Abstract
Objective
Gamma Knife Icon-based hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery (GKI-HSRS) is a novel technical paradigm in the treatment of brain metastases that allows for both the dosimetric benefits of the GKI stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) platform as well as the biologic benefits of fractionation. We report mature local control and adverse radiation effect (ARE) outcomes following 5 fraction GKI-HSRS for intact brain metastases.
Methods
Patients with intact brain metastases treated with 5-fraction GKI-HSRS were retrospectively reviewed. Survival, local control, and adverse radiation effect rates were determined. Univariable and multivariable regression (MVA) were performed on potential predictive factors.
Results
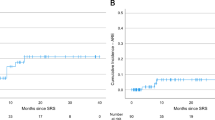
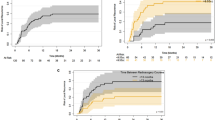
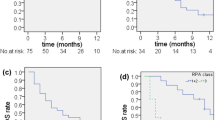
Two hundred and ninety-nine metastases in 146 patients were identified. The median clinical follow-up was 10.7 months (range 0.5–47.6). The median total dose and prescription isodose was 27.5 Gy (range, 20–27.5) in 5 daily fractions and 52% (range, 45–93), respectively. The median overall survival (OS) was 12.7 months, and the 1-year local failure rate was 15.2%. MVA identified a total dose of 27.5 Gy vs. ≤ 25 Gy (hazard ratio [HR] 0.59, p = 0.042), and prior chemotherapy exposure (HR 1.99, p = 0.015), as significant predictors of LC. The 1-year ARE rate was 10.8% and the symptomatic ARE rate was 1.8%. MVA identified a gross tumor volume of ≥ 4.5 cc (HR 7.29, p < 0.001) as a significant predictor of symptomatic ARE.
Conclusion
Moderate total doses in 5 daily fractions of GKI-HSRS were associated with high rates of LC and a low incidence of symptomatic ARE.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is available upon reasonable request from corresponding author.
References
Sahgal A, Aoyama H, Kocher M, Neupane B, Collette S, Tago M et al (2015) Phase 3 trials of stereotactic radiosurgery with or without whole-brain radiation therapy for 1 to 4 brain metastases: individual patient data meta-analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol* Biol* Phys 91(4):710–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.10.024
Brown PD, Jaeckle K, Ballman KV, Farace E, Cerhan JH, Anderson SK et al (2016) Effect of radiosurgery alone vs radiosurgery with whole brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases. JAMA 316(4):401. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.9839
Milano MT, Chiang VLS, Soltys SG, Wang TJC, Lo SS, Brackett A et al (2020) Executive summary from American Radium Society’s appropriate use criteria on neurocognition after stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases. Neuro Oncol 22(12):1728–1741. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noaa192
Gutschenritter T, Venur VA, Combs SE, Vellayappan B, Patel AP, Foote M et al (2020) The judicious use of stereotactic radiosurgery and hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in the management of large brain metastases. Cancers 13(1):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13010070
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, Dinapoli R, Kline R, Loeffler J et al (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90–05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47(2):291–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(99)00507-6
Myrehaug S, Hudson J, Soliman H, Ruschin M, Tseng CL, Detsky J et al (2021) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy for intact brain metastases in 5 daily fractions: effect of dose on treatment response. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.09.003
Brown PD, Brown CA, Pollock BE, Gorman DA, Foote RL (2002) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with “radioresistant” brain metastases. Neurosurgery 51(3):656–667
Barbour AB, Jacobs CD, Williamson H, Floyd SR, Suneja G, Torok JA et al (2020) Radiation therapy practice patterns for brain metastases in the united states in the stereotactic radiosurgery era. Adv Radiat Oncol 5(1):43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adro.2019.07.012
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T et al (1997) Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol* Biol* Phys 37(4):745–751. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360-3016(96)00619-0
Sperduto PW, Mesko S, Li J, Cagney D, Aizer A, Lin NU et al (2020) Survival in patients with brain metastases: summary report on the updated diagnosis-specific graded prognostic assessment and definition of the eligibility quotient. J Clin Oncol 38(32):3773–3784. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.20.01255
