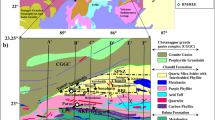
Abstract
The method of bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition (BEMD) and the combined methods of entropy weight–Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to an Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) were used to decompose gravity–magnetic data and evaluate targets in the Luziyuan Pb–Zn–Fe polymetallic ore field and surrounding areas. Three meaningful bi-dimensional intrinsic mode function (BIMF) images were obtained by BEMD at different wavelengths, depicting different layers of geological architectures in the study area. The results are as follows. (1) The BIMF2 images depict the shallow local geological architecture and show positive gravity–magnetic anomalies of the skarn alteration and Pb–Zn–Fe mineralization distributed around concealed granites. (2) The BIMF3 images depict the medium-depth geological architecture, indicating that concealed granitic stocks, which are shallow extensions of a deeply concealed pluton, intruded along the NE-trending fault. (3) The BIMF4 images depict gravity–magnetic anomalies at greater depth, which likely reflect regional geological architectures, indicating the potential presence of a large, concealed intermediate-acid pluton in the negative anomaly zone. Three potential targets (A, B, and C) were delineated based on BEMD results of the original gravity–magnetic data. The entropy weight–TOPSIS evaluation results show that the ranking of the metallogenic potential of the delineated targets in the study area is B, A, and C, with relative proximity values of 0.4576, 0.3925, and 0.1499, respectively. The results of this study can be used to guide future exploration.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, N. L., Essa, K. S., & Elhussein, M. (2020). A comparison study using particle swarm optimization inversion algorithm for gravity anomaly interpretation due to a 2D vertical fault structure. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 179, 104120.
Asadi, H. H., Sansoleimani, A., Fatehi, M., & Carranza, E. J. M. (2016). An AHP-TOPSIS predictive model for district-scale mapping of porphyry Cu–Au potential: A case study from Salafchegan Area (Central Iran). Natural Resources Research, 25, 417–429.
BölvikenStokkeFeder, B. P. R. J. (1992). The fractal nature of geochemical landscapes. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 43, 91–109.
Chen, Y. Q., Zhang, L. N., & Zhao, B. B. (2017a). Application of Bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition (BEMD) modeling for extracting gravity anomaly indicating the ore-controlling geological architectures and granites in the Gejiu tin-copper polymetallic ore field, Southwestern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 88, 832–840.
Chen, F. C., Deng, J., Shu, Q. H., Li, G. J., Cui, X. L., Zhao, F., et al. (2017b). Geology, fluid inclusion and stable isotopes (O, S) of the Hetaoping distal skarn Zn–Pb deposit, northern Baoshan block, SW China. Ore Geology Review, 90, 913–927.
Chen, Y. Q., Zhang, L. N., & Zhao, B. B. (2019). Identification of the anomaly component using BEMD combined with PCA from element concentrations in the Tengchong tin belt, SW China. Geoscience Frontiers, 10, 1561–1576.
Chen, Y. Q., Chen, S. Y., Huang, J. N., Shang, Z., Zhao, B. B., Zhang, L. N., et al. (2020a). Geodynamic background, metallogenic process, and quantitative evaluation of Gejiu super-large tin–copper polymetallic deposit. China Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese).
Chen, F. C., Deng, J., Wang, Q. F., Huizenga, J. M., Li, G. J., & Gu, Y. W. (2020b). LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis of magnetite and pyrite from the Hetaoping Fe–Zn–Pb skarn deposit in Baoshan block, SW China: Implications for ore-forming processes. Ore Geology Review, 117, 103309.
Cheng, Q. M. (2004). A new model for quantifying anisotropic scale invariance and for decomposition of mixing patterns. Mathematical Geology, 36, 345–360.
Cheng, Q. M. (2007). Singular mineralization processes and mineral resources quantitative prediction: New theories and methods. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(5), 42–53. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Cheng, Q. M. (2008). Non-linear theory and power-law models for information integration and mineral resources quantitative assessments. Mathematical Geosciences, 40, 503–532.
Deng, M. G., Xu, R., Wang, P., Sun, B. D., Zeng, L., Yu, H. J., et al. (2016). Geochemistry of the rhodonite in the Luziyuan Pb–Zn–Fe polymetallic deposit in West Yunnan and their genesis significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32, 2248–2264. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Deng, M. G., Chen, W., Wang, X. W., Liu, F. X., Guan, S. J., Lu, Y. X., et al. (2018). Fluid inclusion and ore genesis of the Luziyuan distal skarn Pb–Zn–Fe(-Cu) polymetallic deposit, West Yunnan. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34, 1239–1257. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Dong, W. W. (2007). The metallogenetic conditions and typical model in Baoshan–Zhenkang massif. Yunnan Geology, 26, 56–61. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Dong, W. W., & Chen, S. L. (2007). The characteristics & genesis of Luziyuan Pb–Zn deposit, Zhenkang. Yunnan Geology, 26, 404–410. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Dong, W. W., & Chen, S. L. (2013). Geological characteristics and prospecting potential of Xiaohebian Iron deposit in Zhenkang County. Modern Mining, 536, 72–74. (in Chinese).
