Abstract
Purpose
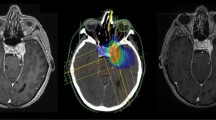
Although stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) has been proven to be effective and safe for treating intracranial meningiomas, concerns have been raised about the use of SRS for large-sized tumors involving the skull base that frequently encroach onto adjacent critical neural structures. The purpose of this study was to investigate the role of hypofractionated SRS as a therapeutic option for large-sized skull base meningiomas.
Methods
Thirty-one consecutive patients (median age: 55 years, 9 men and 22 women) who had been treated with hypofractionated SRS using CyberKnife for large-sized skull base meningiomas (> 10 cm3 in volume, median of 18.9 cm3, range 11.6–58.2 cm3) were enrolled. All patients harbored middle or posterior skull base tumors, most frequently of cavernous sinus (n = 7, 22.6%), petroclival (n = 6, 19.4%), or tentorial edge (n = 6, 19.4%) locations. SRS was delivered in five daily fractions (range 3–5 fractions) with a median cumulative dose of 27.8 Gy (range 22.6–27.8 Gy).
Results
With a median follow-up of 57 months (range 9–98 months), tumor control was achieved for 28 (90.3%) of 31 patients. Treatment response on MRI included partial response (volume decrease > 20%) in 17 (54.8%) patients, stable in 11 (35.5%), and progression (volume increase > 20%) in 3 (9.7%). Of 21 patients with cranial neuropathy, 20 (95.2%) showed improved neurological status.
Conclusions
Our current results suggest a promising role of hypofractionated SRS for large-sized skull base megningiomas in terms of tumor control and neurological outcomes. It is a reasonable therapeutic option for select patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Marosi C, Hassler M, Roessler K, Reni M, Sant M, Mazza E, Vecht C (2008) Meningioma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 67(2):153–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2008.01.010
Goto T, Ohata K (2016) Surgical resectability of skull base meningiomas. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 56(7):372–378. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.ra.2015-0354
Lee EJ, Cho YH, Yoon K, Cho B, Park ES, Kim CJ, Roh SW (2017) Radiosurgical decompression for benign perioptic tumors causing compressive cranial neuropathies: a feasible alternative to microsurgery? J Neurooncol 131(1):73–81
Ichinose T, Goto T, Ishibashi K, Takami T, Ohata K (2010) The role of radical microsurgical resection in multimodal treatment for skull base meningioma. J Neurosurg 113(5):1072–1078. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.2.JNS091118
Mendenhall WM, Friedman WA, Amdur RJ, Foote KD (2004) Management of benign skull base meningiomas: a review. Skull Base 14(1):53–60. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-821364
Rogers L, Barani I, Chamberlain M, Kaley TJ, McDermott M, Raizer J, Schiff D, Weber DC, Wen PY, Vogelbaum MA (2015) Meningiomas: knowledge base, treatment outcomes, and uncertainties. A RANO review. J Neurosurg 122(1):4–23. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.7.jns131644
Tuniz F, Soltys SG, Choi CY, Chang SD, Gibbs IC, Fischbein NJ, Adler JR Jr (2009) Multisession cyberknife stereotactic radiosurgery of large, benign cranial base tumors: preliminary study. Neurosurgery 65(5):898–907. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000359316.34041.A8
Adler JR Jr, Gibbs IC, Puataweepong P, Chang SD (2008) Visual field preservation after multisession cyberknife radiosurgery for perioptic lesions. Neurosurgery 62(Suppl 2):733–743. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000316277.14748.63
Han J, Girvigian MR, Chen JC, Miller MJ, Lodin K, Rahimian J, Arellano A, Cahan BL, Kaptein JS (2014) A comparative study of stereotactic radiosurgery, hypofractionated, and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in the treatment of skull base meningioma. Am J Clin Oncol 37(3):255–260. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0b013e318271b36a
Conti A, Pontoriero A, Midili F, Iati G, Siragusa C, Tomasello C, La Torre D, Cardali SM, Pergolizzi S, De Renzis C (2015) CyberKnife multisession stereotactic radiosurgery and hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for perioptic meningiomas: intermediate-term results and radiobiological considerations. Springerplus 4:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-015-0804-2
Timmerman RD (2008) An overview of hypofractionation and introduction to this issue of seminars in radiation oncology. Semin Radiat Oncol 18(4):215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semradonc.2008.04.001
