Abstract
Purpose
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a standard treatment modality for vestibular schwannomas (VSs). However, there is a paucity of data on tumor control and neurological preservation for larger VSs. We aimed to investigate the long-term effectiveness of SRS for Koos grade IV compared with I-III VSs.
Methods
We included 452 patients with VSs (50 Koos grade IV and 402 Koos grade I‒III) who were treated with SRS at our institution from 1990 to 2021. Tumor control and functional preservation were calculated using the Kaplan–Meier method and compared between groups with the log-rank test.
Results
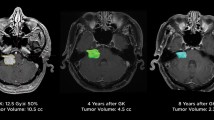
The median post-SRS follow-up period was 68 months. Progression-free survival rates were 91% at 5 and 10 years for Koos grade IV VSs, and 95% and 92%, respectively, for Koos grade I‒III VSs (p = 0.278). In Koos grade IV VSs, functional preservation rates of the facial and trigeminal nerves were both 96% at 5 years (both 98% for Koos grade I‒III VSs; facial, p = 0.410; trigeminal, p = 0.107). Hearing preservation rates were 61% at 5 years for Koos grade IV VSs and 78% for Koos grade I–III VSs (p = 0.645). Symptomatic transient tumor expansion was more common with Koos grade IV VSs (8.0% vs. 2.5%, p = 0.034), although all related symptoms diminished in accordance with tumor shrinkage.
Conclusion
SRS may contribute to long-term tumor control and adequate neurological preservation in the treatment of Koos grade IV VSs, comparable to those in the treatment of Koos grade I‒III VSs.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Goldbrunner R, Weller M, Regis J, Lund-Johansen M, Stavrinou P, Reuss D, Evans DG, Lefranc F, Sallabanda K, Falini A, Axon P, Sterkers O, Fariselli L, Wick W, Tonn JC (2020) EANO guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of vestibular schwannoma. Neuro Oncol 22:31–45. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noz153
Nakatomi H, Jacob JT, Carlson ML, Tanaka S, Tanaka M, Saito N, Lohse CM, Driscoll CLW, Link MJ (2017) Long-term risk of recurrence and regrowth after gross-total and subtotal resection of sporadic vestibular schwannoma. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.11.JNS16498
Gurgel RK, Dogru S, Amdur RL, Monfared A (2012) Facial nerve outcomes after surgery for large vestibular schwannomas: do surgical approach and extent of resection matter? Neurosurg Focus 33:E16. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.7.FOCUS12199
Chen Z, Prasad SC, Di Lella F, Medina M, Piccirillo E, Taibah A, Russo A, Yin S, Sanna M (2014) The behavior of residual tumors and facial nerve outcomes after incomplete excision of vestibular schwannomas. J Neurosurg 120:1278–1287. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.2.JNS131497
Zumofen DW, Guffi T, Epple C, Westermann B, Krahenbuhl AK, Zabka S, Taub E, Bodmer D, Mariani L (2018) Intended near-total removal of Koos grade IV vestibular schwannomas: reconsidering the treatment paradigm. Neurosurgery 82:202–210. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyx143
Chung WY, Pan DH, Lee CC, Wu HM, Liu KD, Yen YS, Guo WY, Shiau CY, Shih YH (2010) Large vestibular schwannomas treated by Gamma Knife surgery: long-term outcomes. J Neurosurg 113(Suppl):112–121. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.8.GKS10954
van de Langenberg R, Hanssens PE, Verheul JB, van Overbeeke JJ, Nelemans PJ, Dohmen AJ, de Bondt BJ, Stokroos RJ (2011) Management of large vestibular schwannoma. Part II. Primary Gamma Knife surgery: radiological and clinical aspects. J Neurosurg 115:885–893. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.6.JNS101963
Yang HC, Kano H, Awan NR, Lunsford LD, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Novotny J Jr, Bhatnagar JP, Kondziolka D (2011) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for larger-volume vestibular schwannomas. Clinical article J Neurosurg 114:801–807. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.8.JNS10674
Williams BJ, Xu Z, Salvetti DJ, McNeill IT, Larner J, Sheehan JP (2013) Gamma Knife surgery for large vestibular schwannomas: a single-center retrospective case-matched comparison assessing the effect of lesion size. J Neurosurg 119:463–471. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.4.JNS122195
Bailo M, Boari N, Franzin A, Gagliardi F, Spina A, Del Vecchio A, Gemma M, Bolognesi A, Mortini P (2016) Gamma Knife radiosurgery as primary treatment for large vestibular schwannomas: clinical results at long-term follow-up in a series of 59 patients. World Neurosurg 95:487–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.07.117
Iorio-Morin C, AlSubaie F, Mathieu D (2016) Safety and efficacy of Gamma Knife radiosurgery for the management of Koos grade 4 vestibular schwannomas. Neurosurgery 78:521–530. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000001154
Huang CW, Tu HT, Chuang CY, Chang CS, Chou HH, Lee MT, Huang CF (2018) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for large vestibular schwannomas greater than 3 cm in diameter. J Neurosurg 128:1380–1387. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.12.JNS161530