Hou, W. S., Yang, Z. J., Zhou, Y. Z., Zhang, L. P., & Wu, W. L. (2012). Extracting magnetic anomalies based on an improved BEMD method: A case study in the Pangxidong Area, South China. Computers & Geosciences, 48, 1–8.
Huang, N. E., Shen, Z., Long, S. R., Wu, M. L. C., Shih, H. H., Zheng, Q. N., et al. (1998). The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proceedings of the Royal Society A-Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences, 454(1971), 903–995.
Huang, J. N., Zhao, B. B., Chen, Y. Q., & Zhao, P. D. (2010). Bidimensional empirical mode decomposition (BEMD) for extraction of gravity anomalies associated with gold mineralization in the Tongshi goldfield, western Shandong uplifted block, eastern China. Computers & Geosciences, 36, 987–995.
Hwang, C. L., & Yoon, K. (1981). Multiple attribute decision making: Methods and applications. CRC Press.
Jiang, C. X., Lu, Y. X., Chen, Y. Q., Yang, S. S., Zhou, D., & Yu, H. J. (2013). Metallogenic model and integrated prospecting pattern of the Luziyuan Pb–Zn polymetallic deposit, southwestern Yunnan Province. Geological Bulletin of China, 32, 1832–1844. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lai, Y. J., Liu, T. Y., & Hwang, C. L. (1994). TOPSIS for MODM. European Journal of Operational Research, 76, 486–500.
Li, Q. (2016). Granite Zircon Dating, Geochemistry, Tectonic setting and Prospecting Significance in Muchang, Zhenkang. China University of Geosciences.
Li, Q. M., & Cheng, Q. M. (2004). Fractal singular-value (eigienvalue) decomposition method for geophysical and geochemical anomaly reconstruction. Journal of Earth Science, 29, 109–118. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, K. B., Yang, S. S., & Cai, X. (2012). The effect and result of high-precision magnetic survey on prospecting in Luziyuan mine in Zhenkang Country. Journal of Yunnan University, 34(S2), 157–162. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, J. L., Chen, Z. L., Zhou, T. F., Gu, X. X., White, N. C., & Gao, H. J. (2020). Genesis of the Xiyi Pb–Zn deposit, Yunnan Province, SW China: Evidence from trace element and fluid inclusion data. Ore Geology Review, 119, 103348.
Liang, G. S. (1999). Fuzzy MCDM based on ideal and anti-ideal concepts. European Journal of Operational Research, 112, 682–691.
Lovejoy, S., Schertzer, D., & Gagnon, J. S. (2005). Multifractal simulations of the Earth’s surface and interior: anisotropic singularities and morphology. Proceedings of international association for mathematical geology 2005. GIS and Spatial Analysis.
Mandal, A., & Niyogi, S. (2018). Filter assisted bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition: A hybrid approach for regional-residual separation of gravity anomaly. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 159, 218–227.
Mandal, A., Niyogi, S., & KemgangGhomsi FE (2017). A comparative study on trend surface analysis (TSA), wavelet filtering and bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition (BEMD) for gravity anomaly separation. In SEG International Exposition and 87th Annual Meeting, August 17, 2017, Houston, Texas (pp. 1791–1796).
Nunes, J. C., Bouaoune, Y., Delechelle, E., Niang, O., & Bunel, P. (2003). Image analysis by bidimensional empirical mode decomposition. Image and Vision Computing, 21(12), 1019–1026.
Nunes, J. C., Guyot, S., & Delechelle, E. (2005). Texture analysis based on local analysis of the bidimensional empirical mode decomposition. Machine Vision and Applications, 16(3), 177–188.
Pazand, K., Hezarkhani, A., & Ataei, M. (2012). Using TOPSIS approaches for predictive porphyry Cu potential mapping: A case study in Ahar-Arasbaran area (NW, Iran). Computers & Geosciences, 49, 62–71.
