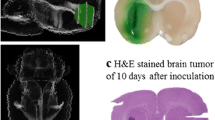
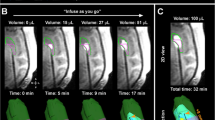
Abstract
Background
The purpose of this review is to summarize our own experimental studies carried out over a 13-year period of time using the F98 rat glioma as model for high grade gliomas. We evaluated a binary chemo-radiotherapeutic modality that combines either cisplatin (CDDP) or carboplatin, administered intracerebrally (i.c.) by means of convection-enhanced delivery (CED) or osmotic pumps, in combination with either synchrotron or conventional X-irradiation.
Methods
F98 glioma cells were implanted stereotactically into the brains of syngeneic Fischer rats. Approximately 14 days later, either CDDP or carboplatin was administered i.c. by CED, followed 24 h later by radiotherapy using either a synchrotron or, subsequently, megavoltage linear accelerators (LINAC).
Results
CDDP was administered at a dose of 3 µg in 5 µL, followed 24 h later with an irradiation dose of 15 Gy or carboplatin at a dose of 20 µg in 10 µL, followed 24 h later with 3 fractions of 8 Gy each, at the source at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF). This resulted in a median survival time (MeST) > 180 days with 33% long term survivors (LTS) for CDDP and a MeST > 60 days with 8 to 22% LTS, for carboplatin. Subsequently it became apparent that comparable survival data could be obtained with megavoltage X-irradiation using a LINAC source. The best survival data were obtained with a dose of 72 µg of carboplatin administered by means of Alzet® osmotic pumps over 7 days. This resulted in a MeST of > 180 days, with 55% LTS. Histopathologic examination of all the brains of the surviving rats revealed no residual tumor cells or evidence of significant radiation related effects.
Conclusions
The results obtained using this combination therapy has, to the best of our knowledge, yielded the most promising survival data ever reported using the F98 glioma model.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AZQ:
-
Aziridinyl-benzoquinone
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- BBB-D:
-
Blood–brain barrier disruption
- BCNU:
-
1,3-Bis (2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea
- C225:
-
Cetuximab
- CED:
-
Convection-enhanced delivery
- CDDP:
-
Cisplatin
- CI:
-
Combination index
- D:
-
Dexamethasone
- DMF:
-
Dexamethasone, mannitol, furosemide
- DRI:
-
Dose reduction index
- DSBs:
-
DNA double strand breaks
- ESRF:
-
European synchrotron radiation facility
- F98EGFR :
-
F98 glioma cells transfected with the human gene encoding EGFR
- F:
-
Furosemide
- i.a.:
-
Intra-arterially
- i.c.:
-
Intra-cerebrally
- i.t.:
-
Intra-tumoral
- i.v.:
-
Intra-venous
- ICP-OES:
-
Inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy
- %ILS:
-
Percent increase in life span
- LET:
-
Linear energy transfer
- LINAC:
-
Linear accelerator
- LTS:
-
Long term survivors
- M:
-
Mannitol
- MeST:
-
Median survival time
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- PAMAM:
-
Polyamidoamine
- PEP382:
-
13 Mer B-cell epitope
- PEP455:
-
16 Mer HER-1 epitope
- SF:
-
Surviving fraction
- SSRT:
-
Stereotactic synchrotron radiotherapy
- Vd :
-
Volume of distribution
- XRT:
-
Conventional radiotherapy
References
Lapointe S, Perry A, Butowski NA (2018) Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet 392(10145):432–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30990-5
Arvanitis CD, Ferraro GB, Jain RK (2020) The blood-brain barrier and blood-tumour barrier in brain tumours and metastases. Nat Rev Cancer 20(1):26–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-019-0205-x
Bobo RH, Laske DW, Akbasak A, Morrison PF, Dedrick RL, Oldfield EH (1994) Convection-enhanced delivery of macromolecules in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(6):2076–2080. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.6.2076
Lieberman DM, Laske DW, Morrison PF, Bankiewicz KS, Oldfield EH (1995) Convection-enhanced distribution of large molecules in gray matter during interstitial drug infusion. J Neurosurg 82(6):1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1995.82.6.1021
Laske DW, Youle RJ, Oldfield EH (1997) Tumor regression with regional distribution of the targeted toxin TF-CRM107 in patients with malignant brain tumors. Nat Med 3(12):1362–1368. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1297-1362
