Abstract
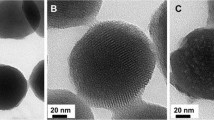
To improve the properties of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs), the surface of MSNs was functionally modified with a pH-sensitive polymer. Using polyethylene glycol 2000-distearoyl phosphatidylethanolamine (PEG2000-DSPE) as a modifier and doxorubicin (DOX) as a model drug, the pH-sensitive mesoporous silica composite nanocarriers were formed. When the MSNs were modified with PEG2000-DSPE at (m(PEG2000-DSPE):m(MSNs) = 1:5), DOX loaded in PEG2000-DSPE-MSNs (DOX-PEG-DSPE-MSNs) possessed good physicochemical properties including the highest drug loading (loading efficiency of (76.58 ± 0.75)% and loading capacity of (9.34 ± 0.03)%), the lowest average particle size ((298 ± 2) nm) and uniform size distribution (PDI of (0.14 ± 0.01)), colloid stability (zeta potential of (− 16.5 ± 0.3) mV), large specific surface area ((512 ± 4) m2g−1) and high pore capacity ((0.29 ± 0.02) cm3g−1). A lipid bilayer formed by PEG-DSPE2000 and phospholipid coated the MSN surface, acting as the “gatekeeper” for blocking the nanopores of MSNs, preventing the leakage and burst release of DOX absorbed in the mesoporous channel. Due to the hydrolysis of the amino group of PEG-DSPE in an acidic media, the “gatekeeper” broken, leading to destabilization and destruction of the lipid bilayer, exhibiting the pH-responsive release of DOX, which was fitted with a bi-phase exponential kinetic release model. PEG-DSPE-MSNs exhibited low cytotoxicity to LO2 cells and improved the biocompatibility of MSNs. PEG-DSPE-MSNs delivered DOX to tumor cells effectively due to pH-sensitive and sustained release, contributing to the significant inhibition of Hepg-2 cells. The results confirm the benefits of surface functionalization of MSNs with PEG-DSPE, and the potential application of tumor-targeted drugs.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saranya S, Radha KV (2014) Review of nanobiopolymers for controlled drug delivery. Polym-Plast Tech Mat 53(15):1636–1646. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602559.2014.915035
Ghaem B, Sadeghi M, Bardajee GR (2020) Synthesis of nano-polymer supported on nano-hydrogel chitosan base and its application for DOX delivery. J Polym Environ 28(9):2457–2468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01775-y
Du C, Li S, Li Y et al (2020) F7 and topotecan co-loaded thermosensitive liposome as a nano-drug delivery system for tumor hyperthermia. Drug Deliv 27(1):836–847. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2020.1772409
Liu Y, Xie C, Zhang F et al (2019) pH-responsive TiO2 nanotube drug delivery system based on iron coordination. J Nanomater 6395760https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6395760
Lila ASA, Ishida T (2017) Liposomal delivery systems: design optimization and current applications. Biol Pharm Bull 40(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b16-00624
Cheng G, Wang H, Zhang C et al (2020) Multifunctional nano-photosensitizer: a carrier-free aggregation-induced emission nanoparticle with efficient photosensitization and pH-responsibility. Chem Eng J 390:124447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124447
Pourjavadi A, Kohestanian M, Yaghoubi M (2019) Poly (glycidyl methacrylate)-coated magnetic graphene oxide as a highly efficient nanocarrier: preparation, characterization, and targeted DOX delivery. New J Chem 43(47):18647–18656. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nj04623b
Singal PK, Iliskovic N (1998) Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. New Engl J Med 339(13):900–905. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199809243391307
Ajzashokouhi AH, Bostan HB, Jomezadeh V et al (2020) A review on the cardioprotective mechanisms of metformin against doxorubicin. Hum Exp Toxicol 39(3):237–248. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327119888277
Yang Y, Zhao W, Tan W et al (2019) An efficient cell-targeting drug delivery system based on aptamer-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett 14(1):390. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-019-3208-3
Qin Y, Shan XQ, Han Y et al (2020) Study of pH-responsive and polyethylene glycol-modified doxorubicin-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. J Nanosci Nanotechno 20(10):5997–6006. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2020.17885
Kresge CT, Leonowicz ME, Roth WJ et al (1992) Ordered mesoporous molecular-sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 359(6397):710–712. https://doi.org/10.1038/359710a0
