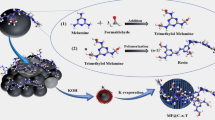
Abstract
Nitrogen-doped porous carbon (NPC) has a rich microporous structure and nitrogen-rich units, and its nitrogen-containing group can interact strongly with the PEO chain segment of Pebax, synergistically improving its CO2 adsorption ability and interface compatibility. This work prepared three types of triazine-based NPCs with mesoporous and high N-content and added NPCs to Pebax-2533 to prepare NPC/Pebax-2533 MMMs. The effects of N-type, N-content, and pore structure of NPCs on the gas separation performance of MMMs were studied. Constructing a continuous meso-microporous structure within the membrane and adding alkaline N-containing groups were beneficial for promoting rapid CO2 transport. Among the three NPCs, NPC-1/Pebax MMMs prepared using NPC-1 with the highest N-content (10.91%) and suitable pore structure exhibited the best gas separation performance. To investigate the gas transport mechanism of NPC in MMMs, NPC-1 was added to Pebax-2533 and Pebax-1657. The permeability of 3NPC-1/Pebax-2533 MMMs and 0.5NPC-1/Pebax-1657 MMMs reached 423 Barrer and 178 Barrer, with a CO2/N2 selectivity of 61 and 75.8, respectively, both higher than the Pebax-2533 and Pebax-1657. Adding NPC-1 to Pebax-2533 and Pebax-1657 increased the solubility and diffusivity coefficient of MMMs by 40 ~ 80%, and the gas separation performance did not rapidly decrease after long-term stability of 120 h (15%CO2/N2). Compared with NPC-1/Pebax-1657 MMMs, NPC-1/Pebax-2533 MMMs had higher CO2 permeability, mechanical properties, solubility, and diffusivity coefficient. The above results indicated that NPC was more suitable for Pebax-2533.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Experimental data
References
B R H A, B L W, C D O C, et al (2022) The natural field freeze-thaw process leads to different performances of soil amendments towards Cd immobilization and enrichment. Sci Total Environ 831: 154880
Li P, Zhong J, Ma W et al (2023) Diethylene glycolamine-assisted rapid synthesis of mechanically robust pyrogallol-based carbon monoliths for CO2 capture and separation. J CO2 Utilization 75: 102550
Mohamed A, Yousef S, Makarevicius V et al (2023) GNs/MOF-based mixed-matrix membranes for gas separations [J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy 48(51):19596–19604
Wang Y, Ma Z, Zhang X et al (2022) Mixed-matrix membranes consisting of Pebax and novel nitrogen-doped porous carbons for CO2 separation [J]. J Membr Sci 644:120182
Park TJ, Reznick J, Peterson BL et al (2017) Fructose-driven glycolysis supports anoxia resistance in the naked mole-rat [J]. Am Assoc Adv Sci 356(6335):307–311
Li H, Tuo L, Yang K et al (2016) Simultaneous enhancement of mechanical properties and CO2 selectivity of ZIF-8 mixed-matrix membranes: Interfacial toughening effect of ionic liquid. J Membr Sci 511:130–142
Zhao H, Feng L, Ding X et al (2018) The nitrogen-doped porous carbons/PIM mixed-matrix membranes for CO2 separation. J Membr Sci 564:800–805
Kosinov N, Gascon J, Kapteijn F et al (2015) Recent developments in zeolite membranes for gas separation. J Membrane ence 499:65–79
Qian Q, Asinger PA, Lee MJ et al (2020) MOF-Based Membranes for Gas Separations. Chem Rev 120(16):8161–8266
Daglar H, Erucar I, Keskin S (2021) Recent advances in simulating gas permeation through MOF membranes. Mater Adv 2:5300–5311
B F C A, B S D A, B Z W A et al (2020) Preparation of mixed-matrix composite membrane for hydrogen purification by incorporating ZIF-8 nanoparticles modified with tannic acid. Intl J Hydro Energy 45(12): 7444-7454
Liu W, Jiang SD, Yan Y et al (2020) A solution-processable and ultra-permeable conjugated microporous thermoset for selective hydrogen separation. Nat Commun 11(1):1633
Lin RB, Xiang S, Zhou W et al (2019) Microporous Metal-Organic Framework Materials for Gas Separation. Chem 6(2):337–363
Fu N, Wei H, Lin H et al (2017) Iron Nanoclusters as Template/Activator for the Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Porous Carbon and Its CO2 Adsorption Application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(11):9955–9963
Zeng S, Zhang X, Bai L et al (2017) Ionic-Liquid-Based CO2 Capture Systems: Structure. Interact Process Chem Rev 117(14):9625–9673
Wang H, Zheng W, Yang X et al (2021) Pebax-based mixed-matrix membranes derived from microporous carbon nanospheres for permeable and selective CO2 separation. Sep Purif Technol 274:119015
Liu N, Cheng J, Hu L et al. Boosting CO2 transport of poly (ethylene oxide) membranes by hollow Rubik-like “expressway” channels with anion-pillared hybrid ultramicroporous materials. Chem Eng J 427: 130845
Dong L, Zhang C, Bai Y et al (2016) High-Performance PEBA2533-Functional MMT Mixed Matrix Membrane Containing High-Speed Facilitated Transport Channels for CO2/N2 Separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4(6):3486–3496