Laske DW, Morrison PF, Lieberman DM, Corthesy ME, Reynolds JC, Stewart-Henney PA, Koong SS, Cummins A, Paik CH, Oldfield EH (1997) Chronic interstitial infusion of protein to primate brain: determination of drug distribution and clearance with single-photon emission computerized tomography imaging. J Neurosurg 87(4):586–594. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1997.87.4.0586
Lonser RR, Corthesy ME, Morrison PF, Gogate N, Oldfield EH (1999) Convection-enhanced selective excitotoxic ablation of the neurons of the globus pallidus internus for treatment of parkinsonism in nonhuman primates. J Neurosurg 91(2):294–302. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1999.91.2.0294
Lonser RR, Walbridge S, Garmestani K, Butman JA, Walters HA, Vortmeyer AO, Morrison PF, Brechbiel MW, Oldfield EH (2002) Successful and safe perfusion of the primate brainstem: in vivo magnetic resonance imaging of macromolecular distribution during infusion. J Neurosurg 97(4):905–913. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2002.97.4.0905
Morrison PF, Laske DW, Bobo H, Oldfield EH, Dedrick RL (1994) High-flow microinfusion: tissue penetration and pharmacodynamics. Am J Physiol 266(1 Pt 2):R292–305. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1994.266.1.R292
Lonser RR, Sarntinoranont M, Morrison PF, Oldfield EH (2015) Convection-enhanced delivery to the central nervous system. J Neurosurg 122(3):697–706. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.10.JNS14229
Jahangiri A, Chin AT, Flanigan PM, Chen R, Bankiewicz K, Aghi MK (2017) Convection-enhanced delivery in glioblastoma: a review of preclinical and clinical studies. J Neurosurg 126(1):191–200. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.1.JNS151591
Shi M, Sanche L (2019) Convection-enhanced delivery in malignant gliomas: a review of toxicity and efficacy. J Oncol 2019:9342796. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9342796
Kelland L (2007) The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 7(8):573–584
Kroin JS, Penn RD (1982) Intracerebral chemotherapy: chronic microinfusion of cisplatin. Neurosurgery 10(3):349–354
Penn RD, Kroin JS, Harris JE, Chiu KM, Braun DP (1983) Chronic intratumoral chemotherapy of a rat tumor with cisplatin and fluorouracil. Appl Neurophysiol 46(1–4):240–244
Kimler BF, Liu C, Evans RG, Morantz RA (1992) Intracerebral chemotherapy in the 9L rat brain tumor model. J Neurooncol 14(3):191–200
Degen JW, Walbridge S, Vortmeyer AO, Oldfield EH, Lonser RR (2003) Safety and efficacy of convection-enhanced delivery of gemcitabine or carboplatin in a malignant glioma model in rats. J Neurosurg 99(5):893–898
Barth RF, Kaur B (2009) Rat brain tumor models in experimental neuro-oncology: the C6, 9L, T9, RG2, F98, BT4C, RT-2 and CNS-1 gliomas. J Neurooncol 94(3):299–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-9875-7
Biston MC, Joubert A, Adam JF, Elleaume H, Bohic S, Charvet AM, Esteve F, Foray N, Balosso J (2004) Cure of fisher rats bearing radioresistant F98 glioma treated with cis-platinum and irradiated with monochromatic synchrotron X-rays. Cancer Res 64(7):2317–2323
Barth RF, Yang W, Al-Madhoun AS, Johnsamuel J, Byun Y, Chandra S, Smith DR, Tjarks W, Eriksson S (2004) Boron-containing nucleosides as potential delivery agents for neutron capture therapy of brain tumors. Cancer Res 64(17):6287–6295. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0437
Yang W, Barth RF, Wu G, Kawabata S, Sferra TJ, Bandyopadhyaya AK, Tjarks W, Ferketich AK, Moeschberger ML, Binns PJ, Riley KJ, Coderre JA, Ciesielski MJ, Fenstermaker RA, Wikstrand CJ (2006) Molecular targeting and treatment of EGFRvIII-positive gliomas using boronated monoclonal antibody L8A4. Clin Cancer Res 12(12):3792–3802. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0141
Yang W, Wu G, Barth RF, Swindall MR, Bandyopadhyaya AK, Tjarks W, Tordoff K, Moeschberger M, Sferra TJ, Binns PJ, Riley KJ, Ciesielski MJ, Fenstermaker RA, Wikstrand CJ (2008) Molecular targeting and treatment of composite EGFR and EGFRvIII-positive gliomas using boronated monoclonal antibodies. Clin Cancer Res 14(3):883–891. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1968
Kawabata S, Yang W, Barth RF, Wu G, Huo T, Binns PJ, Riley KJ, Ongayi O, Gottumukkala V, Vicente MG (2011) Convection enhanced delivery of carboranylporphyrins for neutron capture therapy of brain tumors. J Neurooncol 103(2):175–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0376-5
