Abstract
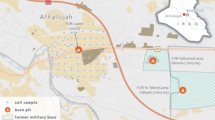
Rare earth element (REE) contamination has major consequences for the environment and humans. Some forms of REEs have more serious environmental impacts than others. It is thus crucial to monitor their levels in areas where they are expected to be released. Concentrations of 13 REEs (La, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, and Lu) around the Barakah nuclear power plant (NPP) area, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates (UAE), were measured. Shore, soil, and marine samples were collected. REE concentrations were measured using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. On average, REE concentrations were highest in the soil samples, followed by the marine samples and then the shore samples. La and Nd were the most abundant REEs in the soil, marine, and shore. The average (La/Yb)n ratios for shore, soil, and marine samples were 8.96, 9.75, and 9.39, respectively. The REE concentrations were strongly positively correlated with Al2O3 values, suggesting low mobility of the REEs in the Barakah NPP area. Light REEs (LREEs) were more enriched than heavy REEs (HREEs). The shore samples have minor enrichments in La and Tm. Otherwise, based on enrichment factors that do not exceed 1.2 and geoaccumulation indices that were all below zero, the Barakah NPP area was considered uncontaminated with REEs. This area was not polluted according to the pollution load indices (0.67, 0.52, and 0.17 for shore, soil, and marine sediments, respectively). The spatial distribution maps show the highest concentrations of REEs in the south area of the Barakah NPP. Overall, the Barakah NPP area does not have any alarming REE concentrations, and the baseline values were provided as a reference for future comparisons.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinlua, A., Olise, F. S., Akomolafe, A. O., & McCrindle, R. I. (2016). Rare earth element geochemistry of petroleum source rocks from northwestern Niger Delta. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 77, 409–417.
Al Rashdi, M. R. A., Alaabed, S., Tokhi, M. E., Howari, F. M., Mowafi, W. E., & Arabi, A. A. (2017). Distribution of heavy metals around the Barakah nuclear power plant in the United Arab Emirates. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 19835–19851.
Alsharhan, A. S., & Kendall, C. G. S. C. (2003). Holocene coastal carbonates and evaporites of the southern Arabian Gulf and their ancient analogues. Earth-Science Reviews, 61(3–4), 191–243.
Antonina, A. N., Shazili, N. A. M., Kamaruzzaman, B. Y., Ong, M. C., Rosnan, Y., & Sharifah, F. N. (2013). Geochemistry of the Rare Earth Elements (REE) Distribution in Terengganu Coastal Waters: A Study Case from Redang Island Marine Sediment. Open Journal of Marine Science, 03(03), 154–159.
Balaram, V. (2019). Rare earth elements: A review of applications, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact. Geoscience Frontiers, 10(4), 1285–1303.
Birch, G. (2003). A Scheme for Assessing Human Impacts on Coastal Aquatic Environments Using sediments.in: Woodcoffe, C. D., Furness, R. A. (Eds.), Coastal GIS (2003). Wollongong University Papers in Center for Maritime Policy, 14, Australia. In Woodcoffe CD, Furness RA.
Bolan, N.S., Adriano, D.C., & Naidu, R. (2003). Role of Phosphorus in (Im)mobilization and Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in the Soil-Plant System. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1–44.
Bourg, S., & Poinssot, C. (2017). Could spent nuclear fuel be considered as a non-conventional mine of critical raw materials? Progress in Nuclear Energy, 94, 222–228.
Byrne, R. H., & Kim, K. H. (1990). Rare earth element scavenging in seawater. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 54(10), 2645–2656.
Caccia, V. G., & Millero, F. J. (2007). Distribution of yttrium and rare earths in Florida Bay sediments. Marine Chemistry, 104(3–4), 171–185.
Chen, Z. (2011). Global rare earth resources and scenarios of future rare earth industry. Journal of Rare Earths, 29, 1–6.
Chen, K., Yang, C., & Jiao, J. J. (2013). Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry and Provenance Discrimination of Sediments in Tolo Harbour, Hong Kong. Journal Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 33, 51–57.
