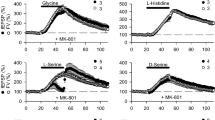
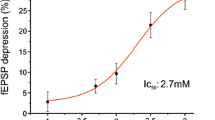
Experiments showed that high-amplitude, long-lasting tetanic potentiation could be induced in synaptic terminals formed by Schaffer collaterals on field CA1 pyramidal cells in rat hippocampal slices in which acetylcholine deficiency was modeled by application of the choline reuptake inhibitor hemicholine and the vesicular acetylcholine uptake inhibitor vesamicol. Deficiencies of different neurotransmitters were modeled by 5-min incubation of slices in solution containing an elevated potassium concentration, which led, as demonstrated previously, to depletion of the release of these neurotransmitters from nerve endings. The result of this procedure was that synapses formed by Schaffer collaterals developed long-term potentiation. Long-term post-tetanic potentiation was also induced in slices on this background in the model of neurotransmitter deficiency. Its amplitude was not significantly different from the amplitude of long-term potentiation in controls but was less than that obtained using vesamicol or hemicholine. As deficiency of serotonin, noradrenaline, and dopamine is known to be able to decrease the extent of long-term potentiation of synaptic transmission between fields CA3 and CA1, these result points to the possibility that acetylcholine deficiency partially compensates for this decrease. Considering known data on the locations of different types of nicotinic and muscarinic cholinoreceptors both on pyramidal cells and on inhibitory interneurons, the possible effects of acetylcholine on the efficiency of the inputs formed by Schaffer collaterals were studied. This analysis and consideration of the data obtained here led to the hypothesis that in conditions of acetylcholine deficiency, the main influence on the efficiency of excitation of pyramidal cells in field CA1 by field CA3 is exerted by disinhibition via a network of interacting interneurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silkis, I. G., “A unified postsynaptic mechanism for the influence of different neurotransmitters on modification of excitatory and inhibitory inputs to hippocampal neurons (a hypothesis),” Usp. Fiziol. Nauk., 33, No. 1, 40–56 (2002a).
Silkis, I. G., “Possible mechanisms of the effects of neurotransmitters and modifiable inhibition on long-term potentiation and depression of the excitatory inputs to main hippocampal neurons,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 52, No. 4, 392–405 (2002b).
Silkis, I. G. and Markevich, V. A., “Possible mechanisms of the effects of different acetylcholine concentrations on the functioning of the hippocampus,” Usp. Fiziol. Nauk., 47, No. 4, 57–76 (2016).
Albiñana, E., Luengo, J. G., Baraibar, et al., “Choline induces opposite changes in pyramidal neuron excitability and synaptic transmission through a nicotinic receptor-independent process in hippocampal slices,” Pflügers Arch., 469, No. 5–6, 779–795 (2017).
Albuquerque, E. X., Pereira, E. F., Alkondon, M., and Rogers, S. W., “Mammalian nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: from structure to function,” Physiol. Rev., 89, No. 1, 73–120 (2009).
Alkondon, M. and Albuquerque, E. X., “Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 and alpha4beta2 subtypes differentially control GABAergic input to CA1 neurons in rat hippocampus,” J. Neurophysiol., 86, No. 6, 3043–3055 (2001).
Alkondon, M., Pereira, E. F., and Albuquerque, E. X., “Endogenous activation of nAChRs and NMDA receptors contributes to the excitability of CA1 stratum radiatum interneurons in rat hippocampal slices: effects of kynurenic acid,” Biochem. Pharmacol., 82, No. 8, 842–851 (2011).
Alkondon, M., Pereira, E. F., Eisenberg, H. M., and Albuquerque, E. X., “Choline and selective antagonists identify two subtypes of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors that modulate GABA release from CA1 in terneurons in rat hippocampal slices,” Neuroscience, 19, No. 7, 2693–2705 (1999).
Aniksztejn, L. and Ben-Ari, Y., “Novel form of long-term potentiation produced by a K+ channel blocker in the hippocampus,” Nature, 349, No. 6304, 67–69 (1991).
Auerbach, J. M. and Segal, M. “Muscarinic receptors mediating depression and long-term potentiation in rat hippocampus,” J. Physiol. (London),492, No. 2, 479–493 (1996).
Banerjee, J., Alkondon, M., Pereira, E. F., and Albuquerque, E. X., “Regulation of GABAergic inputs to CA1 pyramidal neurons by nicotinic receptors and kynurenic acid,” J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 341, No. 2, 500–509 (2012).
