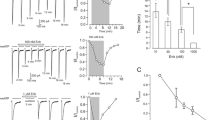
In this study, several properties of modulation of P2X3 currents by an endogenous opioid, leu-enkephalin (LEK), in neurons of the dorsal root and nodose ganglia (DRGs and NGs, respectively) were compared. P2X3-mediated currents were recorded using a patch-clamp technique in the whole-cell configuration. P2X3 receptors in DRG neurons were found to be more sensitive to LEK application compared to NG neurons; complete suppression of the corresponding currents required lower concentrations of LEK and rose more quickly. Short-term preapplication of naloxone (a nonselective opioid receptor antagonist) on NG neurons did not alter the effect of the tested opioid on P2X3 currents, while it dramatically enhanced LEK-induced inhibition in DRG neurons. This fact may be indicative of the existence of specific intracellular pathways involved in opioid-induced modulation of P2X3 receptors of different peripheral ganglia in vertebrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. A. Cockayne, S. G Hamilton, Q. M Zhu, et al., “Urinary bladder hyporeflexia and reduced pain-related behaviour in P2X3-deficient mice,” Nature, 407, No. 6807, 1011–1015 (2000).
R. A. North, “P2X3 receptors and peripheral pain mechanisms,” J. Physiol., 554, Pt. 2, 301–308 (2004).
G.Y. Xu, M. Shenoy, J.H. Winston, et al., “P2X receptormediated visceral hyperalgesia in a rat model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity,” Gut., 57, No. 9, 1230–1237 (2008).
I. Chizhmakov, Y. Yudin, N. Mamenko, et al., “Opioids inhibit purinergic nociceptors in the sensory neurons and fibres of rat via a G protein-dependent mechanism,” Neuropharmacology, 48, No. 5, 639–647 (2005).
Z. Gerevich, Z. Zadori, C. Muller, et al., “Metabotropic P2Y receptors inhibit P2X3 receptor-channels via G protein-dependent facilitation of their desensitization,” Br. J. Pharmacol., 151, No. 2, 226–236 (2007).
F. Wan, G. Li, S. Liu, et al., “P2X2/3 receptor activity of rat nodose ganglion neurons contributing to myocardial ischemic nociceptive signaling,” Auton. Neurosci., 158, Nos. 1-2, 58–64 (2010).
L. Wang, D. Feng, H. Yan, et al., “Comparative analysis of P2X1, P2X2, P2X3, and P2X4 receptor subunits in rat nodose ganglion neurons,” PLoS One, 9, No. 5, 690–699 (2014).
M. C. G. de Oliveira Fusaro, A. Pelegrini-da-Silva, D. Araldi, et al., “P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors mediate mechanical hyperalgesia induced by bradykinin, but not by pro-inflammatory cytokines, PGE(2) or dopamine,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 649, Nos. 1-3, 177–182 (2010).
M. V. Mamenko, I. V. Chizhmakov, T.M. Volkova, et al., “Extracellular cAMP inhibits P2X receptors in rat sensory neurones through G protein-mediated mechanism,” Acta Physiol. (Oxf)., 199, No. 2, 199–204 (2010).
G. Mo, J. C. Peleshok, C. Q. Cao, et al., “Control of P2X3 channel function by metabotropic P2Y2 utp receptors in primary sensory neurons,” Mol. Pharmacol., 83, No. 3, 640–647 (2013).
C. K. Park, J. H. Bae, H. Y. Kim, et al., “Substance P sensitizes P2X3 in nociceptive trigeminal neurons,” J. Dent. Res., 89, No. 10, 1154–1159 (2010).
G. W. Pasternak and Y. X. Pan, “Mu opioids and their receptors: evolution of a concept,” Pharmacol. Rev., 65, No. 4, 1257–1317 (2013).
V. B. Kulyk, I. V. Chizhmakov, T. M. Volkova, et al., “Role of phosphoinositide signaling pathway in opioids control of P2X3 receptors in the primary sensory neurons,” Fiziol. Zh., 4, 22–29 (1994).
E. B. Pratt, T. S. Brink, P. Bergson, et al., “Usedependent inhibition of P2X3 receptors by nanomolar agonist,” J. Neurosci., 25, No. 32, 7359–7365 (2005).
M. Rousset, T. Cens, A. Gouin-Charnet, et al., “Ca2+ and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate stabilize a Gbeta gamma-sensitive state of Ca V2 Ca2+ channels,” J. Biol. Chem., 279, No. 15, 14619 – 14630 (2004).
T. P. Kenakin, “The secret lives of GPCRs,” Drug Discov. Today, 8, 674–685 (2003).
I. Chizhmakov, V. Kulyk, I. Khasabova, “Molecular mechanism for opioid dichotomy: bidirectional effect of mu-opioid receptors on P2X receptor currents in rat sensory neurones,” Purinergic Signal., 11, No. 2, 171–181 (2015).
S. M. Crain and K. F. Shen, “Ultra-low concentrations of naloxone selectively antagonize excitatory effects of morphine on sensory neurons, thereby increasing its antinociceptive potency and attenuating tolerance/dependence during chronic cotreatment,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, No. 23, 10540–10544 (1995).
M. J. Millan, B. J. Morris, and A. Herz, “Antagonistinduced opioid receptor up-regulation. I. Characterization of supersensitivity to selective mu and kappa agonists,” J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 247, No. 2, 721–728 (1988).
X. Pang, M. Yang, and K. Han, “Antagonist binding and induced conformational dynamics of GPCR A2A adenosine receptor,” Proteins, 81, No. 8, 1399–1410 (2013).
U. E. Petäjä-Repo, M. Hogue, S. Bhalla, et al., “Ligands act as pharmacological chaperones and increase the efficiency of δ opioid receptor maturation,” EMBO J., 21, No. 7, 1628–1637 (2002).
A. Tempel, S. M. Crain, E. R. Peterson, et al., “Antagonist-induced opiate receptor upregulation in cultures of fetal mouse spinal cord-ganglion explants,” Brain Res., 390, No. 2, 287–291 (1986).
B. C. Yoburn, V. Purohit, K. Patel, and Q. Zhang, “Opioid agonist and antagonist treatment differentially regulates immunoreactive mu-opioid receptors and dynamin-2 in vivo,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 498, Nos. 1-3, 87–96 (2004).
J. A. Roberts, C. Vial, H. R. Digby, et al., “Molecular properties of P2X receptors,” Pflugers Arch., 452, No. 5, 486–500 (2006).
Q. Zhao, D. E. Logothetis, and P. Séguéla, “Regulation of ATP-gated P2X receptors by phosphoinositides,” Pflugers Arch., 455, No. 1, 181–185 (2007).
A. D. Corbett, G. Henderson, A. T. McKnight, and S. J. Peterson, “75 years of opioid research: the exciting but vain quest for the Holy Grail,” Br. J. Pharmacol., 147, Suppl. 1, 153–162 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulyk, V.B., Chizhmakov, I.V., Iegorova, O.V. et al. Ganglion-Specific Sensitivity of P2X3 Receptors to Leu-Enkephalin. Neurophysiology 52, 186–191 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-020-09869-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-020-09869-y