Cheng, J., Cheng, Z., Hu, R., Cui, Y., Cai, J., Li, N., et al. (2014). Immune dysfunction and liver damage of mice following exposure to lanthanoids. Environmental Toxicology, 29, 64–73.
Cheng, Y., Liu, M., Li, R., Wang, C., Bai, C., & Wang, K. (1999). Gadolinium induces domain and pore formation of human erythrocyte membrane: an atomic force microscopic study. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes, 1421(2), 249–260.
Coats, A. W., & Redferm, J. P. (1964). Kinetic parameters from thermogravimetric data. Nature, 201(68), 1964.
Daley, R. (1991). Atmospheric Data Analysis. Cambridge University Press, 457–458.
Dubinin, A. V. (2004). Geochemistry of Rare Earth Elements in the Ocean. Miner. Resour, 39, 289–307.
El Tokhi, M., Amin, B., & Alaabed, S. (2015). Geochemical behavior of elements of marine sediments of the Abu Dhabi area, United Arab Emirates. p. 340–343. In Third International Conference on Engineering Geophysics.
Fu, X., Wang, J., Zeng, Y., Tan, F., Chen, W., & Feng, X. (2010). Geochemistry of rare earth elements in marine oil shale - a case study from the bilong co area, Northern Tibet, China. Oil Shale, 27(3), 194.
Fu, X., Wang, J., Zeng, Y., Tan, F., & He, L. (2011). Geochemistry and origin of rare earth elements (REEs) in the Shengli River oil shale, northern Tibet, China. Chemie der Erde - Geochemistry, 71(1), 21–30.
Haskin, A., Frey, S. A., & Smith, H. (1966). Meteoritic, solar and terrestrial rare earth distributions (H Ahrens, F Press, K Runcorn, and U C., Eds.). Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Hedrick, J.B. (1997). Rare-earth metal prices in the USA ca. 1960 to 1994. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 250(1–2), 471–481.
Hoffert, M., Caldeira, K., Benford, G., Criswell, D., Green, C., Herzog, H., et al. (2002). Advanced Technology Paths to Global Climate Stability: Energy for a Greenhouse Planet. Science, 298(5595), 981–987.
Kacmaz, H. (2016). Major, trace and rare earth element (REE) characteristics of tuffs in the Yenice-Saraycik area (Demirci, Manisa), Western Anatolia, Turkey. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 168, 169–176.
Kanazawa, Y., & Kamitani, M. (2006). Rare earth minerals and resources in the world. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408–412, 1339–1343.
Kasper-Zubillaga, J. J., Acevedo-Vargas, B., Bermea, O. M., & Zamora, G. O. (2008). Rare earth elements of the Altar Desert dune and coastal sands, Northwestern Mexico. Chemie der Erde - Geochemistry, 68(1), 45–59.
Kendell, C. G. S. C., & Skipwith, P. (1969). Holocene Shallow-Water Carbonate and Evaporite Sediments of Khor al Bazam, Abu Dhabi, Southwest Persian Gulf. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 53, 841–869.
Kimoto, A., Nearing, M. A., Zhang, X. C., & Powell, D. M. (2006). Applicability of rare earth element oxides as a sediment tracer for coarse-textured soils. CATENA, 65(3), 214–221.
Kyung, T. R., Kwon, H. K., Jung, S., & P., (2013). Toxicological Evaluations of Rare Earths and Their Health Impacts to Workers: A Literature Review. Safety and Health at Work, 4(1), 12–26.
Land, L. S., Mack, L. E., Milliken, K. L., & Lynch, F. L. (1997). Burial diagenesis of argillaceous sediment, south Texas Gulf of Mexico sedimentary basin: A reexamination. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 109(1), 2–15.
Liaghat, S., Hosseini, M., & Zarasvandi, A. (2003). Determination of the origin and mass change geochemistry during bauxitization process at the Hangam deposit, SW Iran. Geochemical Journal, 37(5), 627–637.
Manning, C. E. (2006). Mobilizing aluminum in crustal and mantle fluids. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 89(1–3), 251–253.
Massari, S., & Ruberti, M. (2013). Rare earth elements as critical raw materials: Focus on international markets and future strategies. Resources Policy, 38(1), 36–43.