Sha, J. Z., Deng, Z. Q., Wang, T., & Zhang, C. Y. (2019). An analysis of the prospecting potentiality of Luziyuan Pb-Zn multimetallic deposit in western Yunnan. Yunnan Geology, 38(3), 297–302. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Song, X. F., Cao, T., Xie, G. R., Xiao, G. Q., Huang, Y. Y., Dai, D. L., et al. (2017). Application of gravity survey in the exploration of Luziyuan deposit in Zhenkang area of Yunnan province. Journal of Yunnan University, 39(S2), 163–169. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tao, G. S., Wang, G. W., & Zhang, Z. Q. (2019). Extraction of Mineralization-Related Anomalies from Gravity and Magnetic Potential Fields for Mineral Exploration Targeting: Tongling Cu(-Au) District, China. Natural Resources Research, 28(2), 461–486.
Teng, J. W. (2014). Potential metallic mineral resources and oil and gas resources in the second deep space in earth’s crust. Science Press. (in Chinese).
Tzeng, G. H., & Huang, J. J. (2011). Multiple attribute decision making: Methods and applications. CRC Press.
Wang, Q. F., Deng, J., Li, G. J., Liu, J. Y., Li, C. S., & Ripley, E. M. (2018). Geochronological, Petrological, and Geochemical Studies of the Daxueshan Magmatic Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposit in the Tethyan Orogenic Belt, Southwest China. Economic Geology, 113, 1307–1332.
Wu, L. Y., Yang, Y. Z., & Zhang, Q. (2007). TOPSIS method for evaluation on mine ventilation system. Journal of China Coal Society, 32(4), 407–410. (in Chinese).
Wu, J., Sun, J. S., Zha, Y., & Liang, L. (2011). Ranking approach of cross-efficiency based on improved TOPSIS technique. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 22(4), 604–608.
Wu, shou ai li, R. Z., Liang, S. X., & Jiao, Y. J. . (2016). Experimental results of inversion of gravity, magnetic and electric multiple constrains in the location of ore bodies–a case study of Luziyuan, Yunnan. Progress in Geophysics, 31(6), 2682–2689. (in Chinese).
Xia, Q. L., Chen, Y. Q., Lu, Y. X., Jiang, C. X., Liu, H. G., & Lv, Z. C. (2005). Geochemistry, Fluid Inclusion, and Stable Isotope Studies of Luziyuan Pb-Zn Deposit in Yunnan Province, Southwestern China. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 30(2), 177–186. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xiao, C. H., & Li, G. J. (2019). Geological, sulfur isotopic, and mineral trace element constraints on the genesis of the Xiyi Pb-Zn deposit, Baoshan Block, SW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 186, 104056.
Xiao, B., Fan, Y. H., Li, J., Yang, S. S., Lu, Y. Y., Long, T. X., et al. (2015). Zonation features of mineralization and alteration in the Luziyuan lead-zinc deposit of Zhenkang county, western Yunnan Province. Geology and Exploration, 51(3), 0496–0506. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu, R., Li, W. C., Deng, M. G., Zhou, J. X., Ren, T., & Yu, H. J. (2019). Genesis of the superlarge Luziyuan Zn-Pb-Fe(-Cu) distal skarn deposit in western Yunnan (SW China): Insights from ore geology and C-H-O-S isotopes. Ore Geology Review, 107, 944–959.
Yang, Y. L., Ye, L., Chen, Z. T., & Bao, T. (2013). Origin of fluids in the Hetaoping Pb-Zn deposit, Baoshan-Narong-Dongzhi block metallogenic belt, Yunnan Province, SW China. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 73, 362–371.
Yang, F. C., Li, W. C., Liu, X. L., Wang, S. S., Yang, Y. K., Gu, Y. W., et al. (2019). Zircon U-Pb Ages of the Muchang Alkali Granites in Zhenkang Block, Western Yunnan: Implication for the Time Limit on Tectono-Magmatic Activities. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 93(4), 1152–1153.
Yoon, K., & Hwang, C. L. (1995). Multiple attribute decision making: An introduction. Sage.
Zeleny, M. (1982). Multiple criteria decision making. McGraw-Hill.
Кyэнeцoв, O., & Zhang, J. X. (1986). Nonlinear geophysics. World Science, 5, 3–4. (in Chinese).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Yingxiang Lu and Chengxing Jiang senior engineers for their help with data collection, the Editor-in-Chief (Prof. John Carranza), the Guest Editor (Prof. Yue Liu), and the anonymous reviewers for the detailed comments. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers 41972312, 41672329), the National Key Research and Development Project of China (Grant Number 2016YFC0600509), the Project of China Geological Survey (Grant Number 1212011120341), and the Natural Resources Research Student Awards in 2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, Z., Chen, Y., Xu, X. et al. Extraction of Gravity–Magnetic Anomalies Associated with Pb–Zn–Fe Polymetallic Mineralization in Luziyuan Ore Field, Yunnan Province, Southwestern China. Nat Resour Res 31, 1963–1979 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-021-09924-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-021-09924-3