DiBiase SJ, Kwok Y, Yovino S, Arena C, Naqvi S, Temple R, Regine WF, Amin P, Guo C, Chin LS (2004) Factors predicting local tumor control after gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery for benign intracranial meningiomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 60(5):1515–1519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.05.073
Starke RM, Przybylowski CJ, Sugoto M, Fezeu F, Awad AJ, Ding D, Nguyen JH, Sheehan JP (2015) Gamma knife radiosurgery of large skull base meningiomas. J Neurosurg 122(2):363–372. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.10.JNS14198
Mehta VK, Lee QT, Chang SD, Cherney S, Adler JR Jr (2002) Image guided stereotactic radiosurgery for lesions in proximity to the anterior visual pathways: a preliminary report. Technol Cancer Res Treat 1(3):173–180. https://doi.org/10.1177/153303460200100302
Marcu LG (2010) Altered fractionation in radiotherapy: from radiobiological rationale to therapeutic gain. Cancer Treat Rev 36(8):606–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.04.004
Adler JR Jr, Gibbs IC, Puataweepong P, Chang SD (2006) Visual field preservation after multisession cyberknife radiosurgery for perioptic lesions. Neurosurgery 59(2):244–254. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000223512.09115.3E
Mahadevan A, Floyd S, Wong E, Chen C, Kasper E (2011) Clinical outcome after hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (HSRT) for benign skull base tumors. Comput Aided Surg 16(3):112–120. https://doi.org/10.3109/10929088.2011.565160
Han MS, Jang WY, Moon KS, Lim SH, Kim IY, Jung TY, Jung S (2017) Is fractionated gamma knife radiosurgery a safe and effective treatment approach for large-volume (>10 cm(3)) intracranial meningiomas? World Neurosurg 99:477–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.12.056
Park HR, Lee JM, Park KW, Kim JH, Jeong SS, Kim JW, Chung HT, Kim DG, Paek SH (2018) Fractionated gamma knife radiosurgery as initial treatment for large skull base meningioma. Exp Neurobiol 27(3):245–255. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2018.27.3.245
Romanelli P, Wowra B, Muacevic A (2007) Multisession CyberKnife radiosurgery for optic nerve sheath meningiomas. Neurosurg focus 23(6):E11. https://doi.org/10.3171/FOC-07/12/E11
Bria C, Wegner RE, Clump DA, Vargo JA, Mintz AH, Heron DE, Burton SA (2011) Fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of meningiomas. J Cancer Res Ther 7(1):52–57. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1482.80462
Marchetti M, Bianchi S, Milanesi I, Bergantin A, Bianchi L, Broggi G, Fariselli L (2011) Multisession radiosurgery for optic nerve sheath meningiomas—an effective option: preliminary results of a single-center experience. Neurosurgery 69(5):1116–1122; discussion 1122–1113. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e31822932fe
Morimoto M, Yoshioka Y, Shiomi H, Isohashi F, Konishi K, Kotsuma T, Fukuda S, Kagawa N, Kinoshita M, Hashimoto N, Yoshimine T, Koizumi M (2011) Significance of tumor volume related to peritumoral edema in intracranial meningioma treated with extreme hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy in three to five fractions. Jpn J Clin Oncol 41(5):609–616. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyr022
Rashid A, Memon MA, Ahmed U, Saleem MA, Bhatti AI, Ahmed N, Hashim ASM (2012) Multisession stereotactic radiosurgery for large benign brain tumors of >3cm- early clinical outcomes. J Radiosurg SBRT 2(1):29–40
Lau SK, Patel K, Kim T, Knipprath E, Kim GY, Cervino LI, Lawson JD, Murphy KT, Sanghvi P, Carter BS, Chen CC (2017) Clinical efficacy and safety of surface imaging guided radiosurgery (SIG-RS) in the treatment of benign skull base tumors. J Neurooncol 132(2):307–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2370-7
Puataweepong P, Dhanachai M, Hansasuta A, Dangprasert S, Sitathanee C, Ruangkanchanasetr R, Yongvithisatid P (2018) Clinical outcomes of perioptic tumors treated with hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy using CyberKnife(R) stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 139(3):679–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-2913-6
Funding
This work was supported by Soonchunhyang University Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The Human Investigation Committee (IRB) of University of Ulsan approved this study (S2018-1981-0001). All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee. They were also in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study, formal consent was not required.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, HJ., Cho, Y.H., Kim, J.H. et al. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for large-sized skull base meningiomas. J Neurooncol 149, 87–93 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03575-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03575-9