Barth RF, Yang WL, Wu G, Swindall M, Byun YJ, Narayanasamy S, Tjarks W, Tordoff K, Moeschberger ML, Eriksson S, Binne PJ, Riley KJ (2008) Thymidine kinase 1 as a molecular target for boron neutron capture therapy of brain tumors. P Natl Acad Sci USA 105(45):17493–17497
Karnas SJ, Yu E, McGarry RC, Battista JJ (1999) Optimal photon energies for IUdR K-edge radiosensitization with filtered x-ray and radioisotope sources. Phys Med Biol 44(10):2537–2549. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/44/10/312
Corde S, Balosso J, Elleaume H, Renier M, Joubert A, Biston MC, Adam JF, Charvet AM, Brochard T, Le Bas JF, Esteve F, Foray N (2003) Synchrotron photoactivation of cisplatin elicits an extra number of DNA breaks that stimulate RAD51-mediated repair pathways. Cancer Res 63(12):3221–3227
Robar JL, Riccio SA, Martin MA (2002) Tumour dose enhancement using modified megavoltage photon beams and contrast media. Phys Med Biol 47(14):2433–2449. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/47/14/305
Rousseau J, Barth RF, Fernandez M, Adam JF, Balosso J, Esteve F, Elleaume H (2010) Efficacy of intracerebral delivery of cisplatin in combination with photon irradiation for treatment of brain tumors. J Neurooncol 98(3):287–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0074-3
Rousseau J, Boudou C, Barth RF, Balosso J, Esteve F, Elleaume H (2007) Enhanced survival and cure of F98 glioma-bearing rats following intracerebral delivery of carboplatin in combination with photon irradiation. Clin Cancer Res 13(17):5195–5201
Yang W, Barth RF, Huo T, Nakkula RJ, Weldon M, Gupta N, Agius L, Grecula JC (2014) Radiation therapy combined with intracerebral administration of carboplatin for the treatment of brain tumors. Radiat Oncol 9:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-9-25
Bobyk L, Edouard M, Deman P, Rousseau J, Adam JF, Ravanat JL, Esteve F, Balosso J, Barth RF, Elleaume H (2012) Intracerebral delivery of carboplatin in combination with either 6 MV photons or monoenergetic synchrotron X-rays are equally efficacious for treatment of the F98 rat glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 31:78. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-31-78
Barth RF, Yang W, Huo T, Riley KJ, Binns PJ, Grecula JC, Gupta N, Rousseau J, Elleaume H (2011) Comparison of intracerebral delivery of carboplatin and photon irradiation with an optimized regimen for boron neutron capture therapy of the F98 rat glioma. Appl Radiat Isot 69(12):1813–1816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2011.03.019
Yang W, Huo T, Barth RF, Gupta N, Weldon M, Grecula JC, Ross BD, Hoff BA, Chou TC, Rousseau J, Elleaume H (2011) Convection enhanced delivery of carboplatin in combination with radiotherapy for the treatment of brain tumors. J Neurooncol 101(3):379–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0272-z
Rousseau J, Barth RF, Moeschberger ML, Elleaume H (2009) Efficacy of intracerebral delivery of carboplatin in combination with photon irradiation for treatment of F98 glioma-bearing rats. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 73(2):530–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.09.018
Knox RJ, Friedlos F, Lydall DA, Roberts JJ (1986) Mechanism of cytotoxicity of anticancer platinum drugs: evidence that cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) and cis-diammine-(1,1-cyclobutanedicarboxylato)platinum(II) differ only in the kinetics of their interaction with DNA. Cancer Res 46(4 Pt 2):1972–1979
Hongo A, Seki S, Akiyama K, Kudo T (1994) A comparison of in vitro platinum-DNA adduct formation between carboplatin and cisplatin. Int J Biochem 26(8):1009–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-711x(94)90072-8
Wu Q, Guarnieri M, Tyler B, Clatterbuck RE, Liu Y, Carson BS (2004) Section on tumors: Young investigator award: local release of carboplatin via an Alzet mini-osmotic pump prolongs survival in a rat brainstem tumor model. Clin Neurosurg 51:332–339
Guarnieri M, Carson BS (2004) Chronic local therapy for brainstem tumors. Neurosurgery 54(4):1025–1026. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000117119.32806.af
Carson BS Sr, Wu Q, Tyler B, Sukay L, Raychaudhuri R, DiMeco F, Clatterbuck RE, Olivi A, Guarnieri M (2002) New approach to tumor therapy for inoperable areas of the brain: chronic intraparenchymal drug delivery. J Neurooncol 60(2):151–158. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020626419269
