Abstract
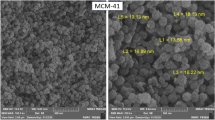
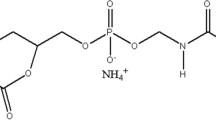
This report describes the synthesis of a controlled drug delivery system that was obtained by coating mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) with poly(β-amino ester) (PbAE), which is a solid and stable material at physiological pH, but is dissolved at acidic pH values, such as those in tumor tissues (from 5.0 to 6.5). To synthesize the system, PbAE chains were grafted onto amino-functionalized MSNs through a reaction between the surface amino groups of MSNs and the ends of acrylate chains of a PbAE. The system was physicochemically characterized by dynamic light scattering (DLS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, X-ray photoelectron spectrometry, and X-ray diffraction analyses. In addition, the in vitro release of doxorubicin (DOX) and doxycycline (DXY) in acidic and physiological media was evaluated. It was observed that the PbAE modification did not affect the mesoporous structure of MSNs. When the amount of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane was increased during functionalization, the amount of PbAE binding to MSNs increased as well. With respect to drug release, the sample with the highest amount of PbAE showed better control in the delivery of DXY and DOX in acidic media, because at pH 5.5, the release of both drugs was 40% higher than that at pH 7.4. These results reveal two aspects about the presence of PbAE in MSNs: PbAE does not affect the mesoporous structure of the nanoparticles, and PbAE is the main factor controlling the delivery of drugs in acidic media.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brey DM, Erickson I, Burdick JA (2008) Influence of macromer molecular weight and chemistry on poly (β-amino ester) network properties and initial cell interactions. J Biomed Mater Res, Part A 85(3):731–741
Chang B, Sha X, Guo J, Jiao Y, Wang C, Yang W (2011) Thermo and pH dual responsive, polymer shell coated, magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug release. J Mater Chem 21(25):9239–9247
Chen L, Zhang F, Wang C (2009) Rational synthesis of magnetic thermosensitive microcontainers as targeting drug carriers. Small 5(5):621–628
Chung P, Kumar R, Pruski M, Lin VS (2008) Temperature responsive solution partition of organic–inorganic hybrid poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)-coated mesoporous silica nanospheres. Adv Funct Mater 18(9):1390–1398
Coradin T, Boissière M, Livage J (2006) Sol–gel chemistry in medicinal science. Curr Med Chem 13(1):99–108
DenizáYilmaz M, FraseráStoddart J (2015) Esterase-and pH-responsive poly (β-amino ester)-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nanoscale 7(16):7178–7183
Du L, Liao S, Khatib HA, Stoddart JF, Zink JI (2009) Controlled-access hollow mechanized silica nanocontainers. J Am Chem Soc 131(42):15136–15142
Duivenvoorden WC, Popovic SV, Lhotak S, Seidlitz E, Hirte HW, Tozer RG et al (2002) Doxycycline decreases tumor burden in a bone metastasis model of human breast cancer. Cancer Res 62(6):1588–1591
Feitosa SA, Palasuk J, Kamocki K, Geraldeli S, Gregory RL, Platt JA et al (2014) Doxycycline-encapsulated nanotube-modified dentin adhesives. J Dent Res 93(12):1270–1276. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034514549997
Feng W, Zhou X, He C, Qiu K, Nie W, Chen L et al (2013) Polyelectrolyte multilayer functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive drug delivery: Layer thickness-dependent release profiles and biocompatibility. J Mater Chem B 1(43):5886–5898
Hu X, Hao X, Wu Y, Zhang J, Zhang X, Wang PC et al (2013) Multifunctional hybrid silica nanoparticles for controlled doxorubicin loading and release with thermal and pH dual response. J Mater Chem B 1(8):1109–1118
Huang IP, Sun SP, Cheng SH, Lee CH, Wu CY, Yang CS et al (2011) Enhanced chemotherapy of cancer using pH-sensitive mesoporous silica nanoparticles to antagonize P-glycoprotein-mediated drug resistance. Mol Cancer Therap 10(5):761–769. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-10-0884