Bell, L. A., Bell, K. A., and McQuiston, A. R., “Synaptic muscarinic response types in hippocampal CA1 interneurons depend on different levels of presynaptic activity and different muscarinic receptor subtypes,” Neuropharmacology, 73, 160–173 (2013).
Bell, K. A., Shim, H., Chen, C. K., and McQuiston, A. R., “Nicotinic excitatory postsynaptic potentials in hippocampal CA1 interneurons are predominantly mediated by nicotinic receptors that contain α4 and β2 subunits,” Neuropharmacology, 61, No. 8, 1379–1388 (2011).
Bezaire, M. J. and Soltesz, I., “Quantitative assessment of CA1 local circuits: knowledge base for interneuron-pyramidal cell connectivity,” Hippocampus, 23, No. 9, 751–785 (2013).
Birman, S. and Meunier, F. M., “Inactivation of acetylcholine release from Torpedo synaptosomes in response to prolonged depolarizations,” J. Physiol., 368, 293–307 (1985).
Blake, M. G., Krawczyk, M. C., Baratti, C. M., and Boccia, M. M., “Neuropharmacology of memory consolidation and reconsolidation: Insights on central cholinergic mechanisms,” J. Physiological. (Paris), 108, No. 4–6, 286–291 (2014).
Buhler, A. V. and Dunwiddie, T. V., “alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on GABAergic interneurons evoke dendritic and somatic inhibition of hippocampal neurons,” J. Neurophysiol., 87, No. 1, 548–557 (2002).
Carroll, P. T., “Evidence to suggest that cytosolic acetylcholine in rat hippocampal nerve terminals is not directly transferred into synaptic vesicles for release,” Brain Res., 725, No. 1, 3–10 (1996).
Cea-del Rio, C. A., Lawrence, J. J., Erdelyi, F., et al., “Cholinergic modulation amplifies the intrinsic oscillatory properties of CA1 hippocampal cholecystokinin-positive interneurons,” J. Physiol., 589, No. 3, 609–627 (2011).
Clarizia, A. D., Gomez, M. V., Romano-Silva, M. A., et al., “Control of the binding of a vesamicol analog to the vesicular acetylcholine transporter,” Neuroreport, 10, No. 13, 2783–2787 (1999).
Cobb, S. R. and Davies, C. H., “Cholinergic modulation of hippocampal cells and circuits,” J. Physiol., 562, No. 1, 81–88 (2005).
Colom, L. V., Castaneda, M. T., Reyna, T., et al., “Characterization of medial septal glutamatergic neurons and their projection to the hippocampus,” Synapse, 58, No. 3, 151–164 (2005).
Davis, J. A., Kenney, J. W., and Gould, T. J., “Hippocampal alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor involvement in the enhancing effect of acute nicotine on contextual fear conditioning,” J. Neurosci., 27, 10,870–10,877 (2007).
Dennis, S. H., Pasqui, F., Colvin, E. M., et al., “Activation of Muscarinic M1 Acetylcholine Receptors Induces Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus,” Cereb. Cortex, 26, No. 1, 414–426 (2016).
Dobryakova, Y. V., Gurskaya, O. Y., and Markevich, V. A., “Administration of nicotinic receptor antagonists during the period of memory consolidation affects passive avoidance learning and modulates synaptic efficiency in the CA1 region in vivo,” Neuroscience, 284, 865–871 (2015).
Dobryakova, Y. V., Gurskaya, O., and Markevich, V. A., “Participation of muscarinic receptors in memory consolidation in passive avoidance learning,” Acta Neurobiol. Exp. (Wars.), 74, No. 2, 211–217 (2014).
Dolleman-Van der Weel, M. J., and Witter, M. P., “Nucleus reuniens thalami innervates gamma aminobutyric acid positive cells in hippocampal field CA1 of the rat,” Neurosci. Lett., 278, No. 3, 145–148 (2000).
Domínguez, S., Fernández de Sevilla, D., and Buño, W., “Acetylcholine facilitates a depolarization-induced enhancement of inhibition in rat CA1 pyramidal neurons,” Cereb. Cortex, 27, No. 1, 852–862 (2017).
Domínguez, S., Fernández de Sevilla, D., and Buño, W., “Muscarinic longterm enhancement of tonic and phasic GABAA inhibition in rat CA1 pyramidal neurons,” Front. Cell. Neurosci, 10, 244 (2016).
