Abstract
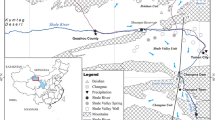
Groundwater resource management is crucial for promoting sustainable development in areas with surface water scarcity, such as Hua County in China. This paper aims to estimate groundwater recharge and evaporation during the pre- and post-rainy seasons in Hua County. The non-equilibrium evaporation model was established to quantify the degree of evaporation. Ternary end-member mixing analysis (EMMA) was used to evaluate the contributions of recharge sources to groundwater recharge. The concentrations of major ions in surface water and groundwater showed some differences, which may be due to differences in their lithological classes and hydrogeochemical evolution. The ion concentrations of both surface water and groundwater were observed to be lower in the post-rainy season, because rainfall infiltration during the rainy season diluted ion concentrations. The Gibbs diagram, end-member diagram, and δ2H versus δ18O diagram all revealed that groundwater was affected by evaporation to some extent, especially in the pre-rainy season. The non-equilibrium evaporation model showed that the remaining proportions of evaporation calculated using 18O and 2H were 0.96 and 0.94%, respectively, during the pre-rainy season and 0.97% and 0.96%, respectively, during the post-rainy season. According to EMMA, the mean contributions of subsurface lateral flow, precipitation infiltration, and river percolation to groundwater were 47%, 28%, and 25%, respectively, during the pre-rainy season and 57%, 30%, and 13%, respectively, in the post-rainy season. The findings of the present study demonstrated that integration of hydrochemistry and isotopic signatures supports better understanding of groundwater recharge and evaporation processes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu Jabal, M. S., Abustan, I., Rozaimy, M. R., & El Najar, H. (2018). The deuterium and oxygen-18 isotopic composition of the groundwater in Khan Younis City, southern Gaza Strip (Palestine). Enviromental Earth Sciences, 77(4), 155.
Ashraf, B., AghaKouchak, A., Alizadeh, A., Baygi, M. M., Moftakhari, H. R., Mirchi, A., Anjileli, H., & Madani, K. (2017). Quantifying anthropogenic stress on groundwater resources. Scientific Reports, 7, 12910.
Castano-Sanchez, A., Hose, G. C., & Reboleira, A. S. P. S. (2020). Salinity and temperature increase impact groundwater crustaceans. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 12328.
Chakraborty, B., Roy, S., Bera, A., Adhikary, P. P., Bera, B., Sengupta, D., Bhunia, G. S., & Shit, P. K. (2021). Eco-restoration of river water quality during COVID-19 lockdown in the industrial belt of eastern India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(20), 25514–25528.
Chen, J., Gao, Y., Qian, H., Ren, W., & Qu, W. (2021). Hydrogeochemical evidence for fluoride behavior in groundwater and the associated risk to human health for a large irrigation plain in the Yellow River Basin. Science of the Total Environment, 800, 149428.
Chen, M., Qin, X., & Zeng, G. (2016). Impacts of human activity modes and climate on heavy metal “spread” in groundwater are biased. Chemosphere, 152, 439–445.
Cheng, Z. S., Zhang, Y. B., Su, C., & Chen, Z. (2017). Chemical and isotopic response to intensive groundwater abstraction and its implications on aquifer sustainability in Shijiazhuang, China. Journal of Earth Science, 28(3), 523–534.
Craig, H. I. (1961). Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science, 133(3465), 1702–1703.
Dansgaard, W. (1964). Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus, 16, 436–468.
Du, Q., Wu, J., Xu, F., Yang, Y., & Li, F. (2023). Occurrence, species, and health effects of groundwater arsenic in typical rural areas along the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains, China. Exposure and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-023-00576-7
Elaid, M., Hind, M., Abdelmadiid, B., & Mohamed, M. (2020). Contribution of hydrogeochemical and isotopic tools to the management of upper and middle Cheliff aquifers. Journal of Earth Science, 31(5), 993–1006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1293-y
Gaillardet, J., Dupre, B., Louvat, P., & Allegre, C. J. (1999). Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chemical Geology, 159(1–4), 3–30.
Gat, J. R. (1996). Oxygen and hydrogen Isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 24, 225–262.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science, 17, 1088–1090.
