman H, Sahgal A, Stanisz GJ (2017) Differentiation between radiation necrosis and tumor progression using chemical exchange saturation transfer. Clin Cancer Res 23(14):3667–3675. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-2265
Mouraviev A, Detsky J, Sahgal A, Ruschin M, Lee YK, Karam I et al (2020) Use of radiomics for the prediction of local control of brain metastases after stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurooncology 22(6):797–805. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noaa007
Soliman H, Myrehaug S, Tseng C-L, Ruschin M, Hashmi A, Mainprize T et al (2019) Image-guided, linac-based, surgical cavity-hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in 5 daily fractions for brain metastases. Neurosurgery 85(5):E860–E869. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyz162
Myrehaug S, Hudson J, Soliman H, Ruschin M, Tseng CL, Detsky J et al (2021) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy for intact brain metastases in 5 daily fractions: effect of dose on treatment response. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.09.003
Lin NU, Lee EQ, Aoyama H, Barani IJ, Barboriak DP, Baumert BG et al (2015) Response assessment criteria for brain metastases: proposal from the RANO group. Lancet Oncol 16(6):e270–e278. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(15)70057-4
Faruqi S, Ruschin M, Soliman H, Myrehaug S, Zeng KL, Husain Z et al (2020) Adverse radiation effect after hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery in 5 daily fractions for surgical cavities and intact brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 106(4):772–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.12.002
Kim I-Y, Jung S, Jung T-Y, Moon K-S, Jang W-Y, Park J-Y et al (2018) Repeat stereotactic radiosurgery for recurred metastatic brain tumors. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 61(5):633–639. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2017.0238
Koffer P, Chan J, Rava P, Gorovets D, Ebner D, Savir G et al (2017) Repeat stereotactic radiosurgery for locally recurrent brain metastases. World Neurosurg 104:589–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.04.103
Andruska N, Kennedy WR, Bonestroo L, Anderson R, Huang Y, Robinson CG et al (2021) Dosimetric predictors of symptomatic radiation necrosis after five-fraction radiosurgery for brain metastases. Radiother Oncol 156:181–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2020.12.011
Rana N, Pendyala P, Cleary RK, Luo G, Zhao Z, Chambless LB et al (2017) Long-term outcomes after salvage stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) following in-field failure of initial SRS for brain metastases. Front Oncol 7:279. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2017.00279
Angelov L, Mohammadi AM, Bennett EE, Abbassy M, Elson P, Chao ST et al (2018) Impact of 2-staged stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases ≥ 2 cm. J Neurosurg 129(2):366–382. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.3.jns162532
Higuchi Y, Serizawa T, Nagano O, Matsuda S, Ono J, Sato M et al (2009) Three-staged stereotactic radiotherapy without whole brain irradiation for large metastatic brain tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74(5):1543–1548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.10.035
Detsky JS, Keith J, Conklin J, Symons S, Myrehaug S, Sahgal A et al (2017) Differentiating radiation necrosis from tumor progression in brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiotherapy: utility of intravoxel incoherent motion perfusion MRI and correlation with histopathology. J Neurooncol 134(2):433–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2545-2
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MY, AS, and HS developed study concept. MY, ML, and HS obtained study data. MY was responsible for statistical analysis. MY and HS wrote the initial manuscript draft. MY and LH prepared all figures and tables. All authors reviewed manuscript and final approval.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
HS reports travel and education grants from Elekta. SD reports research grants from Alkermes Medical and consultant fees from Medexus. SM reports research support and honoraria from AAA/Novartis and Ipsen. CLT reports honoraria from Elekta and serves on the advisory board for Sanofi. AS reports consulting fees and grants from Varian and Elekta, as well as honoraria from Varian, BrainLab, and Elekta. MR owns intellectual property related to the image-guidance component on the Elekta Gamma Knife system. All other authors have no disclosures.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, M., Lee, M., Myrehaug, S. et al. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery (HSRS) as a salvage treatment for brain metastases failing prior stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). J Neurooncol 162, 119–128 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-023-04265-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-023-04265-y