Abstract
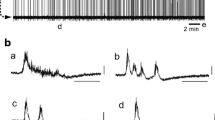
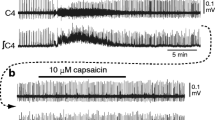
Studies of transverse slices of Wistar rat brainstem using a patch clamp technique addressed the effects of the opioid peptide leucine-enkephalin (10 nM–1 μM) on the membrane potential and pattern of spontaneous activity of neurons in two parts of the respiratory center: the ventrolateral area of the solitary tract nucleus and the pre-Bötzinger complex. Leucine-enkephalin induced membrane hyperpolarization of respiratory center neurons and decreased the level of spike activity in spontaneously active cells. In pre-Bötzinger complex neurons showing a burst pattern of activity, leucine-enkephalin decreased the burst frequency, and two cells showed a transition from burst activity to tonic activity. These results provide evidence that the mechanism of the central respiratory activity of leucine-enkephalin results from its direct action on the membranes of respiratory center neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. N. Inyushkin, “Effects of thyroliberin on the membrane potential and the pattern of spontaneous activity of rat respiratory center neurons in vitro,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh. im. I. M. Sechenova, 88, No. 11, 1467–1476 (2002).
A. N. Inyushkin, “The respiratory effects of leucine-enkephalin: the role of the ventrolateral parts of the medulla oblongata,” in: The Neurohumoral Mechanisms of Control of Respiration and Circulation [in Russian], Samara (1991), pp. 34–40.
A. N. Inyushkin, “Respiratory and hemodynamic reactions to microinjections of opioids into the solitary tract nucleus in rats,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh. im. I. M. Sechenova, 83, No. 3, 112–121 (1997).
U. Arvidsson, R. J. Dado, J. H. Lee, P. Y. Law, H. H. Loh, R. Elde, and M. W. Wessendorf, “δ-Opioid receptor immunoreactivity: distribution in brainstem and spinal cord, and relationship to biogenic amines and enkephalin,” J. Neurosci., 15, 1215–1235 (1995).
K. Ballanyi, P. M. Lalley, B. Hoch, and D. W. Richter, “C-AMP-dependent reversal of opioid-and prostaglandin-mediated depression of the isolated respiratory network in newborn rats,” J. Physiol. (London), 504, 127–134 (1997).
K. Ballanyi, H. Onimura, and I. Homma, “Respiratory network function in the isolated brainstem-spinal cord of newborn rats,” Progr. Neurobiol., 59, 583–634 (1999).
P. Y. Cheng, L. Y. Liu-Chen, C. Chen, and V. M. Pickel, “Immunolabeling of mu opioid receptors in the rat nucleus of the solitary tract: extrasynaptic plasmalemmal localization and association with Leu5-enkephalin,” J. Comp. Neurol., 371, 522–536 (1996).
A. D. Corbett, S. J. Paterson, and H. W. Kosterlitz, “Selectivity of ligands for opioid receptors,” in: Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Opioids I, Springer, Berlin (1993), pp. 645–679.
D. De Castro, J. Lipski, and R. Kanjhan, “Electrophysiological study of dorsal respiratory neurons in the medulla oblongata of the rat,” Brain Res., 639, 49–56 (1994).
J. M. Delfs, H. Kong, A. Mestek, Y. Y. L. Chen, T. Reisine, and M. F. Chesselet, “Expression of mu opioid mRNA in rat brain: an in situ hybridisation study at the single cell level,” J. Comp. Neurol., 345, 46–68 (1994).
C. A. Del Negro, S. M. Johnson, R. J. Butera, and J. C. Smith, “Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Bötzinger complex. III. Experimental tests of model predictions,” J. Neurophysiol., 86, No. 1, 59–74 (2001).
M. Denavit-Saubie and A. S. Foutz, “Neuropharmacology of respiration,” in: Neural Control of Respiratory Muscles, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida (1997), pp. 143–157.
H. U. Dodt and W. Zieglgansberger, “Visualizing unstained neurones in living brain slices by infrared DIC-videomicroscopy,” Brain Res., 537, 333–336 (1990).
G. D. Funk, J. C. Smith, and J. L. Friedman, “Generation and transmission of respiratory oscillations in medullary slices: role of excitatory amino acids,” J. Neurophysiol., 70, 1497–1515 (1993).
P. A. Gray, J. C. Reckling, M. Bocchiaro, and J. L. Feldman, “Modulation of respiratory frequency by peptidergic input to thythmogenic neurons in the pre-Bötzinger complex,” Science, 286, 1566–1568 (1999).
J. J. Greer, J. E. Carter, and Z. Al-Zubaidy, “Opioid depression of respiration in neonatal rats,” J. Physiol. (London), 485, 845–855 (1995).
A. Haji, R. Takeda, and M. Okazaki, “Neuropharmacology of control of respiratory rhythm and pattern in mature mammals,” Pharmacol. Ther., 86, 277–304 (2000).
G. Hilaire and B. Duron, “Maturation of the mammalian respiratory system,” Physiol. Rev., 79, No. 2, 325–360 (1999).
A. N. Inyushkin, S. A. Chepurnov, and N. A. Merkulova, “Respiratory and circulatory effects of opioid peptides microinjected into the solitary tract nucleus,” Regul. Peptides, 64, No. 1–3, 75 (1996).