Liu N, Cheng J, Hou W et al (2021) Pebax-based mixed matrix membranes loaded with graphene oxide/core-shell ZIF-8@ZIF-67 nanocomposites improved CO2 permeability and selectivity. J Appl Polym Sci 138(23):1–16
Dong L, Chen M, Wu X et al (2016) Multi-functional polydopamine coating: simultaneous enhancement of interfacial adhesion and CO2 separation performance of mixed matrix membranes. New J Chem 40(11):9148–9159
Liu N, Cheng J, Hou W et al. Bottom-up synthesis of two-dimensional composite via CuBDC-ns growth on multilayered MoS2 to boost CO2 permeability and selectivity in Pebax-based mixed matrix membranes. Separ Purif Technol 282: 120007
Shao L, Li Y, Huang J et al (2018) Synthesis of Triazine-Based Porous Organic Polymers Derived N-Enriched Porous Carbons for CO2 Capture. Ind Eng Chem Res 57(8):2856–2865
Zhang X, Rong M, Qin P et al (2022) PEO-based CO2 philic mixed matrix membranes compromising N-rich ultramicroporous polyamines for superior CO2 capture. J Membr Sci 644:120111
Shao L, Wang S, Liu M et al (2018) Triazine-based hyper-cross-linked polymers derived porous carbons for CO2 capture. Chem Eng J 339:509–518
Zhang, Xinru, Zhang, et al (2018) Mixed-matrix membranes based on Zn/Ni-ZIF-8-PEBA for high-performance CO2 separation. J Membr Sci 560: 38-46
Dong L, Sun Y, Zhang C et al (2015) Efficient CO2 capture by metallo-supramolecular polymers as fillers to fabricate a polymeric blend membrane. RSC Adv 5:67658–67661
Shao L, Liu M, Sang Y et al (2019) One-pot synthesis of melamine-based porous polyamides for CO2 capture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 285:1387–1811
Lee S, Park, et al (2018) Direct molecular interaction of CO2 with KTFSI dissolved in Pebax 2533 and their use in facilitated CO2 transport membranes. J Membr Sci 548:358–362
Xin Q, Liu T, Li Z et al (2015) Mixed matrix membranes composed of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) and a sulfonated metal–organic framework for gas separation. J Membr Sci 488:67–78
Dong L, Chen M, Li J et al (2016) Metal-organic framework-graphene oxide composites: A facile method to highly improve the CO2 separation performance of mixed matrix membranes. J Membr Sci 520:801–811
Waheed N, Mushtaq A, Tabassum S et al (2016) Mixed Matrix Membranes Based on Polysulfone and Rice Husk Extracted Silica for CO2 Separation. Sep Purif Technol 170:122–129
Zhang C, Wu Y, Zhang Y et al (2016) Poly(ether-b-amide)/ethylene glycol monophenyl ether gel membrane with superior CO2/N2 separation performance fabricated by thermally induced phase separation method. J Membr Sci 508:136–145
Tae-Hyun, Bae, Jong et al (2010) A High-Performance Gas-Separation Membrane Containing Submicrometer-Sized Metal-Organic Framework Crystals. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 49(51): 9863-9866
Dai Y, Ruan X, Yan Z et al (2016) Imidazole functionalized graphene oxide/PEBAX mixed matrix membranes for efficient CO2 capture. Sep Purif Technol 166:171–180
Zhang H, Guo R, Hou J et al (2016) Mixed Matrix Membranes Containing Carbon Nanotubes Composite with Hydrogel for Efficient CO2 Separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:29044–29051
Li X, Yu S, Li K et al (2020) Enhanced gas separation performance of Pebax mixed matrix membranes by incorporating ZIF-8 in situ inserted by multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Sep Purif Technol 248:117080
Y Zhang M Z, X Li, et al (2023) Constructing mixed matrix membranes for CO2 separation based on light lanthanide fluoride nanosheets with mesoporous structure. J Industr Eng Chem 125: 200-210
Acknowledgements
Thanks for the help of the Analysis and Testing Center, International Joint Lab of Jiangsu Education Department, and NERC Biomass of Changzhou University.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFB3805003), the Changzhou Sci&Tech Program (CZ20220033 and CZ20230022), the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX22_3026), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22108015). This work was also partially supported by the Kobe University Strategic International Collaborative Research Grant (Type B Fostering Joint Research).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peilin Li: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Experiment, Writing-Original Draft. Wenzhong Ma: Methodology, Writing Review & Editing. Jing Zhong: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing Review & Editing. Yang Pan: Investigation, Methodology. Xiuxiu Ren: Investigation, Methodology. Meng Guo: Resources, Supervision. Nanhua Wu: Investigation, Methodology. Hideto Matsuyama: Writing Review & Editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Ma, W., Zhong, J. et al. Research on triazine-based nitrogen-doped porous carbon/Pebax mixed-matrix membranes for CO2 separation and its gas transport mechanism. J Nanopart Res 26, 108 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-024-06015-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-024-06015-1