Iwasaki H, Inoue H, Mitsuke Y, Badran A, Ikegaya S, Ueda T (2002) Doxycycline induces apoptosis by way of caspase-3 activation with inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase in human T-lymphoblastic leukemia CCRF-CEM cells. J Lab Clin Med 140(6):382–386
Jakša G, Štefane B, Kovač J (2013) XPS and AFM characterization of aminosilanes with different numbers of bonding sites on a silicon wafer. Surf Interface Anal 45(11–12):1709–1713
Kecht J, Bein T (2008) Oxidative removal of template molecules and organic functionalities in mesoporous silica nanoparticles by H2O2 treatment. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 116(1):123–130
Kecht J, Schlossbauer A, Bein T (2008) Selective functionalization of the outer and inner surfaces in mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem Mater 20(23):7207–7214
Kim Y, Zhang C, Cho C, Cho M, Jiang H (2013) Poly (amino ester)s-based polymeric gene carriers in cancer gene therapy. In: Wei M, Good D (eds) Novel gene therapy approaches. https://doi.org/10.5772/54740
Kleitz F, Schmidt W, Schüth F (2003) Calcination behavior of different surfactant-templated mesostructured silica materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 65(1):1–29
Lee C, Cheng S, Huang I, Souris JS, Yang C, Mou C et al (2010) Intracellular pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the controlled release of anticancer chemotherapeutics. Angew Chem 122(44):8390–8395
Lin Y, Wallace G (1994) Factors influencing electrochemical release of 2, 6-anthraquinone disulphonic acid from polypyrrole. J Control Release 30(2):137–142
Lynn DM, Amiji MM, Langer R (2001) pH-responsive polymer microspheres: Rapid release of encapsulated material within the range of intracellular pH. Angew Chem Int Ed 40(9):1707–1710
Meng H, Liong M, Xia T, Li Z, Ji Z, Zink JI et al (2010a) Engineered design of mesoporous silica nanoparticles to deliver doxorubicin and P-glycoprotein siRNA to overcome drug resistance in a cancer cell line. ACS Nano 4(8):4539–4550
Meng H, Xue M, Xia T, Zhao Y, Tamanoi F, Stoddart JF et al (2010b) Autonomous in vitro anticancer drug release from mesoporous silica nanoparticles by pH-sensitive nanovalves. J Am Chem Soc 132(36):12690–12697
Mura S, Nicolas J, Couvreur P (2013) Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat Mater 12(11):991
Na K (2007) pH-sensitive polymeric micelles for the effective delivery of anti-cancer drug. Korean J Gastroenterol Taehan Sohwagi Hakhoe Chi 49(5):314–319
Naruphontjirakul P, Viravaidya-Pasuwat K (2011) Development of doxorubicin—core–shell chitosan nanoparticles to treat cancer. In: Paper presented at the proceedings of the international conference on biomedical engineering and technology, IACSIT Press, Singapore, vol 11, pp 90–94
Pang J, Luan Y, Li F, Cai X, Du J, Li Z (2011) Ibuprofen-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) films for controlled drug release. Int J Nanomed 6:659–665. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s17011
Peng C, Zhao Q, Gao C (2010) Sustained delivery of doxorubicin by porous CaCO3 and chitosan/alginate multilayers-coated CaCO3 microparticles. Colloid Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 353(2):132–139
Petrescu M, Mitran RA, Luchian AM, Matei C, Berger D (2015) Mesoporous ceria-silica composites as carriers for doxycycline. UPB Sci Bull Ser B: Chem Mater Sci 77(3):13–24
Potineni A, Lynn DM, Langer R, Amiji MM (2003) Poly (ethylene oxide)-modified poly (β-amino ester) nanoparticles as a pH-sensitive biodegradable system for paclitaxel delivery. J Control Release 86(2):223–234
Radu DR, Lai C, Wiench JW, Pruski M, Lin VS (2004) Gatekeeping layer effect: A poly (lactic acid)-coated mesoporous silica nanosphere-based fluorescence probe for detection of amino-containing neurotransmitters. J Am Chem Soc 126(6):1640–1641
Roberts JR, Ritter DW, McShane MJ (2013) A design full of holes: Functional nanofilm-coated microdomains in alginate hydrogels. J Mater Chem B 1(25):3195–3201
Rosenholm JM, Meinander A, Peuhu E, Niemi R, Eriksson JE, Sahlgren C et al (2008) Targeting of porous hybrid silica nanoparticles to cancer cells. ACS Nano 3(1):197–206