Gong, Y., Liu, X., Ma, B., Qi, P., & Li, Y. (2021). Using geochemistry and environmental tracers to study shallow unconfined aquifer recharge and mineralization processes in the Yinchuan Plain, arid Northwest China. Hydrology Research, 52(3), 658–675.
Guo, W., Li, P., Du, Q., Zhou, Y., Xu, D., & Zhang, Z. (2023). Hydrogeochemical processes regulating the groundwater geochemistry and human health risk of groundwater in the rural areas of the Wei River Basin, China. Exposure and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-023-00555-y
Halder, J., Terzer, S., Wassenaar, L. I., Araguas-Araguas, L. J., & Aggarwal, P. K. (2015). The Global Network of Isotopes in Rivers (GNIR): Integration of water isotopes in watershed observation and riverine research. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 19(8), 3419–3431.
He, X., Wu, J., & He, S. (2019). Hydrochemical characteristics and quality evaluation of groundwater in terms of health risks in Luohe aquifer in Wuqi County of the Chinese Loess Plateau, northwest China. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 25(1–2), 32–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1531693
He, X., Li, P., Wu, J., Wei, M., Ren, X., & Wang, D. (2021). Poor groundwater quality and high potential health risks in the Datong Basin, northern China: Research from published data. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43(2), 791–812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00520-7
Hooper, R. P., Christophersen, N., & Peters, N. E. (1990). Modelling streamwater chemistry as a mixture of soilwater end-members-An application to the Panola Mountain catchment, Georgia, USA. Journal of Hydrology, 116(1–4), 321–343.
Hu, H., Bao, W., Qu, S., & Wang, T. (2007). Fractionation mechanism of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope in water body evaporating. Journal of China Hydrology, 27(3), 1–5. (in Chinese).
Jin, X., Zhang, M., Wang, S., Zhu, X., Dong, L., Ren, Z., & Chen, F. (2015). Effect of below-cloud secondary evaporation in precipitations over the Loess Plateau based on the stable isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen. Environmental Science, 36(4), 8. (in Chinese).
Kong, F., Song, J., Zhang, Y., Fu, G., Cheng, D., Zhang, G., & Xue, Y. (2019). Surface water-groundwater interaction in the Guanzhong section of the Weihe River Basin, China. Groundwater, 57(4), 647–660.
Kazantseva, A. S., Kadebskaya, O. I., & Dublyansky, Y. V. (2022). Isotopic composition of atmospheric precipitation in the Cis-Ural region. Journal of Earth Science, 33, 831–838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-021-1429-8
Lall, U., Josset, L., & Russo, T. (2020). A snapshot of the world’s groundwater challenges. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 45, 171–194.
Li, P., & Qian, H. (2018). Water resources research to support a sustainable China. International Journal of Water Resources Development, 34(3), 327–336. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2018.1452723
Li, P., Qian, H., & Wu, J. (2011). Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution laws of drinking groundwater in Pengyang County, Ningxia, Northwest China. E-Journal of Chemistry, 8(2), 565–575.
Li, P., Qian, H., Wu, J., Chen, J., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2014). Occurrence and hydrogeochemistry of fluoride in alluvial aquifer of Weihe River. China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(7), 3133–3145.
Li, P., Wu, J., & Qian, H. (2016a). Preliminary assessment of hydraulic connectivity between river water and shallow groundwater and estimation of their transfer rate during dry season in the Shidi River, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(2), 99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4949-7
Li, P., Wu, J., & Qian, H. (2016b). Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major influencing factors: a case study in and around Hua County, China. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2059-1
Li, P., Wu, J., Qian, H., Zhang, Y., Yang, N., Jing, L., & Yu, P. (2016c). Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater in and around a wastewater irrigated forest in the southeastern edge of the Tengger desert, Northwest China. Exposure and Health, 8(3), 331–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0193-y
Li, P., He, X., & Guo, W. (2019). Spatial groundwater quality and potential health risks due to nitrate ingestion through drinking water: A case study in Yan’an City on the Loess Plateau of northwest China. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 25(1–2), 11–31.