Liu J, Liu W, Zhang K et al (2020) A magnetic drug delivery system with “off–on” state via specific molecular recognition and conformational changes for precise tumor therapy. Adv Healthc Mater 9(3):1901316. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201901316
Nguyen TNT, Nguyen-Tran DH, Bach LG et al (2019) Surface PEGylation of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles via aminated intermediate. Prog Nat Sci-Mater 29(6):612–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2019.10.002
Huang L, Wu J, Liu MY et al (2017) Direct surface grafting of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with phospholipid choline-containing copolymers through chain transfer free radical polymerization and their controlled drug delivery. J Colloid Interf Sci 508:396–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.08.071
Yang PP, Gai SL, Lin J (2012) Functionalized mesoporous silica materials for controlled drug delivery. Chem Soc Rev 41(9):3679–3698. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs15308d
Tian Y, Glogowska A, Zhong W et al (2013) Polymeric mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a pH-responsive switch to control doxorubicin intracellular delivery. J Mater Chem B 1(39):5264–5272. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb20544d
Anon E, Costero AM, Gavina P et al (2019) Not always what closes best opens better: mesoporous nanoparticles capped with organic gates. Sci Technol Adv Mat 20(1):699–709. https://doi.org/10.1080/14686996.2019.1627173
Tian Y, Guo RR, Jiao YF et al (2016) Redox stimuli-responsive hollow mesoporous silica nanocarriers for targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy. Nanoscale Horiz 1(6):480–487. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6nh00139d
Deng C, Liu YH, Zhou FZ et al (2021) Engineering of dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient delivery of water-insoluble paclitaxel in cancer therapy. J Colloid Interf Sci 593:424–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.02.098
Rydberg HA, Arteta MY, Berg S et al (2016) Probing adsorption of DSPE-PEG2000 and DSPE-PEG5000 to the surface of felodipine and griseofulvin nanocrystals. Int J Pharmaceut 510(1):232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.06.046
Che J, Okeke CI, Hu ZB et al (2015) DSPE-PEG: a distinctive component in drug delivery system. Curr Pharm Design 21(12):1598–1605. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612821666150115144003
Cheng Y, Zou T, Dai M et al (2019) Doxorubicin loaded tumor-triggered targeting ammonium bicarbonate liposomes for tumor-specific drug delivery. Colloid Surface B 178:263–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.03.002
Gill KK, Kaddoumi A, Nazzal S (2015) PEG-lipid micelles as drug carriers: physiochemical attributes, formulation principles and biological implication. J Drug Target 23(3):222–231. https://doi.org/10.3109/1061186x.2014.997735
Wang RR, Xiao RZ, Zeng ZW et al (2012) Application of poly (ethylene glycol)-distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine (PEG-DSPE) block copolymers and their derivatives as nanomaterials in drug delivery. Int J Nanomed 7:4185–4198. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.S34489
Yuan L, Tang QQ, Yang D et al (2011) Preparation of pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their application in controlled drug delivery. J Phys Chem C 115(20):9926–9932. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp201053d
Lin YX, Zhou Q, Zeng YY et al (2018) Liposome-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with L-cysteine for photoelectrochemical immunoassay of aflatoxin B1. Microchim Acta 185:311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2848-9
Dolinina ES, Vlasenkova MI, Parfenyuk EV (2017) Effect of trehalose on structural state of bovine serum albumin adsorbed onto mesoporous silica and the protein release kinetics in vitro. Colloid Surface A 527:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.05.014
Antonow MB, Lorenzoni R, Barbosa GM et al (2016) Development and physicochemical characterization of desonide-loaded nanocapsule suspensions. Adv Mater Sci Eng 7395896https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7395896
Chen JY, Liu MY, Huang L et al (2018) Preparation of zwitterionic polymers functionalized fluorescent mesoporous silica nanoparticles through photoinduced surface initiated RAFT polymerization in the presence of oxygen. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 91:570–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.06.008