Doralp, S. and Leung, L. S., “Cholinergic modulation of hippocampal CA1 basal-dendritic long-term potentiation,” Neurobiol. Learn. Mem., 90, No. 2, 382–388 (2008).
Dunwiddie, T. V., Taylor, M., Heginbotham, L. R., and Proctor, W. R., “Long-term increases in excitability in the CA1 region of rat hippocampus induced by β-adrenergic stimulation: possibly mediation by cAMP,” J. Neurosci., 12, No. 2, 506–517 (1992).
Easton, A., Douchamps, V., Eacott, M., and Lever, C., “A specific role for septohippocampal acetylcholine in memory,” Neuropsychologia, 50, No. 13, 3156–3168 (2012).
Ezrokhi, V. L., Zosimovskii, V. A., Korshunov, V. A., and Markevich, V. A., “Restoration of decaying long-term potentiation in the hippocampal formation by stimulation of neuromodulatory nuclei in freely moving rats,” Neuroscience, 88, No. 3, 741–753 (1999).
Figenschou, A., Hu, G. Y., and Storm, J. F., “Cholinergic modulation of the action potential in rat hippocampal neurons,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 8, No. 1, 211–219 (1996).
Fleck, M. W., Palmer, A. M., and Barrionuevo, G., “Potassium-induced long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal slices,” Brain Res., 580, No. 1–2, 100–105 (1992).
Frotscher, M., Soriano, E., and Leranth, C., “Cholinergic and GABAergic neurotransmission in the fascia dentata: electron microscopic immunocytochemical studies in rodents and primates,” Epilepsy Res., 7, Supplement, 65–78 (1992).
Ge, S. and Dani, J. A., “Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at glutamate synapses facilitate long-term depression or potentiation,” J. Neurosci., 25, No. 26, 6084–6091 (2005).
Gennaro, J. F., Nastuk, W. L., and Rutherford, D. T., “Reversible depletion of synaptic vesicles induced by application of high external potassium to the frog neuromuscular junction,” J. Physiol., 280, 237–247 (1978).
Glavinović, M., Ropert, N., Krnjević, K., and Collier, B., “Hemicholinium impairs septo-hippocampal facilitatory action,” Neuroscience, 9, No. 2, 319–330 (1983).
Gu, Z., Lamb, P. W., and Yakel, J. L., “Cholinergic coordination of presynaptic and postsynaptic activity induces timing-dependent hippocampal synaptic plasticity,” J. Neurosci., 32, No. 36, 12337–12348 (2012).
Hartmann, J., Kiewert, C., Duysen, E. G., Lockridge, O., and Klein, J., “Choline availability and acetylcholine synthesis in the hippocampus of acetylcholinesterase-deficient mice,” Neurochem. Int., 52, No. 6, 972–978 (2008).
Hasselmo, M. E. and Sarter, M., “Modes and models of forebrain cholinergic neuromodulation of cognition,” Neuropsychopharmacology, 36, 52–73 (2011).
Herrera-Morales, W., Mar, I., Serrano, B., and Bermudez-Rattoni, F., “Activation of hippocampal postsynaptic muscarinic receptors is involved in long-term spatial memory formation,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 25, No. 5, 1581–1588 (2007).
Huh, C. Y., Goutagny, and R. Williams, S., “Glutamatergic neurons of the mouse medial septum and diagonal band of Broca synaptically drive hippocampal pyramidal cells: relevance for hippocampal theta rhythm,” J. Neurosci., 30, No. 47, 15,951–15,961 (2010).
Ivanov, A. D., Tukhbatova, G. R., Salozhin, S. V., and Markevich, V. A., “NGF but not BDNF overexpression protects hippocampal LTP from beta-amyloid-induced impairment,” Neuroscience, 289, 114–122 (2015).
Izumi, Y. and Zorumski, C. F., “Norepinephrine promotes long-term potentiation in the adult rat hippocampus in vitro,” Synapse, 31, No. 3,196–202 (1999).
Ji, D. and Dani, J. A., “Inhibition and disinhibition of pyramidal neurons by activation of nicotinic receptors on hippocampal interneurons,” J. Neurophysiol., 83, No. 5, 2682–2690 (2000).
Kikusui, T., Aoyagi, A., and Kaneko, T., “Spatial working memory is independent of hippocampal CA1 long-term potentiation in rats,” Behav. Neurosci., 114, No. 4, 700–706 (2000).