Millero, F. J. (1992). Stability constants for the formation of rare earth-inorganic complexes as a function of ionic strength. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 56(8), 3123–3132.
Müller, G. (1979). Heavy Metals in the Sediment of the Rhine – Changes seity. 1971. Umschau in Wissenschaft und Technik, 79, 778–783.
Müller, P. (1986). Rare Earth Mineral Deposits and Their Industrial Importance. In: Müller, P. Cerny, P., & Saupe, F. (Eds.), Lanthanides, Tanta1um and Niobium. Proceedings of a workshop in Berlin. Springer-Verlag.
Naidu, K.B., Reddy, K.S.N., Sekhar, C.R., Rao, P.G., & Krishna, K.N.M. (2016). REE geochemistry of monazites from coastal sands between Bhimunipatnam and Konada, Andhra Pradesh, East coast of India. Current Science, (00113891) 110(8), 1550–1559.
Nieuwenhuize, J., Poley-Vos, C. H., van den Akker, A. H., & Van Delft, W. (1991). Comparison of microwave and conventional extraction techniques for the determination of metals in soils, sediment and sludge samples by atomic spectrometry. Analyst, 116, 347–351.
Okay, C., Şükrü, K., & Ali, S. (2013). Rare Earth Element (REE) Geochemistry and Genesis of Oil Shales around Dağhacılar Village, Göynük-Bolu, Turkey. Oil Shale, 30, 419–440.
Oliveira, S. M. B., Silva, P. S. C., Mazzilli, B. P., Favaro, D. I. T., & Saueia, C. H. (2007). Rare earth elements as tracers of sediment contamination by phosphogypsum in the Santos estuary, southern Brazil. Applied Geochemistry, 22(4), 837–850.
Pang, X., Li, D., & Peng, A. (2001). Application of rare-earth elements in the agriculture of china and its environmental behavior in soil. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 1(2), 124–129.
Perryman, M. (2011). The Exoplanet Handbook. 1st Edition. Cambridge University Press.
Piper, D. Z., & Bau, M. (2013). Normalized Rare Earth Elements in Water, Sediments, and Wine: Identifying Sources and Environmental Redox Conditions. American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 04(10), 69–83.
Prudincio, M. I. (1995). REE Distribution in Present-Day and Ancient Surface Environments of Basaltic Rocks (Central Portugal). Clay Minerals, 30(3), 239–248.
Ravichandran, M. (1996). Distribution of rare earth elements in sediment cores of Sabine-Neches Estuary. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 32(10), 719–726.
Rollinson, H.R. (1993). Using Geochemical Data. Taylor & Francis Ltd.
Rubio, B., Nombela, M., & Vilas, F. (2000). Geochemistry of major and trace elements in sediments of the Ria de Vigo (NW Spain): an assessment of metal pollution. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40, 968–980.
Schropp, S. J., Lewis, F. G., Windom, H. L., Ryan, J. D., Calder, F. D., & Burney, L. C. (1990). Interpretation of Metal Concentrations in Estuarine Sediments of Florida Using Aluminum as a Reference Element. Estuaries, 13(3), 227.
Shan, G., & Zhang, B. (1991). Al2O3-REE correlations in sedimentary rocks. Geochemical Journal, 25, 147–161.
Sheppard, C.J.R., Price, A., & Roberts, C. (1992). Marine Ecology of the Arabian Region: Patterns and Processes in Extreme Tropical Environments. Academic Press Inc.
Shiller, A. M., & Boyle, E. (1985). Dissolved zinc in rivers. Nature, 317(6032), 49–52.
Sholkovitz, E. R. (1988). Rare earth elements in the sediments of the North Atlantic Ocean, Amazon Delta, and East China Sea; reinterpretation of terrigenous input patterns to the oceans. American Journal of Science, 288(3), 236–281.
Simandl, G. J. (2014). Geology and market-dependent significance of rare earth element resources. Mineralium Deposita, 49(8), 889–904.
Stegen, A. (2015). Heavy rare earths, permanent magnets, and renewable energies: An imminent crisis. Energy Policy, 79, 1–8.
