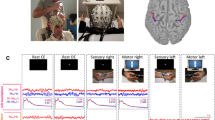
A method was developed for the noninvasive mapping of the primary motor cortex in humans. Magnetic responses evoked by repeated voluntary movements of the right index finger were studied in 18 healthy right-handed subjects. Finger movement periods were assessed using accelerometer signals. Continuous evoked brain magnetic activity recorded in the subjects throughout the experimental sessions was assembled into a single sequence which was then fragmented into independent components by independent components analysis and ranked in terms of the quantity of mutual information with the modified accelerometer signal. Averaging of the independent components demonstrating strongest links with finger movements was performed relative to the moment at which the movement started. Modeling of the distribution of the cerebral sources of the two independent components with the largest amounts of mutual information showed that their sources were located in the contralateral motor areas of the cortex, corresponding to anatomical markers of the hand representation area in the primary motor and primary somatosensory cortex. This method provided the fundamental ability to localize the M1 zone at the group level in healthy subjects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell, A. J. and Sejnowski, T. J., “An information-maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution,” Neural Computation, 7, No. 6, 1129–1159 (1995).
Burgess, R. C., Funke, M. E., Bowyer, S. M., et al., “American Clinical Magnetoencephalography Society Clinical Practice Guideline 2: presurgical functional brain mapping using magnetic evoked fields,” J. Clin. Neurophysiol., 28, No. 4, 355–361 (2011).
Chayanov, N. V., Prokof’ev, A. O., Morozov, A. A, and Stroganov, T. A., “Localization of the motor zones of the human cerebral cortex by magnetoencephalography,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 62, No. 5, 629–640 (2012).
Cheyne, D., Bakhtazad, L., and Gaetz, W., “Spatiotemporal mapping of cortical activity accompanying voluntary movements using an eventrelated beam-forming approach,” Hum. Brain Mapp., 27, No. 3, 213–229 (2006).
Dale, A. M., Fischl, B., and Sereno, M. L C., “Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction,” Neuroimage, 9, No. 2, 179–194 (1999).
Dale, A. M., Liu, A. K., Fischl, B. R., et al., “Dynamic statistical parametric mapping: combining fMRI and MEG for high-resolution imaging of cortical activity,” Neuron, 26, No. 1, 55–67 (2000).
De Tiege, X., Connelly, A., Liegeois, F., et al., “Influence of motor functional magnetic resonance imaging on the surgical management of children and adolescents with symptomatic focal epilepsy,” Neurosurgery, 64, No. 5, 856–864; discussion 864 (2009).
Dechent, P. and Frahm, J., “Functional somatotopy of finger representations in human primary motor cortex,” Hum. Brain Mapp., 18, No. 4, 272–283 (2003).
Delorme, A. and Makeig, S., “EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis,” J. Neurosci. Methods., 134, No. 1, 9–21 (2004).
Fischl, B., Sereno, M. I., and Dale, A. M., “Cortical surface-based analysis. II: Inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system,” Neuroimage, 9, No. 2, 195–207 (1999).
Gerloff, C., Uenishi, N., Nagamine, T., et al., “Cortical activation during fast repetitive finger movements in humans: steady-state movement-related magnetic fields and their cortical generators,” EEG Clin. Neurophysiol., 109, No. 5, 444–453 (1998).
Geyer, S., Schormann, T., Mohlberg, H., and Zilles, K., “Areas 3a, 3b, and 1 of human primary somatosensory cortex. Part 2. Spatial normalization to standard anatomical space,” Neuroimage, 11, No. 6, 684–696 (2000).
Hadoush, H., Sunagawa, T., Nakanishi, K., et al., “Motor somatotopy of extensor indicis proprius and extensor pollicis longus,” Neuroreport, 22, No. 11, 559–564 (2011).
Haseeb, A., Asano, E., Juhasz, C., et al., “Young patients with focal seizures may have the primary motor area for the hand in the post-central gyrus,” Epilepsy Res., 76, No. 2–3, 131–139 (2007).
Hoshiyama, M., Kakigi, R., Berg, P., et al., “Identification of motor and sensory brain activities during unilateral finger movement: spatiotemporal source analysis of movement-associated magnetic fields,” Exp. Brain Res., 115, No. 1, 6–14 (1997).
Kobayashi, M., Hutchinson, S., Schlaug, G., and Pascual-Leone, A., “Ipsilateral motor cortex activation on functional magnetic resonance imaging during unilateral hand movements is related to interhemispheric interactions,” Neuroimage, 20, No. 4, 2259–2270 (2003).