Rosenholm JM, Sahlgren C, Lindén M (2010) Towards multifunctional, targeted drug delivery systems using mesoporous silica nanoparticles–opportunities and challenges. Nanoscale 2(10):1870–1883
Shen Y, Tang H, Zhan Y, Van Kirk EA, Murdoch WJ (2009) Degradable poly (β-amino ester) nanoparticles for cancer cytoplasmic drug delivery. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 5(2):192–201
Siepmann J, Siepmann F (2008) Mathematical modeling of drug delivery. Int J Pharm 364(2):328–343
Silvestri B, Guarnieri D, Luciani G, Costantini A, Netti P, Branda F (2012) Fluorescent (rhodamine), folate decorated and doxorubicin charged, PEGylated nanoparticles synthesis. J Mater Sci Mater Med 23(7):1697–1704
Stuart BH (2004) Organic molecules. I: David JA, Dartford K (ed), Infrared spectroscopy: Fundamentals and applications (pp. 71–80, 83). John Wiley & Sons Ltd, The Atrium, Southern Gate, Chichester, West Sussex PO19 8SQ, England, Wiley
Talavera-Pech WA, Esparza-Ruiz A, Quintana-Owen P, Vilchis-Nestor AR, Carrera-Figueiras C, Ávila-Ortega A (2016) Effects of different amounts of APTES on physicochemical and structural properties of amino-functionalized MCM-41-MSNs. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 80(3):697–708
Talelli M, Iman M, Varkouhi AK, Rijcken CJ, Schiffelers RM, Etrych T et al (2010) Core-crosslinked polymeric micelles with controlled release of covalently entrapped doxorubicin. Biomaterials 31(30):7797–7804
Tang H, Guo J, Sun Y, Chang B, Ren Q, Yang W (2011) Facile synthesis of pH sensitive polymer-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their application in drug delivery. Int J Pharm 421(2):388–396
Tang S, Yin Q, Zhang Z, Gu W, Chen L, Yu H et al (2014) Co-delivery of doxorubicin and RNA using pH-sensitive poly (β-amino ester) nanoparticles for reversal of multidrug resistance of breast cancer. Biomaterials 35(23):6047–6059
Van Speybroeck M, Barillaro V, Thi TD, Mellaerts R, Martens J, Van Humbeeck J et al (2009) Ordered mesoporous silica material SBA-15: A broad-spectrum formulation platform for poorly soluble drugs. J Pharm Sci 98(8):2648–2658
Victor SP, Kumar TS (2008) BCP ceramic microspheres as drug delivery carriers: synthesis, characterisation and doxycycline release. J Mater Sci Mater Med 19(1):283–290
Wallace SJ, Li J, Nation RL, Boyd BJ (2012) Drug release from nanomedicines: Selection of appropriate encapsulation and release methodology. Drug Deliv Transl Res 2(4):284–292
Wang C, Whitten PG, Too CO, Wallace GG (2008) A galvanic cell driven controlled release system based on conducting polymers. Sens Actuators B Chem 129(2):605–611
Yang Y, Yan X, Cui Y, He Q, Li D, Wang A et al (2008) Preparation of polymer-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles used for cellular imaging by a “graft-from” method. J Mater Chem 18(47):5731–5737
Yang P, Gai S, Lin J (2012) Functionalized mesoporous silica materials for controlled drug delivery. Chem Soc Rev 41(9):3679–3698
Yang K, Zhang C, Wang W, Wang PC, Zhou J, Liang X (2014) pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles employed in controlled drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. Cancer Biol Med 11(1):34
Zhu Y, Shi J (2007) A mesoporous core-shell structure for pH-controlled storage and release of water-soluble drug. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 103(1):243–249
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the program of competitive funds within the 2015 FIQ-UADY call. SAXRD and XPS measurements were performed at LANNBIO Cinvestav Mérida, under support from projects FOMIX-Yucatán 2008-108160 and CONACYT LAB-2009-01 No. 123913. MSc. D. Aguilar and Ing. W. Cauich are acknowledged for their technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talavera-Pech, W.A., Esparza-Ruiz, A., Quintana-Owen, P. et al. Synthesis of pH-sensitive poly(β-amino ester)-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the controlled release of drugs. Appl Nanosci 8, 853–866 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0716-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0716-x