Li, X., Ye, S., Wang, L., & Zhang, J. (2017). Tracing groundwater recharge sources beneath a reservoir on a mountain-front plain using hydrochemistry and stable isotopes. Water Science and Technology-Water Supply, 17(5), 1447–1457.
Liotta, M., Favara, R., & Valenza, M. (2006). Isotopic composition of the precipitations in the central Mediterranean: Origin marks and orographic precipitation effects. Journal of Geophysical Research-Part D-Atmospheres, 111(19), 1–12.
Liu, F., Williams, M. W., & Caine, N. (2004). Source waters and flow paths in an alpine catchment, Colorado Front Range, United States. Water Resources Research, 40(9), W09401.
Liu, G., Ma, F., Liu, G., Guo, J., Duan, X., & Gu, H. (2020a). Quantification of water sources in a coastal gold mine through an end-member mixing analysis combining multivariate statistical methods. Water, 12(2), 580.
Liu, K., Qian, X., Li, B., Sun, Y., Li, Z., & Pu, C. (2016). Characteristics of deuterium excess parameters for geothermal water in Beijing. Enviromental Earth Sciences, 75(23), 1485.
Liu, L., Wu, J., He, S., & Wang, L. (2022). Occurrence and distribution of groundwater fluoride and manganese in the Weining Plain (China) and their probabilistic health risk quantification. Exposure and Health, 14(2), 263–279.
Liu, M., He, T., Wu, Q., & Guo, Q. (2020b). Hydrogeochemistry of geothermal waters from Xiongan New Area and its indicating significance. Earth Science, 45(6), 2221–2231. (in Chinese).
Liu, Y., & Yamanaka, T. (2012). Tracing groundwater recharge sources in a mountain–plain transitional area using stable isotopes and hydrochemistry. Journal of Hydrology, 464, 116–126.
Majoube, M. (1971). Fractionnement en oxygène 18 et en deutérium entre l’eau et sa vapeur. Journal of Chemical Physics, 68(1971), 1423–1436.
Mohammed, N., Celle-Jeanton, H., Huneau, F., Le Coustumer, P., Lavastre, V., Bertrand, G., Charrier, G., & Clauzet, M. L. (2014). Isotopic and geochemical identification of main groundwater supply sources to an alluvial aquifer, the Allier River valley (France). Journal of Hydrology, 508, 181–196.
Mu, D., Wu, J., Li, X., Xu, F., & Yang, Y. (2023). Identification of the spatiotemporal variability and pollution sources for potential pollutants of the Malian River water in northwest China using the PCA-APCS-MLR receptor model. Exposure and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-023-00537-0
Peng, T. R., Huang, C. C., Chen, J. E., Zhan, W. J., Chiang, W., & Chang, L. C. (2016). Evaluating the relative importance of groundwater recharge sources in a subtropical alluvial plain using tracer-based ternary end member mixing analysis (EMMA). Water Resources Management, 30(11), 3861–3878.
Peng, T. R., Zhan, W. J., Tong, L. T., Chen, C. T., Liu, T. S., & Lu, W. C. (2018). Assessing the recharge process and importance of montane water to adjacent tectonic valley-plain groundwater using a ternary end-member mixing analysis based on isotopic and chemical tracers. Hydrogeology Journal, 26(6), 2041–2055.
Qian, H., Li, P., Wu, J., & Zhou, Y. (2013). Isotopic characteristics of precipitation, surface and ground waters in the Yinchuan plain, Northwest China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 70(1), 57–70.
Qian, H., Wu, J., Zhou, Y., & Li, P. (2014). Stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes as indicators of lake water recharge and evaporation in the lakes of the Yinchuan Plain. Hydrological Processes, 28(10), 3554–3562.
Qin, D. J., Turner, J. V., & Pang, Z. H. (2005). Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater circulation in the Xi’an geothermal field, China. Geothermics, 34(4), 471–494.
Sefie, A., Aris, A. Z., Ramli, M. F., Narany, T. S., Shamsuddin, M. K. N., Saadudin, S. B., & Zali, M. A. (2018). Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment of the multilayered aquifer in Lower Kelantan Basin, Kelantan, Malaysia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77(10), 397.
Shi, H., Liu, S., & Zhao, X. (2003). Application of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope in water circulation. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 17(2), 163–166. (in Chinese).