S. M. Johnson, N. Koshiva, and J. C. Smith, “Isolation of the kernel for respiratory rhythm generation in novel preparation. The pre-Bötzinger complex ‘island’,” J. Neurophysiol., 85, No. 4, 1772–1776 (2001).
S. M. Johnson, J. C. Smith, and J. L. Feldman, “Modulation of respiratory rhythm in vitro: role of Gi/0 protein-mediated mechanisms,” J. Appl. Physiol., 80, 2120–2133 (1996).
N. Koshiya and J. C. Smith, “Neuronal pacemaker for breathing visualized in vitro,” Nature, 400, No. 6742, 360–363 (1999).
A. Laferriere, J. K. Liu, and I. R. Moss, “Mu-and delta-opioid receptor densities in respiratory-related brainstem regions of neonatal swine,” Dev. Brain Res., 112, 1–9 (1999).
Y. Y. Liu, M. T. Wong-Riley, J. P. Liu, X. Y. Wei, Y. Jia, H. L. Liu, F. Fujiyama, and G. Ju, “Substance P and enkephalinergic synapses into neurokinin-1 receptor-immunoreactive neurons in the pre-Bö tzinger complex of rats,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 19, 65–75 (2004).
T. Lonerghan, A. K. Goodchild, M. J. Christie, and P. M. Pilowski, “Presynaptic delta opioid receptors differentially modulate rhythm and pattern generation in the ventral respiratory group of the rat,” Neurosci., 121, 959–973 (2003).
A. Mansour, C. A. Fox, S. Burke, F. Meng, R. C. Thompson, H. Akil, and S. J. Watson, “Mu, delta and kappa opioid receptor mRNA expression in the rat CNS: an in situ hybridisation study,” J. Comp. Neurol., 350, 412–438 (1994).
N. M. Mellen and J. L. Feldman, “Phasic vagal sensory feedback transforms respiratory neuron activity in vitro,” J. Neurosci., 21, 7363–7371 (2001).
N. M. Mellen, W. A. Janczewski, C. M. Bocchiaro, and J. L. Feldman, “Opioid-induced quantal slowing reveals dual networks for respiratory rhythm generation,” Neuron, 37, 821–826 (2003).
M.-P. Morin-Surun, E. Boudinot, C. Dubois, H. W. Matthes, B. L. Kieffer, M. Denavit-Saubie, J. Champagnat, and A. S. Foutz, “Respiratory function in adult mice lacking the μ-opioid receptor: role of δ-receptors,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 13, 1703–1710 (2001).
M.-P. Morin-Surun, E. Boudinot, M. C. Fournie-Zaluski, J. Champagnat, B. P. Roques, and M. Denavit-Saubie, “Control of breathing by endogenous opioid peptides: possible involvement in sudden infant death syndrome,” Neurochem. Int., 20, 103–107 (1992).
J. F. R. Paton, J.-M. Ramirez, and D. W. Richter, “Mechanisms of respiratory rhythm generation change profoundly during early life in mice and rats,” Neurosci. Lett., 170, 167–170 (1994).
O. Pierrefiche, A. S. Foutz, and M. Denavit-Saubie, “NMDA and non-NMDA receptors may play different roles in timing mechanisms and transmission in the feline respiratory network,” J. Physiol. (London), 474, 509–523 (1994).
J.-M. Ramirez and D. W. Richter, “The neuronal mechanisms of respiratory rhythm generation,” Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 6, 817–825 (1996).
J. C. Rekling and J. L. Feldman, “Pre-Bötzinger complex and pacemaker neurons: hypothesized site and kernel for respiratory rhythm generation,” Ann. Rev. Physiol., 60, 385–405 (1998).
H. Sontheimer, “Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings,” in: Patch-Clamp Applications and Protocols, Humana Press, Totowa (1995), pp. 37–73.
J. W. Spain, B. L. Roth, and C. J. Cascia, “Differential ontogeny of multiple opioid receptors (μ, δ, and κ),” J. Neurosci., 5, 584–588 (1985).
T. Stasinopoulos, A. K. Goodchild, J. P. Chalmers, M. J. Christie, and P. M. Pilowsky, “Delta opioid receptors are presynaptic and mu opioid receptors are postsynaptic on bulbospinal neurons in rat ventral respiratory group,” Soc. Neurosci. Abstr., 26, 929 (2000).
S. Takeda, L. I. Eriksson, Y. Yamamoto, H. Joensen, H. Onimary, and S. G. Lindahl, “Opioid action on respiratory neuron activity of the isolated respiratory network in newborn rats,” Anesthesiology, 95, 740–749 (2001).
K. Takita, E. A. P. Herlenius, S. G. E. Lindahl, and Y. Yamamoto, “Actions of opioids on respiratory activity via activation of brainstem by μ-, δ-and κ-receptors; an in vitro study,” Brain Res., 778, 233–241 (1997).
M. Thoby-Brisson and J.-M. Ramirez, “Identification of two types of inspiratory pacemaker neurons in the isolated respiratory neural network of mice,” J. Neurophysiol., 86, No. 1, 104–112 (2001).
M. Yeadon and I. Kitchen, “Opioids and respiration,” Progr. Neurobiol., 33, 1–16 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 91, No. 6, pp. 656–665, June, 2005.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inyushkin, A.N. The effects of leucine-enkephalin on the membrane potential and activity of rat respiratory center neurons in vitro. Neurosci Behav Physiol 36, 573–579 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-006-0059-z
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-006-0059-z