Chou TC, Martin N (2005) Software and user's guide: a computer program for quantitation of synergism and antagonism in drug combinations, and the determination of IC50, ED50 and LD50 values. ComboSyn, Paramus
Chou TC (2010) Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res 70(2):440–446. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-09-1947
Boucher Y, Salehi H, Witwer B, Harsh GR, Jain RK (1997) Interstitial fluid pressure in intracranial tumours in patients and in rodents. Br J Cancer 75(6):829–836
Huo T, Barth RF, Yang W, Nakkula RJ, Koynova R, Tenchov B, Chaudhury AR, Agius L, Boulikas T, Elleaume H, Lee RJ (2012) Preparation, biodistribution and neurotoxicity of liposomal cisplatin following convection enhanced delivery in normal and F98 glioma bearing rats. PLoS ONE 7(11):e48752. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048752
Boulikas T (2004) Low toxicity and anticancer activity of a novel liposomal cisplatin (Lipoplatin) in mouse xenografts. Oncol Rep 12(1):3–12
Barth RF, Wu G, Meisen WH, Nakkula RJ, Yang W, Huo T, Kellough DA, Kaumaya P, Turro C, Agius LM, Kaur B (2016) Design, synthesis, and evaluation of cisplatin-containing EGFR targeting bioconjugates as potential therapeutic agents for brain tumors. OncoTargets Ther 9:2769–2781. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s99242
Wu G, Barth RF, Yang W, Chatterjee M, Tjarks W, Ciesielski MJ, Fenstermaker RA (2004) Site-specific conjugation of boron-containing dendrimers to anti-EGF receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab (IMC-C225) and its evaluation as a potential delivery agent for neutron capture therapy. Bioconjugate Chem 15(1):185–194. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc0341674
Yang W, Barth RF, Wu G, Ciesielski MJ, Fenstermaker RA, Moffat BA, Ross BD, Wikstrand CJ (2005) Development of a syngeneic rat brain tumor model expressing EGFRvIII and its use for molecular targeting studies with monoclonal antibody L8A4. Clin Cancer Res 11(1):341–350
Pallares R, Albergel R (2020) Nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Nano Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2957-8
Hoppenz P, Els-Heindl S, Beck-Sickinger A (2020) Peptide-drug conjugates and their targets in advanced cancer. Front Chem. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00571
Drapeau A, Fortin D (2015) Chemotherapy delivery strategies to the central nervous system: neither optional nor superfluous. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 15(9):752–768
Fortin D (2019) Drug delivery technology to the CNS in the treatment of brain tumors: the sherbrooke experience. Pharmaceutics. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11050248
Charest G, Sanche L, Fortin D, Mathieu D, Paquette B (2013) Optimization of the route of platinum drugs administration to optimize the concomitant treatment with radiotherapy for glioblastoma implanted in the Fischer rat brain. J Neurooncol 115(3):365–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1238-8
Shi M, Fortin D, Paquette B, Sanche L (2016) Convection-enhancement delivery of liposomal formulation of oxaliplatin shows less toxicity than oxaliplatin yet maintains a similar median survival time in F98 glioma-bearing rat model. Invest New Drugs 34(3):269–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-016-0340-0
Shi M, Fortin D, Sanche L, Paquette B (2015) Convection-enhancement delivery of platinum-based drugs and Lipoplatin(TM) to optimize the concomitant effect with radiotherapy in F98 glioma rat model. Invest New Drugs 33(3):555–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-015-0228-4
Charest G, Sanche L, Fortin D, Mathieu D, Paquette B (2012) Glioblastoma treatment: bypassing the toxicity of platinum compounds by using liposomal formulation and increasing treatment efficiency with concomitant radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84(1):244–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.10.054
Vogelbaum MA, Sampson JH, Kunwar S, Chang SM, Shaffrey M, Asher AL, Lang FF, Croteau D, Parker K, Grahn AY, Sherman JW, Husain SR, Puri RK (2007) Convection-enhanced delivery of cintredekin besudotox (interleukin-13-PE38QQR) followed by radiation therapy with and without temozolomide in newly diagnosed malignant gliomas: phase 1 study of final safety results. Neurosurgery 61(5):1031–1037. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000303199.77370.9e(discussion 1037–1038)