Lefranc M, Da Roz LM, Balossier A, Thomassin JM, Roche PH, Regis J (2018) Place of Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery in grade 4 vestibular schwannoma based on case series of 86 patients with long-term follow-up. World Neurosurg 114:e1192–e1198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.03.175
Watanabe S, Yamamoto M, Kawabe T, Koiso T, Aiyama H, Kasuya H, Barfod BE (2019) Long-term follow-up results of stereotactic radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas larger than 8 cc. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 161:1457–1465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-03951-z
Hasegawa T, Kato T, Naito T, Tanei T, Ishii K, Tsukamoto E, Okada K, Ito R, Kouketsu Y (2021) Predictors of long-term tumor control after stereotactic radiosurgery for Koos grade 4 vestibular schwannomas. J Neurooncol 151:145–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03622-5
Ogino A, Lunsford LD, Long H, Johnson S, Faramand A, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Kano H (2021) Stereotactic radiosurgery as the primary management for patients with Koos grade IV vestibular schwannomas. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2020.8.JNS201832
Collen C, Ampe B, Gevaert T, Moens M, Linthout N, De Ridder M, Verellen D, D’Haens J, Storme G (2011) Single fraction versus fractionated linac-based stereotactic radiotherapy for vestibular schwannoma: a single-institution experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:e503-509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.04.066
Kirkpatrick JP, Soltys SG, Lo SS, Beal K, Shrieve DC, Brown PD (2017) The radiosurgery fractionation quandary: single fraction or hypofractionation? Neuro Oncol 19:ii38–ii49. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/now301
Teo M, Zhang M, Li A, Thompson PA, Tayag AT, Wallach J, Gibbs IC, Soltys SG, Hancock SL, Chang SD (2016) The outcome of hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for large vestibular schwannomas. World Neurosurg 93:398–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.06.080
Koos WT, Day JD, Matula C, Levy DI (1998) Neurotopographic considerations in the microsurgical treatment of small acoustic neurinomas. J Neurosurg 88:506–512. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1998.88.3.0506
Kawashima M, Hasegawa H, Shin M, Takahashi W, Shinya Y, Iwasaki S, Kashio A, Nakatomi H, Saito N (2020) Long-term outcomes of Gamma knife radiosurgery for treating vestibular schwannoma with a lower prescription dose of 12 Gy compared with higher dose treatment. Otol Neurotol 41:e1314–e1320. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000002885
Shinya Y, Hasegawa H, Shin M, Sugiyama T, Kawashima M, Takahashi W, Iwasaki S, Kashio A, Nakatomi H, Saito N (2019) Long-term outcomes of stereotactic radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma associated with neurofibromatosis type 2 in comparison to sporadic schwannoma. Cancers (Basel) 11:1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101498
Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA, Cloughesy TF, Sorensen AG, Galanis E, Degroot J, Wick W, Gilbert MR, Lassman AB, Tsien C, Mikkelsen T, Wong ET, Chamberlain MC, Stupp R, Lamborn KR, Vogelbaum MA, van den Bent MJ, Chang SM (2010) Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol 28:1963–1972. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.26.3541
Phi JH, Kim DG, Chung HT, Lee J, Paek SH, Jung HW (2009) Radiosurgical treatment of vestibular schwannomas in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2: tumor control and hearing preservation. Cancer 115:390–398. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.24036
Sun S, Liu A (2014) Long-term follow-up studies of Gamma Knife surgery for patients with neurofibromatosis type 2. J Neurosurg 121(Suppl):143–149. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.8.GKS141503
Mindermann T, Schlegel I (2014) How to distinguish tumor growth from transient expansion of vestibular schwannomas following Gamma Knife radiosurgery. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 156:1121–1123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2063-3
Nagano O, Higuchi Y, Serizawa T, Ono J, Matsuda S, Yamakami I, Saeki N (2008) Transient expansion of vestibular schwannoma following stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 109:811–816. https://doi.org/10.3171/JNS/2008/109/11/0811
Gardner G, Robertson JH (1988) Hearing preservation in unilateral acoustic neuroma surgery. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 97:55–66. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348948809700110
House JW, Brackmann DE (1985) Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 93:146–147. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459988509300202
Johnson S, Kano H, Faramand A, Pease M, Nakamura A, Hassib M, Spencer D, Sisterson N, Faraji AH, Arai Y, Monaco E, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2019) Long term results of primary radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas. J Neurooncol 145:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03290-0
