Abstract
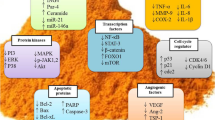
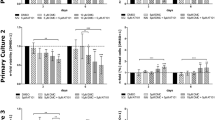
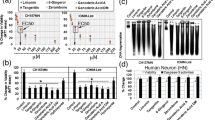
Meningiomas, the most frequent benign intracranial and intraspinal types of tumors are normally removed by surgery. Complications can occur when the tumor is critically localized and cannot be completely removed or when comorbidities of the mostly elder patients increase the general surgical risk. Thus, alternate medical treatment concepts for the therapy of meningiomas would be desirable. Curcumin, the active ingredient of the spice plant Curcuma longa has shown anti-tumorigenic actions in many different types of tumors and therefore, its effect on growth and apoptosis of meningioma cells was studied in the present paper. In vitro, treatment of the human Ben-Men-1 meningioma cell line and of a series of 21 primary human meningioma cell cultures with curcumin (1–20 μM) strongly reduced the proliferation in all cases in a dose dependent manner. Cell cycle analysis by fluorescence-activated cell sorting showed growth arrest at G2/M phase, which was confirmed by demonstrating the corresponding modulation of proteins involved in G2/M arrest by immunoblotting and/or confocal laser microscopy. High dosages (20, 50 μM) of curcumin induced a significant increase of apoptosis in Ben-Men-1 and primary meningioma cell cultures as demonstrated by morphological changes of cell nuclei, DNA fragmentation, translocation of cell membrane associated phosphatidyl serine and the induction of apoptotic-acting cleaved caspase-3. Our results suggest that the multi-targeting drug curcumin has potent anti-tumorigenic actions in meningioma cells and might therefore be a putative candidate for the pharmacological treatment of meningiomas.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mawrin C, Perry A (2010) Pathological classification and molecular genetics of meningiomas. J Neurooncol 99:379–391
Choy W, Kim W, Nagasawa D, Stramotas S, Yew A, Gopen Q, Parsa AT, Yang I (2011) The molecular genetics and tumor pathogenesis of meningiomas and the future directions of meningioma treatments. Neurosurg Focus 30:E6
Marosi C, Hassler M, Roessler K, Reni M, Sant M, Mazza E, Vecht C (2008) Meningioma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 67:153–171
Louis DN, Scheithauer BW, Budka H, von Deimling A, Kepes JJ (2000) Meningiomas. In: Kleihues P, Cavenee WK (eds) World health organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the nervous system. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 176–184
Ruttledge MH, Sarrazin J, Rangaratnam S, Phelan CM, Twist E, Merel P, Delattre O, Thomas G, Nordenskjold M, Collins VP (1997) Evidence for the complete inactivation of the NF2 gene in the majority of sporadic meningiomas. Nat Genet 6:180–184
Gutmann DH, Donahoe J, Perry A, Lemk N, Gorse K, Kittiniyom K, Rempel SA, Gutierrez JA, Newsham IF (2000) Loss of DAL-1, a protein 4.1-related tumor suppressor, is an important early event in the pathogenesis of meningiomas. Hum Mol Genet 9:1495–1500
Smith MJ, O’Sullivan J, Bhaskar SS, Hadfield KD, Poke G, Caird J, Sharif S, Ecles D, Fitzpatrick D, Rawluk D, du Plessis D, Newman WG, Evans DG (2013) Loss-of-function mutations in SMARCE1 cause an inherited disorder of multiple spinal meningiomas. Nat Genet 45:295–298
Clark VE, Erson-Omay EZ, Serin A, Yin J, Cotney J, Ozduman K, Avsar T, Li J, Murray PB, Henegariu O, Yilmaz S, Günel JM et al (2013) Genomic analysis of non-NF2 meningiomas reveals mutations in TRAF7, KLF4, AKT1, and SMO. Science 339:1077–1080
Perry A, Cai DX, Scheithauer BW, Swanson PE, Lohse CM, Newsham IF, Weaver A, Gutmann DH (2000) Merlin, DAL-1, and progesterone receptor expression in clinicopathologic subsets of meningioma: a correlative immunohistochemical study of 175 cases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 59:872–879
Bostrom J, Meyer-Puttlitz B, Wolter M, Blaschke B, Weber RG, Lichter P, Ichimura K, Collins VP, Reifenberger G (2001) Alterations of the tumor suppressor genes CDKN2A (p16INK4a), p14ARF, CDKN2B (p15INK4b), and CDKN2C (p18INK4c) in atypical and anaplastic meningiomas. Am J Pathol 159:661–669
Dutour A, Kumar U, Panetta R, Quafik L, Fina F, Sasi R, Patel YC (1998) Expression of somatostatin receptor subtypes in human brain tumors. Int J Cancer 76:620–627
