Abstract
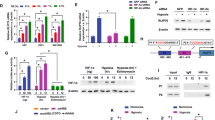
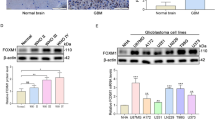
Glioma cells rely on glycolysis to obtain energy and sustain their survival under microenvironmental stress in vivo. The mechanisms of regulation of glycolysis in glioma cells are unclear. Signaling pathway mediated by the transcription factor X box-binding protein 1 (XBP1) is one of the most important pathways of unfolded protein response which is comprehensively activated in cancer cells upon the microenvironmental stress. Here we showed that XBP1 was significantly activated in glioma tissues in vivo. XBP1 silencing resulted in decreasing of glioma cell viability and ATP/lactate production under hypoxia, which is possibly mediated by inhibition of Hexokinase II (HK2)’s expression. More importantly, XBP1 silenced glioma cells showed the decrease of tumor formation capacity. Our results revealed that XBP1s activation was involved in glioma glycolysis regulation and might be a potential molecular target for glioma treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kathagen A, Schulte A, Balcke G, Phillips HS, Martens T, Matschke J, Günther HS, Soriano R, Modrusan Z, Sandmann T, Kuhl C, Tissier A, Holz M, Krawinkel LA, Glatzel M, Westphal M, Lamszus K (2013) Hypoxia and oxygenation induce a metabolic switch between pentose phosphate pathway and glycolysis in glioma stem-like cells. Acta Neuropathol 126(5):763–780
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674
Lai JH, Jan HJ, Liu LW, Lee CC, Wang SG, Hueng DY, Cheng YY, Lee HM, Ma HI (2013) Nodal regulates energy metabolism in glioma cells by inducing expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Neuro-oncology 15(10):1330–1341
Wolf A, Agnihotri S, Micallef J, Mukherjee J, Sabha N, Cairns R, Hawkins C, Guha A (2011) Hexokinase 2 is a key mediator of aerobic glycolysis and promotes tumor growth in human glioblastoma multiforme. J Exp Med 208(2):313–326
Wang M, Kaufman RJ (2014) The impact of the endoplasmic reticulum protein-folding environment on cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer 14(9):581–597
Calfon M, Zeng H, Urano F, Till JH, Hubbard SR, Harding HP, Clark SG, Ron D (2002) IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP-1 mRNA. Nature 415(6867):92–96
Lee K, Tirasophon W, Shen X, Michalak M, Prywes R, Okada T, Yoshida H, Mori K, Kaufman RJ (2002) IRE1-mediated unconventional mRNA splicing and S2P-mediated ATF6 cleavage merge to regulate XBP1 in signaling the unfolded protein response. Genes Dev 16(4):452–466
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T, Mori K (2001) XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 107(7):881–891
Hetz C (2012) The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(2):89–102
Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Glimcher LH (2003) XBP-1 regulates a subset of endoplasmic reticulum resident chaperone genes in the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell Biol 23(21):7448–7459
Acosta-Alvear D, Zhou Y, Blais A, Tsikitis M, Lents NH, Arias C, Lennon CJ, Kluger Y, Dynlacht BD (2007) XBP1 controls diverse cell type- and condition-specific transcriptional regulatory networks. Mol Cell 27(1):53–66
Romero-Ramirez L, Cao H, Nelson D, Hammond E, Lee AH, Yoshida H, Mori K, Glimcher LH, Denko NC, Giaccia AJ, Le QT, Koong AC (2004) XBP1 is essential for survival under hypoxic conditions and is required for tumor growth. Cancer Res 64(17):5943–5947
Koumenis C (2006) ER stress, hypoxia tolerance and tumor progression. Curr Mol Med 6(1):55–69