Krings, T, Reinges, M. H., Erberich, S., et al., “Functional MRI for presurgical planning: problems, artefacts, and solution strategies,” J. Neurol., Neurosurg. Psychiatry, 70, No. 6, 749–760 (2001).
Krubitzer, L., Huffman, K. J., Disbrow, E., and Recanzone, G., “Organization of area 3a in macaque monkeys: contributions to the cortical phenotype,” J. Comp. Neurol., 471, No. 1, 97–111 (2004).
Matyas, F., Sreenivasan, V., Marbach, F., et al., “Motor control by sensory cortex,” Science, 330, No. 6008, 1240–1243 (2010).
Meier, J. D., Aflalo, T. N., Kastner, S., and Graziano, M. S.,” Complex organization of human primary motor cortex: a high-resolution fMRI study,” J. Neurophysiol., 100, No. 4, 1800–1812 (2008).
Miller, K. J., Zanos, S., Fetz, E. E., et al., “Decoupling the cortical power spectrum reveals real-time representation of individual finger movements in humans,” J. Neurosci., 29, No. 10, 3132–3137 (2009).
Nii, Y., Uematsu S., Lesser, R. P., and Gordon, B., “Does the central sulcus divide motor and sensory functions? Cortical mapping of human hand areas as revealed by electrical stimulation through subdural grid electrodes,” Neurology, 46, No. 2, 360–367 (1996).
Ohara, S., Ikeda, A., Kunieda, T., et al., “Movement-related change of electrocorticographic activity in human supplementary motor area proper,” Brain, 123, 1203–1215 (2000).
Oishi, M., Fukuda, M., Kameyama, S., et al., “Magnetoencephalographic representation of the sensorimotor hand area in cases of intracerebral tumour,” J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry, 74, No. 12, 1649–1654 (2003).
Onishi, H., Oyama, M., Soma, T., et al., “Muscle-afferent projection to the sensorimotor cortex after voluntary movement and motor-point stimulation: an MEG study,” Clin. Neurophysiol., 122, No. 3, 605–610 (2011).
Ossadtchi, A., Baillet, S., Mosher, J. C., and Leahy, R. M., “Using mutual information to select event-related components in ICA,” in: 12th Int. Conf. on Biomagnetism, Nenonen, J., Ilmoniemi, R., and Katila, T. (eds.), Helsinki University of Technol. (2000).
Pollok, B., Gross, J., and Schnitzler, A., “Asymmetry of interhemispheric interaction in left-handed subjects,” Exp. Brain Res., 175, No. 2, 268–275 (2006).
Riehle, A., “Preparation for action: one of the key functions of motor cortex,” in: Motor Cortex in Voluntary Movements: A Distributed System for Distributed Functions, Riehle, A. and Vaadia, E. (eds.), CRC Press, Boca Raton (2005), pp. 213–240.
Schieber, M. H., “Constraints on somatotopic organization in the primary motor cortex,” J. Neurophysiol., 86, No. 5, 2125–2143 (2001).
Shibasaki, H. and Hallett, M., “What is the Bereitschaftspotential?” Clin. Neurophysiol., 117, No. 11, 2341–2356 (2006).
Solodkin, A., Hlustik, P., Noll, D. C., and Small, S. L., “Lateralization of motor circuits and handedness during finger movements,” Eur. J. Neurol., 8, No. 5, 425–434 (2001).
Widener, G. L. and Cheney, P. D., “Effects on muscle activity from microstimuli applied to somatosensory and motor cortex during voluntary movement in the monkey,” J. Neurophysiol., 77, No. 5, 2446–2465 (1997).
Witham, C. L., Wang, M., and Baker, S. N., “Corticomuscular coherence between motor cortex, somatosensory areas and forearm muscles in the monkey,” Front. Syst. Neurosci. , 4, 1–14 (2010).
Yousry, T. A., Schmid, U. D., Alkadhi, H., et al., “Localization of the motor hand area to a knob on the precentral gyrus. A new landmark,” Brain., 120, 141–157 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 64, No. 2, pp. 218–230, March–April, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pron’ko, P.K., Prokofiev, A.O., Osadchii, A.E. et al. Functional Segregation of Parts of the “Sensorimotor Complex” of the Human Cerebral Cortex by Magnetoencephalography. Neurosci Behav Physi 45, 1068–1076 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-015-0187-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-015-0187-4