Barresi V (2011) Angiogenesis in meningiomas. Brain Tumor Pathol 28:99–106
Norden AD, Drappatz J, Wen PY (2007) Targeted drug therapy for meningiomas. Neurosurg Focus 23:E12
Wen PY, Quant E, Drappatz J, Beroukhim R, Norden AD (2010) Medical therapies for meningiomas. J Neurooncol 99:365–378
Kunnumakkara AB, Anand P, Aggarwal BB (2008) Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett 269:199–225
Gupta SC, Kim JH, Prasad S, Aggarwal BB (2010) Regulation of survival, proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis of tumor cells through modulation of inflammatory pathways by nutraceuticals. Cancer Metastasis Rev 29:405–434
James MF, Han S, Polizzano C, Plotkin SR, Manning BD, Stemmer-Rachaminmov AO, Gusella JF, Ramesh V (2009) NF2/merlin is a novel negative regulator of mTOR complex 1, and activation of mTORC1 is associated with meningioma and schwannoma growth. Mol Cell Biol 29:4250–4261
Angelo LS, Wu YJ, Meng F, Sun M, Kopetz S, McCutcheon IE, Slopis JM, Kurzrock R (2011) Combining curcumin (diferuloylmethane) and heat shock protein inhibition for neurofibromatosis 2 treatment: analysis of response and resistance pathways. Mol Cancer Ther 10:2094–2103
Pagotto U, Arzberger T, Hopfner U, Sauer J, Renner U, Newton CJ, Lange M, Uhl E, Weindl A, Stalla GK (1995) Expression and localization of endothelin-1 and endothelin receptors in human meningiomas: evidence for a role in tumoral growth. J Clin Invest 96:2017–2025
Schaaf C, Shan B, Buchfelder M, Losa M, Kreutzer J, Rachinger W, Stalla GK, Schilling T, Arzt E, Perone MJ, Renner U (2009) Curcumin acts as anti-tumorigenic and hormone-suppressive agent in murine and human pituitary tumour cells in vitro and in vivo. Endocr Rel Cancer 16:1339–1350
Tichomirowa M, Theodoropoulou M, Daly AF, Yassourides A, Hansen S, Lu J, Lange M, Goldbrunner RH, Stalla GK, Renner U (2008) Toll-like receptor 4 is expressed in meningiomas and mediates the antiproliferative action of paclitaxel. Int J Cancer 123:1956–1963
Shezad A, Wahid F, Lee YS (2010) Curcumin in cancer chemoprevention: molecular targets, pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and clinical trials. Arch Pharm Chem Life Sci 9:489–499
Gupta SC, Prasad S, Kim JH, Patchva S, Webb LJ, Priyadarsini IK, Aggarwal BB (2011) Multitargeting by curcumin as revealed by molecular interaction studies. Nat Prod Rep 28:1937–1955
Yadav VR, Aggarwal BB (2011) Curcumin: a component of the golden spice, targets multiple angiogenic pathways. Cancer Biol Ther 11:236–241
Sung B, Prasad S, Yadav VR, Aggarwal BB (2012) Cancer cell signaling pathways targeted by spice-derived nutraceuticals. Nutr Cancer 64:173–197
Schaaf C, Shan B, Onofri C, Stalla GK, Arzt E, Schilling T, Perone MJ, Renner U (2010) Curcumin inhibits the growth, induces apoptosis and modulates the function of pituitary folliculostellate cells. Neuroendocrinology 91:200–210
Aoki H, Takada Y, Kondo S, Sawaya R, Aggarwal BB, Kondo Y (2007) Evidence that curcumin suppresses the growth of malignant gliomas in vitro and in vivo through induction of autophagy: role of Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways. Mol Pharmacol 72:29–39
Weir NM, Selvendiran K, Kutala VK, Tong L, Vishwanath S, Rajaram M, Tridandapani S, Anant S, Kuppusamy P (2007) Curcumin induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cells by modulating Akt and p38 MAPK. Cancer Biol Ther 6:178–184
Lee SJ, Krauthauser C, Maduskuie V, Fawcett PT, Olson JM, Rajasekaran SA (2011) Curcumin-induced HDAC inhibition and attenuation of medulloblastoma growth in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer 11:144–152
Lim KJ, Bisht S, Bar EE, Maitra A, Eberhart CG (2001) A polymeric nanoparticle formulation of curcumin inhibits growth, clonogenicity and stem-like fraction in malignant brain tumors. Cancer Biol Ther 11:464–473
Liu H-S, Ke C-S, Cheng H-C, Huang C-YF, Su C-L (2011) Curcumin-induced mitotic spindle defect and cell cycle arrest in human bladder cancer cells occurs partly through inhibition of Aurora A. Mol Pharmacol 80:638–648
Zanotto-Filho A, Braganhol E, Edelweiss M, Behr GA, Zanin R, Schröder R, Simoes-Pires A, Battastini AM, Moreira JC (2012) The curry spice curcumin selectively inhibits cancer cell growth in vitro and in a preclinical model of glioblastoma. J Nutr Biochem 23:591–601