Shukla, S., & Saxena, A. (2021). Appraisal of groundwater quality with human health risk assessment in parts of indo-gangetic alluvial plain, north India. Archives Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 80(1), 55–73.
Snousy, M. G., Wu, J., Su, F., Abdelhalim, A., & Ismail, E. (2022). Groundwater quality and its regulating geochemical processes in Assiut Province, Egypt. Exposure and Health, 14(2), 305–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-021-00445-1
Sun, L. H. (2014). Statistical analysis of hydrochemistry of groundwater and its implications for water source identification: A case study. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 7(9), 3417–3425.
Vadiati, M., Adamowski, J., & Beynaghi, A. (2018). A brief overview of trends in groundwater research: Progress towards sustainability? Journal of Environmental Management, 223, 849–851.
Wang, B. G., Jin, M. G., & Liang, X. (2015). Using EARTH model to estimate groundwater recharge at five representative zones in the Hebei plain, China. Journal of Earth Science, 26(3), 425–434.
Wang, P., Hu, G., & Cao, J. H. (2017). Stable carbon isotopic composition of submerged plants living in karst water and its eco-environmental importance. Aquatic Botany, 140, 78–83.
Wang, S., He, X., Ding, Y., Chang, F., Wu, J., Hu, Z., Wang, L., Yang, G., & Deng, M. (2020). Characteristics and influencing factors of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in groundwater in the permafrost region of the source region of the Yangtze River. Environmental Science, 41(1), 7. (in Chinese).
Wang, Y., & Li, P. (2022). Appraisal of shallow groundwater quality with human health risk assessment in different seasons in rural areas of the Guanzhong Plain (China). Environmental Research, 207, 112210.
Wang, J., Jin, M., Jia, B., & Kang, F. (2022). Numerical investigation of residence time distribution for the characterization of groundwater flow system in three dimensions. Journal of Earth Science, 33, 1583–1600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-022-1623-3
Wei, M., Wu, J., Li, W., Zhang, Q., Su, F., & Wang, Y. (2022). Groundwater geochemistry and its impacts on groundwater arsenic enrichment, variation, and health risks in Yongning County, Yinchuan Plain of northwest China. Exposure and Health, 14(2), 219–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-021-00391-y
Wu, J., Li, P., & Qian, H. (2013). Variations of hydrogeochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater caused by agricultural activities. Asian Journal of Chemistry, 25(13), 7441–7444.
Wu, J., & Sun, Z. (2016). Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities, mid-west China. Exposure and Health, 8(3), 311–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-015-0170-x
Xu, J. (2011). Study on Rational Exploitation and Utilization of Groundwater Resources of Weisan Village Drinking Water Area in Hua County. A dissertation submitted for the degree of master, Chang’an University, Xi’an. (in Chinese)
Yang, Q., Xiao, H., Zhao, L., Yang, Y., Li, C., Zhao, L., & Yin, L. (2011). Hydrological and isotopic characterization of river water, groundwater, and groundwater recharge in the Heihe River Basin, northwestern China. Hydrological Processes, 25(8), 1271–1283.
Yang, R., Zhou, J., Wei, X., Chen, Y., Lei, M., & Chen, J. (2022). Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the eastern plain of Hotian Prefecture, Xinjiang. Environmental Chemistry, 41(4), 1367–1379. (in Chinese).
Zhou, Z., Zhang, G., Yan, M., & Wang, J. (2012). Spatial variability of the shallow groundwater level and its chemistry characteristics in the low plain around the Bohai Sea, North China. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 184(6), 3697–3710.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support granted by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [42072286 and 41761144059]; the Qinchuangyuan “Scientist + Engineer” Team Development Program of the Shaanxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology [2022KXJ-005]; the Fok Ying Tong Education Foundation [161098]; the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of CHD [300102299301], and the National Ten Thousand Talent Program [W03070125].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Li, P., Wang, Y. et al. Integration of Hydrochemistry and Stable Isotopes for Assessing Groundwater Recharge and Evaporation in Pre- and Post-Rainy Seasons in Hua County, China. Nat Resour Res 32, 1959–1973 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-023-10235-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-023-10235-y