Won SY, Kilian A, Dubinski D, Gessler F, Dinc N, Lauer M, Wolff R, Freiman T, Senft C, Konczalla J, Forster MT, Seifert V (2020) Microsurgical treatment and follow-up of KOOS grade IV vestibular schwannoma: therapeutic concept and future perspective. Front Oncol 10:605137. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.605137
Huang MJ, Kano H, Mousavi SH, Niranjan A, Monaco EA 3rd, Arai Y, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2017) Stereotactic radiosurgery for recurrent vestibular schwannoma after previous resection. J Neurosurg 126:1506–1513. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.5.JNS1645
Radwan H, Eisenberg MB, Sandberg Knisely JP, Ghaly MM, Schulder M (2016) Outcomes in patients with vestibular schwannoma after subtotal resection and adjuvant radiosurgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 94:216–224. https://doi.org/10.1159/000447520
Starnoni D, Daniel RT, Tuleasca C, George M, Levivier M, Messerer M (2018) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the technique of subtotal resection and stereotactic radiosurgery for large vestibular schwannomas: a “nerve-centered” approach. Neurosurg Focus 44:E4. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.12.FOCUS17669
Breshears JD, Chang J, Molinaro AM, Sneed PK, McDermott MW, Tward A, Theodosopoulos PV (2019) temporal dynamics of pseudoprogression after Gamma Knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas-A retrospective volumetric study. Neurosurgery 84:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyy019
Hayhurst C, Zadeh G (2012) Tumor pseudoprogression following radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma. Neuro Oncol 14:87–92. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nor171
Pollock BE (2006) Management of vestibular schwannomas that enlarge after stereotactic radiosurgery: treatment recommendations based on a 15 year experience. Neurosurgery 58:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000194833.66593.8B
Johnson S, Kano H, Faramand A, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2019) Predicting hearing outcomes before primary radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2019.5.JNS182765
Frischer JM, Gruber E, Schoffmann V, Ertl A, Hoftberger R, Mallouhi A, Wolfsberger S, Arnoldner C, Eisner W, Knosp E, Kitz K, Gatterbauer B (2018) Long-term outcome after Gamma Knife radiosurgery for acoustic neuroma of all Koos grades: a single-center study. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.8.JNS171281
Ruess D, Pohlmann L, Grau S, Hamisch C, Hoevels M, Treuer H, Baues C, Kocher M, Ruge M (2020) Outcome and toxicity analysis of single dose stereotactic radiosurgery in vestibular schwannoma based on the Koos grading system. Sci Rep 10:9309. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66213-4
Jacob JT, Carlson ML, Schiefer TK, Pollock BE, Driscoll CL, Link MJ (2014) Significance of cochlear dose in the radiosurgical treatment of vestibular schwannoma: controversies and unanswered questions. Neurosurgery 74:466–474. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000299
Patel KS, Ng E, Kaur T, Miao T, Kaprealian T, Lee P, Pouratian N, Selch MT, De Salles AAF, Gopen Q, Tenn S, Yang I (2019) Increased cochlear radiation dose predicts delayed hearing loss following both stereotactic radiosurgery and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for vestibular schwannoma. J Neurooncol 145:329–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03299-5
Han JH, Kim DG, Chung HT, Paek SH, Park CK, Kim CY, Hwang SS, Park JH, Kim YH, Kim JW, Kim YH, Song SW, Kim IK, Jung HW (2012) The risk factors of symptomatic communicating hydrocephalus after stereotactic radiosurgery for unilateral vestibular schwannoma: the implication of brain atrophy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84:937–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.01.048
Powell C, Micallef C, Gonsalves A, Wharram B, Ashley S, Brada M (2011) Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in the treatment of vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma): predicting the risk of hydrocephalus. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 80:1143–1150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.04.019
Acknowledgements
None
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (grant number 20K17919 to Yuki Shinya).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: MU and YS; Methodology: MUand YS; Formal analysis and investigation: MU and YS; Writing—original draft preparation: MU; Writing—review and editing: YS, HH, MK, MS, AK, MM, AK, KK, and NS; Funding acquisition: YS; Resources: YS, HH, AK, and MM; Supervision: NS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of The University of Tokyo Hospital (approval #2231) and performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
All patients provided written informed consent for study participation.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umekawa, M., Shinya, Y., Hasegawa, H. et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery ensures an effective and safe long-term control of Koos grade IV vestibular schwannomas: a single-center, retrospective, cohort study. J Neurooncol 159, 201–209 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04058-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04058-9