Karunagaran D, Joseph J, Kumar TR (2007) Cell growth regulation. Adv Exp Med Biol 595:245–268
Lee SJ, Langhans SA (2012) Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome protein Cdc27 is a target for curcumin-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. BMC Cancer 12:44–56
Shishodia S, Amin HM, Lai R, Aggarwal BB (2005) Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) inhibits constitutive NF-kappaB activation, induces G1/S arrest, suppresses proliferation, and induces apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma. Biochem Pharmacol 70:700–713
Srivastava RK, Chen Q, Siddiqui I, Sarva K, Shankar S (2007) Linkage of curcumin-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21/waf1/cip. Cell Cycle 6:2953–2961
Teiten M-H, Gaascht F, Cronauer M, Henry E, Dicato M, Diederich M (2011) Anti-proliferative potential of curcumin in androgen-dependent prostate cancer cells occurs through modulation of the Wingless signaling pathway. Int J Cancer 38:603–611
Wu JC, Lai CS, Badmaev V, Nagabhushanam K, Ho CT, Pan MH (2011) Tetrahydrocurcumin, a major metabolite of curcumin, induced autophagic cell death through coordinative modulation of PI3 K/Akt-mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways in human leukemia HL 60 cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 55:1646–1654
Jia YL, Li J, Qin ZH, Liang ZQ (2009) Autophagic and apoptotic mechanisms of curcumin-induced death in K562 cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res 11:918–928
Qian H, Yang Y, Wang X (2011) Curcumin enhanced adriamycin-indued human liver-derived Hepatoma G2 cell death through activation of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis and autophagy. Eur J Pharmacol Sci 43:125–131
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA, Aggarwal BB (2007) Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises. Mol Pharm 4:807–818
Cheng AL, Hsu CH, Lin JK, Hsu MM, Yo YF, Shen TS, Ko JY, Lin JT, Lin BR, Ming-Shiang W, Yu HS, Jee SH et al (2001) Phase I clinical trial of curcumin, a chemopreventive agent in patients with high-risk of pre-malignant lesions. Anticancer Res 21:2895–2900
Sharma RA, Euden SA, Patton SL, Cooke DN, Shafayat A, Hewitt HR, Marczylo TH, Morgan B, Hemingway D, Plummer SM, Pirmohamed M, Gescher AJ et al (2004) Phase I clinical trial of curcumin: biomarkers of systemic activity and compliance. Clin Cancer Res 10:6847–6854
Garcea G, Jones DJ, Singh R, Dennison AR, Farmer PB, Sharma RA, Steward WP, Gescher AJ, Berry DP (2004) Detection of curcumin and its metabolites in hepatic tissue and portal blood of patients following oral administration. Br J Cancer 90:1011–1015
Thomas SL, Zhong D, Zhou W, Malik S, Liotta D, Snyder JP, Hamel E, Giannakakou P (2008) EF24, a novel curcumin analog, disrupts the microtubule cytoskeleton and inhibits HIF-1. Cell Cycle 7:2409–2417
Li J, Wang Y, Yang C, Wang P, Oelschlager DK, Zheng Y, Tian D-A, Grizzle WE, Buchsbaum DJ, Wan M (2009) Polyethylene glycosylated curcumin conjugate inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth through inactivation of Jab1. Mol Pharmacol 76:81–90
Selvendiran K, Kuppusamy ML, Bratasz A, Tong L, Rivera BK, Rink C, Sen CK, Kalai T, Hideg K, Kuppusamy P (2009) Inhibition of vascular smooth-muscle cell proliferation and arterial restenosis by HO-3867, a novel synthetic curcumoid, through up-regulation of PTEN expression. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 329:959–966
Shahani K, Swaminathan SK, Freeman D, Blum A, Ma L, Panyam J (2010) Injectable sustained release microparticles of curcumin: a new concept for cancer chemoprevention. Cancer Res 70:4443–4452
Acknowledgments
This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sector. We gratefully acknowledge proofreading of the paper by Kristin Lucia.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
S. Curic, Y. Wu are joint first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curic, S., Wu, Y., Shan, B. et al. Curcumin acts anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic in human meningiomas. J Neurooncol 113, 385–396 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1148-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1148-9