Poon I, Erler D, Dagan R, Redmond KJ, Foote M, Badellino S et al (2020) Evaluation of definitive stereotactic body radiotherapy and outcomes in adults with extracranial oligometastasis. JAMA Netw Open 3(11):e2026312. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.26312
Paddick I (2000) A simple scoring ratio to index the conformity of radiosurgical treatment plans. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2000.93.supplement_3.0219
Paddick I, Lippitz B (2006) A simple dose gradient measurement tool to complement the conformity index. J Neurosurg 105(Supplement):194–201. https://doi.org/10.3171/sup.2006.105.7.194
Macdonald RL, Lee Y, Schasfoort J, Soliman H, Sahgal A, Ruschin M (2020) Real-Time Infrared Motion Tracking Analysis for Patients Treated With Gated Frameless Image Guided Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol* Biol* Phys 106(2):413–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.10.030
Lin NU, Lee EQ, Aoyama H, Barani IJ, Barboriak DP, Baumert BG et al (2015) Response assessment criteria for brain metastases: proposal from the RANO group. Lancet Oncol 16(6):e270–e278. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(15)70057-4
Mehrabian H, Desmond KL, Soliman H, Sahgal A, Stanisz GJ (2017) Differentiation between radiation necrosis and tumor progression using chemical exchange saturation transfer. Clin Cancer Res 23(14):3667–3675. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-2265
Navarria P, Clerici E, Carta G, Attuati L, Picozzi P, Franzese C et al (2018) Randomized phase III Trial Comparing Gamma Knife and Linac Based (EDGE) approaches for brain metastases radiosurgery: results from the gadget trial. Int J Radiat Oncol* Biol* Phys 102(3):S143–S144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.06.349
Tuleasca C, Negretti L, Faouzi M, Magaddino V, Gevaert T, Von Elm E et al (2018) Radiosurgery in the management of brain metastasis: a retrospective single-center study comparing Gamma Knife and LINAC treatment. J Neurosurg 128(2):352–361. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.10.jns161480
Soliman H, Myrehaug S, Tseng C-L, Ruschin M, Hashmi A, Mainprize T et al (2019) Image-guided, linac-based, surgical cavity-hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in 5 daily fractions for brain metastases. Neurosurgery 85(5):E860–E869. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyz162
Ma L, Nichol A, Hossain S, Wang B, Petti P, Vellani R et al (2014) Variable dose interplay effects across radiosurgical apparatus in treating multiple brain metastases. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 9(6):1079–1086. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-014-1001-4
Kennedy WR, Dewees TA, Acharya S, Mahmood M, Knutson NC, Goddu SM et al (2021) Internal dose escalation associated with increased local control for melanoma brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 135(3):855–861. https://doi.org/10.3171/2020.7.jns192210
Lucia F, Key S, Dissaux G, Goasduff G, Lucia A-S, Ollivier L et al (2019) Inhomogeneous tumor dose distribution provides better local control than homogeneous distribution in stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases. Radiother Oncol 130:132–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2018.06.039
Dong P, Pérez-Andújar A, Pinnaduwage D, Braunstein S, Theodosopoulos P, Mcdermott M et al (2016) Dosimetric characterization of hypofractionated Gamma Knife radiosurgery of large or complex brain tumors versus linear accelerator based treatments. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.7.gks16881
Schasfoort J, Ruschin M, Sahgal A, MacDonald RL, Lee Y, van Pul C et al (2021) Quantifying the sensitivity of target dose on intra-fraction displacement in intra-cranial stereotactic radiosurgery. Pract Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2021.11.012
Samanci Y, Karakose F, Senyurek S, Peker S (2021) Single-fraction versus hypofractionated gamma knife radiosurgery for small metastatic brain tumors. Clin Exp Metas 38(3):305–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-021-10086-y
Minniti G, Scaringi C, Paolini S, Lanzetta G, Romano A, Cicone F et al (2016) Single-fraction versus multifraction (3 × 9 Gy) stereotactic radiosurgery for large (>2 cm) brain metastases: a comparative analysis of local control and risk of radiation-induced brain necrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol* Biol* Phys 95(4):1142–1148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.03.013
Kim Y-J, Cho KH, Kim J-Y, Lim YK, Min HS, Lee SH et al (2011) Single-dose versus fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol* Biol* Phys 81(2):483–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.05.033
Remick JS, Kowalski E, Khairnar R, Sun K, Morse E, Cherng H-RR et al (2020) A multi-center analysis of single-fraction versus hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of brain metastasis. Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-020-01522-6