Chen X, Iliopoulos D, Zhang Q, Tang Q, Greenblatt MB, Hatziapostolou M, Lim E, Tam WL, Ni M, Chen Y, Mai J, Shen H, Hu DZ, Adoro S, Hu B, Song M, Tan C, Landis MD, Ferrari M, Shin SJ, Brown M, Chang JC, Liu XS, Glimcher LH (2014) XBP1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer by controlling the HiF1alpha pathway. Nature 508(7494):103–107
Hart LS, Cunningham JT, Datta T, Dey S, Tameire F, Lehman SL, Qiu B, Zhang H, Cerniglia G, Bi M, Li Y, Gao Y, Liu H, Li C, Maity A, Thomas-Tikhonenko A, Perl AE, Koong A, Fuchs SY, Diehl JA, Mills IG, Ruggero D, Koumenis C (2012) ER stress-mediated autophagy promotes Myc-dependent transformation and tumor growth. J Clin Investig 122(12):4621–4634
Li H, Chen X, Gao Y, Wu J, Zeng F, Song F (2015) XBP1 induces snail expression to promote epithelial- to-mesenchymal transition and invasion of breast cancer cells. Cell Signal 27(1):82–89
Liu Y, Zhang X, Liang Y, Yu H, Chen X, Zheng T, Zheng B, Wang L, Zhao L, Shi C, Zhao S (2011) Targeting X box-binding protein-1 (XBP1) enhances sensitivity of glioma cells to oxidative stress. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37(4):395–405
Hu R, Warri A, Jin L, Zwart A, Riggins RB, Fang HB, Clarke R (2015) NF-kappaB signaling is required for XBP1 (unspliced and spliced)-mediated effects on antiestrogen responsiveness and cell fate decisions in breast cancer. Mol Cell Biol 35(2):379–390
Koong AC, Chauhan V, Romero-Ramirez L (2006) Targeting XBP-1 as a novel anti-cancer strategy. Cancer Biol Ther 5(7):756–759
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB (2009) Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 324(5930):1029–1033
Warburg O (1956) On respiratory impairment in cancer cells. Science 124(3215):269–270
Lee CH, Wu SB, Hong CH, Liao WT, Wu CY, Chen GS, Wei YH, Yu HS (2011) Aberrant cell proliferation by enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis via mtTFA in arsenical skin cancers. Am J Pathol 178(5):2066–2076
Jiang S, Yan C, Fang QC, Shao ML, Zhang YL, Liu Y, Deng YP, Shan B, Liu JQ, Li HT, Yang L, Zhou J, Dai Z, Liu Y, Jia WP (2014) Fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by the IRE1α-XBP1 branch of the unfolded protein response and counteracts endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced hepatic steatosis. J Biol Chem 289(43):29751–29765
Rouault-Pierre K, Lopez-Onieva L, Foster K, Anjos-Afonso F, Lamrissi-Garcia I, Serrano-Sanchez M, Mitter R, Ivanovic Z, de Verneuil H, Gribben J, Taussig D, Rezvani HR, Mazurier F, Bonnet D (2013) HIF-2alpha protects human hematopoietic stem/progenitors and acute myeloid leukemic cells from apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Stem Cell 13(5):549–563
Margariti A, Li H, Chen T, Martin D, Vizcay-Barrena G, Alam S, Karamariti E, Xiao Q, Zampetaki A, Zhang Z, Wang W, Jiang Z, Gao C, Ma B, Chen YG, Cockerill G, Hu Y, Xu Q, Zeng L (2013) XBP1 mRNA splicing triggers an autophagic response in endothelial cells through BECLIN-1 transcriptional activation. J Biol Chem 288(2):859–872
Cheung EC, Ludwig RL, Vousden KH (2012) Mitochondrial localization of TIGAR under hypoxia stimulates HK2 and lowers ROS and cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(50):20491–20496
Acknowledgments
The funding of this study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81172388 and 81372701 to Yaohua Liu, No. 81272788 to Shiguang Zhao).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exist.
Additional information
Yaohua Liu, Xu Hou and Min Liu have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Hou, X., Liu, M. et al. XBP1 silencing decreases glioma cell viability and glycolysis possibly by inhibiting HK2 expression. J Neurooncol 126, 455–462 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-2003-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-2003-y