Bogdahn U, Hau P, Stockhammer G, Venkataramana NK, Mahapatra AK, Suri A, Balasubramaniam A, Nair S, Oliushine V, Parfenov V, Poverennova I, Zaaroor M, Jachimczak P, Ludwig S, Schmaus S, Heinrichs H, Schlingensiepen KH (2011) Targeted therapy for high-grade glioma with the TGF-beta2 inhibitor trabedersen: results of a randomized and controlled phase IIb study. Neuro Oncol 13(1):132–142. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noq142
Desjardins A, Gromeier M, Herndon JE 2nd, Beaubier N, Bolognesi DP, Friedman AH, Friedman HS, McSherry F, Muscat AM, Nair S, Peters KB, Randazzo D, Sampson JH, Vlahovic G, Harrison WT, McLendon RE, Ashley D, Bigner DD (2018) Recurrent glioblastoma treated with recombinant poliovirus. N Engl J Med 379(2):150–161. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1716435
Wang J, Barth RF, Cavaliere R, Puduvalli V, Giglio P, Lonser RR, Elder JB (2020) Phase 1 trial of intracerebral convection-enhanced delivery of carboplatin for treatment of recurrent high-grade gliomas. Plos One
Souweidane MM, Kramer K, Pandit-Taskar N, Zhou Z, Haque S, Zanzonico P, Carrasquillo JA, Lyashchenko SK, Thakur SB, Donzelli M, Turner RS, Lewis JS, Cheung NV, Larson SM, Dunkel IJ (2018) Convection-enhanced delivery for diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: a single-centre, dose-escalation, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol 19(8):1040–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30322-X
Lewis O, Woolley M, Johnson DE, Fletcher J, Fenech J, Pietrzyk MW, Baruab NU, Bienemann AS, Singleton W, Evans SL, Gill SS (2018) Maximising coverage of brain structures using controlled reflux, convection-enhanced delivery and the recessed step catheter. J Neurosci Meth 308:337–345
Arshad A, Yang B, Bienemann AS, Barua NU, Wyatt MJ, Woolley M, Johnson DE, Edler KJ, Gill SS (2015) Convection-enhanced delivery of carboplatin PLGA nanoparticles for the treatment of glioblastoma. PLoS ONE 10(7):e0132266
Singleton WGB, Bieneman AS, Woolley M, Johnson D, Lewis O, Wyatt MJ, Damment SJP, Boulter LJ, Killick-Cole CL, Asby DJ, Gill SS (2018) The distribution, clearance, and brainstem toxicity of panobinostat administered by convection-enhanced delivery. J Neurosurg-Pediatr 22(3):288–296
Acknowledgements
We thank Michael Weldon, Nilendu Gupta, and John C. Grecula for their help in carrying out radiation studies for the Barth Laboratory, W. Hans Meisen, Balveen Kaur, Pravin Kaumaya and Robert Lee for their assistance in carrying out studies relating to molecular targeting, Gong Wu for preparation of bioconjugates and Delisa Watkins and David Carpenter for their assistance in the preparation of this manuscript. We thank the ESRF for their technical support and for providing beam time and special thanks to Thierry Brochard, Christian Nemoz and Dominique Dallery. Finally, we thank Marie-Claude Biston, Jean-François Adam, Anne-Marie Charvet, Caroline Boudou and François Estève, for their help in carrying out radiation studies in Grenoble.
Funding
Support for studies, carried out by Barth and his co-workers, has been provided by the Musella Foundation, Voices against Brain Cancer, The Ohio State University Department of Pathology and the Kevin J. Mullin Memorial Fund for Brain Tumor Research. Those carried out by Elleaume and her research team were supported by the University Grenoble Alpes, INSERM, the Auvergne Rhône Alpes region and the Labex Primes (ANR-11-LABX-0063).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All animal studies performed by Hélène Elleaume’s team were performed in compliance with the European Directive 2010/63/EU. The protocols were submitted to the ESRF ethical committee reference number ETHAX N°113. Animal studies carried out by Rolf Barth and his research team were in accordance with the Guide for the Care and the Use of Laboratory Animals (National Academy press, Washington DC, 1996) and the protocols were approved by the Institutional Laboratory Care and Use Committee of The Ohio State University.
Research involving human and animal participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elleaume, H., Barth, R.F., Rousseau, J. et al. Radiation therapy combined with intracerebral convection-enhanced delivery of cisplatin or carboplatin for treatment of the F98 rat glioma. J Neurooncol 149, 193–208 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03600-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03600-x