Krnjević, K., Ropert, N., and Casullo, J., “Septohippocampal disinhibition,” Brain Res., 438, No. 1–2, 182–192 (1988).
Laezza, F. and Dingledine, R., “Voltage-controlled plasticity at GluR2-deficient synapses onto hippocampal interneurons,” J. Neurophysiol., 92, 3575–3581 (2004).
Lamsa, K., Heeroma, J. H., and Kullmann, D. M., “Hebbian LTP in feed-forward inhibitory interneurons and the temporal fidelity of input discrimination,” Nat. Neurosci., 8, No. 7, 916–924 (2005).
Levey, A. I., Edmunds, S. M., Koliatsos, V., et al., “Expression of m1-m4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor proteins in rat hippocampus and regulation by cholinergic innervation,” J. Neurosci., 15, No. 5, Part 2, 4077–4092 (1995).
Levin, E. D., Petro, A., Rezvani, A. H., et al., “Nicotinic alpha7-or beta2-containing receptor knockout: effects on radial-arm maze learning and long-term nicotine consumption in mice,” Behav. Brain Res., 196, No. 2, 207–213 (2009).
Li, S. F., Wu, M. N., Wang, X. H., et al., “Requirement of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors for amyloid β protein-induced depression of hippocampal long-term potentiation in CA1 region of rats in vivo,” Synapse, 65, No. 11, 1136–1143 (2011).
Mans, R. A., Warmus, B. A., Smith, C. C., and McMahon, L. L., “An acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, eserine, induces long-term depression at CA3-CA1 synapses in the hippocampus of adult rats,” J. Neurophysiol., 112, No. 10, 2388–9237 (2014).
Markevich, V., Scorsa, A. M., Dawe, G. S., and Stephenson, J. D., “Cholinergic facilitation and inhibition of long-term potentiation of CA1 in the urethane-anaesthetized rats,” Brain Res., 754, No. 1–2, 95–102 (1997).
May, P. B., Goh, J. W., and Sastry, B. R., “Induction of hippocampal longterm potentiation in the absence of extracellular Ca2+,” Synapse, 1, No. 3, 273–278 (1987).
McCutchen, E., Scheiderer, C. L., Dobrunz, L. E., and McMahon, L. L., “Coexistence of muscarinic long-term depression with electrically induced long-term potentiation and depression at CA3–CA1 synapses,” J. Neurophysiol., 96, No. 6, 3114–3121 (2006).
McKenna, J. T. and Vertes, R. P., “Afferent projections to nucleus reuniens of the thalamus,” J. Comp. Neurol., 480, No. 2, 115–142 (2004).
McQuiston, A. R., “Acetylcholine release and inhibitory interneuron activity in hippocampal CA1,” Front. Synaptic Neurosci., 6, 20 (2014).
Mielke, J. G., Ahuja, T. K., Comas, T., and Mealing, G. A., “Cholinemediated depression of hippocampal synaptic transmission,” Nutr. Neurosci., 14, No. 5, 186–194 (2011).
Mlinar, B., Stocca, G., and Corradetti, R., “Endogenous serotonin facilitates hippocampal long-term potentiation at CA3/CA1 synapses,” J. Neural Transm. (Vienna), 122, No. 2, 177–185 (2015).
Murray, A. J., Sauer, J. F., Riedel, G., et al., “Parvalbumin-positive CA1 interneurons are required for spatial working but not for reference memory,” Nat. Neurosci., 14, No. 3, 297–299 (2011).
Ormond, J. and Woodin, M. A., “Disinhibition mediates a form of hippocampal long-term potentiation in area CA1,” PLoS One, 4, No. 9, e7224 (2009).
Ormond, J. and Woodin, M. A., “Disinhibition-Mediated LTP in the hippocampus is synapse specific,” Front. Cell. Neurosci, 5, 17 (2011).
Ovsepian, S. V., Anwyl, R., and Rowan, M. J., “Endogenous acetylcholine lowers the threshold for long-term potentiation induction in the CA1 area through muscarinic receptor activation: in vivo study,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 20, No. 5, 1267–1275 (2004).
Rouse, S. T., Thomas, T. M. and Levey, A. I., “Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtype, m2: diverse functional implications of differential synaptic localization,” Life Sci., 60, No. 13–14, 1031–1038 (1997).