Weingart J, Vabbilisetty P, Sun XL (2013) Membrane mimetic surface functionalization of nanoparticles: methods and applications. Adv Colloid Interfac 197:68–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2013.04.003
Liu JW, Stace-Naughton A, Jiang XM et al (2009) Porous nanoparticle supported lipid bilayers (protocells) as delivery vehicles. J Am Chem Soc 131(4):1354–1355. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja808018y
Kurdyukov DA, Eurov DA, Kirilenko DA et al (2016) High-surface area spherical micro-mesoporous silica particles. Micropor Mesopor Mat 223:225–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.11.018
Tarn D, Ashley CE, Xue M et al (2013) Mesoporous silica nanoparticle nanocarriers: biofunctionality and biocompatibility. Accounts Chem Res 46(3):792–801. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar3000986
Samanta S, Pradhan L, Bahadur D (2018) Mesoporous lipid-silica nanohybrids for folate-targeted drug-resistant ovarian cancer. New J Chem 42(4):2804–2814. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nj03334f
Liu Y, Si YY, Di MY et al (2021) A novel microwave stimulus remote-controlled anticancer drug release system based on Janus TiO2-x&mSiO2 nanocarriers. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 11968https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2021.111968
Peng SY, Yuan XZ, Lin WJ et al (2019) pH-responsive controlled release of mesoporous silica nanoparticles capped with Schiff base copolymer gatekeepers: experiment and molecular dynamics simulation. Colloid Surface B 176:394–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.01.024
Ravi S, Lee YR, Yu K et al (2018) Benzene triamido-tetraphosphonic acid immobilized on mesoporous silica for adsorption of Nd3+ ions in aqueous solution. Micropor Mesopor Mat 258:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.09.006
Zhao ZH, Wang XM, Zhang ZJ et al (2015) Real-time monitoring of arsenic trioxide release and delivery by activatable t-1 imaging. ACS Nano 9(3):2749–2759. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn506640h
Piperoudi S, Fatouros D, Ioannou PV et al (2006) Incorporation of PEG-lipids in arsonoliposomes results in formation of highly stable arsenic-containing vesicles. Chem Phys Lipids 139(2):96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2005.11.003
Wang F, Liu JW (2015) A stable lipid/TiO2 interface with headgroup-inversed phosphocholine and a comparison with SiO2. J Am Chem Soc 137(36):11736–11742. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b06642
Pieri L, Bittelli M, Pisa PR (2006) Laser diffraction, transmission electron microscopy and image analysis to evaluate a bimodal Gaussian model for particle size distribution in soils. Geoderma 135:118–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.11.009
Wang YM, Li W, Liu TT et al (2019) Design and preparation of mesoporous silica carriers with chiral structures for drug release differentiation. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 103:109737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.109737
Wen Z, Su JQ, Chen Q et al (2016) Characterization and properties of solid lipid nanoparticles modified with polyethylene glycol-2000-1, 2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine. Sci Adv Mater 8(8):1617–1627. https://doi.org/10.1166/sam.2016.2776
Fahami A, Fathi M (2018) Development of cress seed mucilage/PVA nanofibers as a novel carrier for vitamin A delivery. Food Hydrocolloid 81:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.02.008
Agili FA, Aly SFM (2020) Physicochemical characterization and release properties of oral drug delivery: a pH-sensitive nanocomposite based on sodium alginate-pectin-tannic acid-silver. Polym Polym Compos 28(8–9):598–608. https://doi.org/10.1177/0967391119895073
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22078198), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (NO. 2021A1515010687), and the Basic Research Project of Shenzhen city, China (NO. JCYJ20170818093429961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jinglu Zhou: methodology; experiment on preparation and characterization; writing—original draft. Zhen Wen: supervision; funding acquisition; writing—review and editing. Shilun Yan: experiment on drug release. Hui Guo: data processing. Chuyue Zhou: experiment on BET; cytotoxicity and inhibition of tumor cells; writing—revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Wen, Z., Yan, S. et al. Preparation and release properties of pH-sensitive mesoporous silica composite nanocarriers. J Nanopart Res 24, 45 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05433-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05433-3