Marcrom SR, Mcdonald AM, Thompson JW, Popple RA, Riley KO, Markert JM et al (2017) Fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy for intact brain metastases. Adv Radiat Oncol 2(4):564–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adro.2017.07.006
Zhou C, Xia Y, Huang P, Guan L, Shen X, Hao D et al (2020) Fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy using volumetric modulated arc therapy in patients with solitary brain metastases. Biomed Res Int 2020:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6342057
Milano MT, Grimm J, Niemierko A, Soltys SG, Moiseenko V, Redmond KJ et al (2021) Single- and multifraction stereotactic radiosurgery dose/volume tolerances of the brain. Int J Radiat Oncol* Biol* Phys 110(1):68–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.08.013
Faruqi S, Ruschin M, Soliman H, Myrehaug S, Zeng KL, Husain Z et al (2020) Adverse radiation effect after hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery in 5 daily fractions for surgical cavities and intact brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol* Biol* Phys 106(4):772–779
Di Perri D, Tanguy R, Malet C, Robert A, Sunyach M-P (2020) Risk of radiation necrosis after hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (HFSRT) for brain metastases: a single center retrospective study. J Neurooncol 149(3):447–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03628-z
Lehrer EJ, Peterson JL, Zaorsky NG, Brown PD, Sahgal A, Chiang VL et al (2019) Single versus multifraction stereotactic radiosurgery for large brain metastases: an International Meta-analysis of 24 Trials. Int J Radiat Oncol* Biol* Phys 103(3):618–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.10.038
Higuchi Y, Serizawa T, Nagano O, Matsuda S, Ono J, Sato M et al (2009) Three-staged stereotactic radiotherapy without whole brain irradiation for large metastatic brain tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol* Biol* Phys 74(5):1543–1548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.10.035
Yamamoto M, Higuchi Y, Serizawa T, Kawabe T, Nagano O, Sato Y et al (2018) Three-stage Gamma Knife treatment for metastatic brain tumors larger than 10 cm3: a 2-institute study including re-analyses of earlier results using competing risk analysis. J Neurosurg 129(Suppl1):77–85. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.7.gks181392
Mouraviev A, Detsky J, Sahgal A, Ruschin M, Lee YK, Karam I et al (2020) Use of radiomics for the prediction of local control of brain metastases after stereotactic radiosurgery. Neuro Oncol 22(6):797–805. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noaa007
Moraes FY, Winter J, Atenafu EG, Dasgupta A, Raziee H, Coolens C et al (2019) Outcomes following stereotactic radiosurgery for small to medium-sized brain metastases are exceptionally dependent upon tumor size and prescribed dose. Neuro Oncol 21(2):242–251. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noy159
Alvarez-Breckenridge C, Remon J, Piña Y, Nieblas-Bedolla E, Forsyth P, Hendriks L et al (2022) Emerging systemic treatment perspectives on brain metastases: moving toward a better outlook for patients. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 42:147–165. https://doi.org/10.1200/edbk_352320
Id Said B, Chen H, Jerzak KJ, Warner E, Myrehaug S, Tseng C-L et al (2022) Trastuzumab emtansine increases the risk of stereotactic radiosurgery-induced radionecrosis in HER2 + breast cancer. J Neurooncol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04055-y
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Collins Yeboah for his direction with physics support, and Pejman Maralani for his guidance with imaging outcomes evaluation.
Funding
This study was not supported by any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EA: author responsible for statistical analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
HS reports travel and education grants from Elekta. SD reports research grants from Alkermes Medical and consultant fees from Medexus. SM reports research support and honoraria from AAA/Novartis and Ipsen. CLT reports honoraria from Elekta and serves on the advisory board for Sanofi. AS reports consulting fees and grants from Varian and Elekta, as well as honoraria from Varian, BrainLab, and Elekta. He is also an associate editor for the Journal of Neuro-Oncology. All other authors have no disclosures.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, M., Holden, L., Wang, M. et al. Gamma knife icon based hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery (GKI-HSRS) for brain metastases: impact of dose and volume. J Neurooncol 159, 705–712 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04115-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04115-3