Schmitz, D., Empson, R. M., and Heinemann, U., “Serotonin and 8-OHDPAT reduce excitatory transmission in rat hippocampal area CA1 via reduction in presumed presynaptic Ca2+ entry,” Brain Res., 701, No. 1–2, 249–254 (1995).
Seeger, T., Fedorova, I., Zheng, F., et al., “M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor knock-out mice show deficits in behavioral flexibility, working memory hippocampal plasticity,” J. Neurosci., 24, No. 45, 10117–10127 (2004).
Segal, M. and Auerbach, J. M., “Muscarinic receptors involved in hippocampal plasticity,” Life Sci., 60, No. 13–14, 1085–1091 (1997).
Shen, J. X., Tu, B., and Yakel, J. L., “Inhibition of alpha 7-containing nicotinic ACh receptors by muscarinic M1 ACh receptors in rat hippocampal CA1 interneurones in slices,” J. Physiol., 587, No. 5, 1033–1042 (2009).
Shimoshige, Y., Maeda, T., Kaneko, S., et al., “Involvement of M2 receptor in an enhancement of long-term potentiation by carbachol in Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses of hippocampal slices,” Neurosci. Res., 27, No. 2, 175–180 (1997).
Shivarama Shetty, M., Gopinadhan, S., and Sajikumar, S., “Dopamine D1/D5 receptor signaling regulates synaptic cooperation and competition in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons via sustained ERK1/2 activation,” Hippocampus, 26, No. 2, 137–150 (2016).
Sotty, F., Danik, M., Manseau, F., et al., “Distinct electrophysiological properties of glutamatergic, cholinergic and GABAergic rat septohippocampal neurons: novel implications for hippocampal rhythmicity,” J. Physiol., 551, No. 3, 927–943 (2003).
Takkala, P. and Woodin, M. A., “Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor activation prevents disinhibition-mediated LTP in the hippocampus,” Front. Cell. Neurosci, 7, 16 (2013).
Teles-Grilo Ruivo, L. M. and Mellor, J. R., “Cholinergic modulation of hippocampal network function,” Front. Synaptic Neurosci., 5, 2 (2013).
Thomas, M. J., Moody, T. D., Makhinson, and M. O’Dell, T. J., “Activitydependent beta-adrenergic modulation of low frequency stimulation induced LTP in the hippocampal CA1 region,” Neuron, 17, No. 3, 475–482 (1996).
Townsend, M., Whyment, A., Walczak, J. S., et al., “α7-nAChR agonist enhances neural plasticity in the hippocampus via a GABAergic circuit,” J. Neurophysiol., 116, No. 6, 2663–2675 (2016).
Wang, R. Y. and Arvanov, V. L., “M100907, a highly selective 5-HT2A receptor antagonist and a potential atypical antipsychotic drug, facilitates induction of long-term potentiation in area CA1 of the rat hippocampal slice,” Brain Res., 779, No. 1–2, 309–313 (1998).
Widmer, H., Ferrigan, L., Davies, C. H., and Cobb, S. R., “Evoked slow muscarinic acetylcholinergic synaptic potentials in rat hippocampal interneurons,” Hippocampus, 16, No. 7, 617–628 (2006).
Wu, M. N., He, Y. X., Guo, F., and Qi, J. S., “Alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are required for the amyloid beta protein-induced suppression of long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal CA1 region in vivo,” Brain Res. Bull., 77, No. 2–3, 84–90 (2008).
Xiang, P. Y., Janc, O., Grochowska, K. M., et al., “Dopamine agonists rescue Aβ-induced LTP impairment by Src-family tyrosine kinases,” Neurobiol. Aging, 40, 98–102 (2016).
Yi, F., Ball, J., Stoll, K. E., et al., “Direct excitation of parvalbumin-positive interneurons by M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: roles in cellular excitability, inhibitory transmission and cognition,” J. Physiol., 592, No. 16, 3463–3494 (2014).
Zhang, W. P., Guzowski, J. F., and Thomas, S. A. “Mapping neuronal activation and the influence of adrenergic signaling during contextual memory retrieval,” Learn. Mem., 12, No. 3, 239–247 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 68, No. 6, pp. 732–746, November–December, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravodina, A.M., Silkis, I.G. & Markevich, V.A. A Study of Synaptic Plasticity in the Rat Hippocampal Field CA1 in Conditions of Deficiency of Acetylcholine and Other Neurotransmitters. Neurosci Behav Physi 50, 63–72 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-019-00870-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-019-00870-5