Sultan, K., & Shazili, N. A. (2009). Rare earth elements in tropical surface water, soil and sediments of the Terengganu River Basin, Malaysia. Journal of Rare Earths, 27(6), 1072–1078.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39(6), 611–627.
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1985). The continental crust: Its composition and evolution. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1995). The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(2), 241.
Timothy, A., Steven, K., & Allen, C. (2015). Radiological Impacts and Regulation of Rare Earth Elements in Non-Nuclear Energy Production. Energies, 8, 2066–2081.
Tomlinson, D. L., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgolander Meeresuntersuchungen, 33(1–4), 566–575.
Tranchida, G., Oliveri, E., Angelone, A., Bellanca, A., Censi, P., Delia, M., et al. (2011). Distribution of rare earth elements in marine sediments from the Strait of Sicily (western Mediterranean Sea), Evidence of phosphogypsum waste contamination. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(1), 182–191.
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. W. (1961). Distribution of the Elements in Some Major Units of the Earth’s Crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72(2), 175.
Wang, X., Motto-Ros, V., Panczer, G., De Ligny, D., Yu, J. M., Benoit, J., et al. (2013). Mapping of rare earth elements in nuclear waste glass–ceramic using micro laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 87, 139–146.
Vural, A. (2015a). Biogeochemical characteristics of Rosa canina grown in hydrothermally contaminated soils of the Gümüşhane Province, Northeast Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(8), 486.
Vural, A. (2015b). Assessment of metal pollution associated with an alteration area: Old Gümüşhane, NE Black Sea. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(5), 3219–3228.
Wagner, C.W., & Togt, C. (1973). Holocene Sediment Types and Their Distribution in the Southern Persian Gulf. p. 123–155.
Wang, L., & Liang, T. (2015). Geochemical fractions of rare earth elements in soil around a mine tailing in Baotou, China. Scientific Reports, 5(1).
Weifang, Z., Suqin, X., Pingping, S., Hui, Z., Jia, F., Donglin, W., et al. (1997). Investigation on intake allowance of rare earth–A study on bio-effect of rare earth in South Jiangxi. Zhongguo Huanjing Kexue, 17(1), 63–66.
Wenhua, J., Dong, C., Xiaoting, M., & Yuxiu, N. (2004). Inhibitive effect and mechanism of lanthanum nitrate on preneoplastic lesion in rat liver. Journal-Chinese Rare Earth Society, 22(2), 292–294.
Xu, Z., Lim, D., Choi, J., Yang, S., & Jung, H. (2009). Rare earth elements in bottom sediments of major rivers around the Yellow Sea: implications for sediment provenance. Geo-Marine Letters, 29(5), 291–300.
Yang, S. Y., Jung, H. S., Choi, M. S., & Li, C. X. (2002). The rare earth element compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtze) and Huanghe (Yellow) river sediments. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 201(2), 407–419.
Zaremotlagh, S., & Hezarkhani, A. (2016). A geochemical modeling to predict the different concentrations of REE and their hidden patterns using several supervised learning methods: Choghart iron deposit, bafq, Iran. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 165, 35–48.
Zhang, H., Feng, J., Zhu, W., Liu, C., Wu, D., Yang, W., et al. (2000). Rare-Earth Element Distribution Characteristics of Biological Chains in Rare-Earth Element-High Background Regions and Their Implications. Biological Trace Element Research, 73(1), 19–28.
Zhenghua, W., Xiaorong, W., Yufeng, Z., Lemei, D., & Yijun, C. (2001). Effects of apatite and calcium oxyphosphate on speciation and bioavailability of exogenous rare earth elements in the soil-plant system. Chemical Speciation & Bioavailability, 13(2), 49–56.
Zuoping, Z., & Chuanxian, L. (1996). The behaviour of rare-earth elements (REE) during weathering of granites in southern Guangxi, China. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 15(4), 344–352.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the College of Graduate Studies at the United Arab Emirates University, UAEU, for covering all the costs associated with this research project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al Rashdi, M.R., El Tokhi, M., Alaabed, S. et al. Rare Earth Elements Around the Barakah Nuclear Power Plant, UAE. Nat Resour Res 29, 4149–4160 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09661-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09661-z