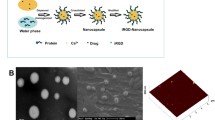
Abstract
Although the nanodrug-loading system provides new ideas for the effective treatment of cancer, the lack of active cancer targeting, easy to be cleared by the reticuloendothelial system (RES), and may cause potential safety issues are still problems that needs urgent solution. Herein, the authors fabricated platelet membrane (PM)-coated docetaxel (DTX)-loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) nanoparticles (PM/PLGA/DTX) that possessed unique advantages for satisfactory lung cancer therapy. The resulting core–shell nanoplatform exhibited proper size (hydrodynamic diameter was 98.2 nm) for the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, slowed down the release of loaded DTX, and effectively suppressed the growth of tumor cells in vitro. More importantly, due to the immune escape and cancer-targeting capacities of PM, the PM/PLGA/DTX showed long circulation and effective lung tumor-targeting ability. After administration in vivo antitumor activity, the PM/PLGA/DTX significantly inhibited the tumor growth of A549 cell-bearing nude mice. In addition, the PM/PLGA/DTX strongly reduced the DTX toxicity compared with that of free DTX. Therefore, the results here demonstrated this biomimetic nanoparticle is a promising nanosized drug delivery system for targeted lung cancer therapy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelaziz HM, Gaber M, Abd-Elwakil MM, Mabrouk MT, Elgohary MM, Kamel NM, Kabary DM, Freag MS, Samaha MW, Mortada SM (2018) Inhalable particulate drug delivery systems for lung cancer therapy: nanoparticles, microparticles, nanocomposites and nanoaggregates. J Control Release 269:374–392
Chen L, Zang F, Wu H, Li J, Xie J, Ma M, Gu N, Zhang Y (2018) Using PEGylated magnetic nanoparticles to describe the EPR effect in tumor for predicting therapeutic efficacy of micelle drugs. Nanoscale 10(4):1788–1797
Davis ME, Chen Z, Shin DM (2010) Nanoparticle therapeutics: an emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nanoscience and technology: a collection of reviews from nature journals. World Scientific, pp 239–250
Duncan R (2003) The dawning era of polymer therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2(5):347–360
Gao Y, Ren F, Ding B, Sun N, Liu X, Ding X, Gao S (2011) A thermo-sensitive PLGA-PEG-PLGA hydrogel for sustained release of docetaxel. J Drug Target 19(7):516–527
Gao C, Lin Z, Lin X, He Q (2018) Cell membrane–camouflaged colloid motors for biomedical applications. Adv Ther 1(5):1800056
Hu C-MJ, Zhang L, Aryal S, Cheung C, Fang RH, Zhang L (2011) Erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged polymeric nanoparticles as a biomimetic delivery platform. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(27):10980–10985
Hu C-MJ, Fang RH, Wang K-C, Luk BT, Thamphiwatana S, Dehaini D, Nguyen P, Angsantikul P, Wen CH, Kroll AV (2015a) Nanoparticle biointerfacing by platelet membrane cloaking. Nature 526(7571):118–121
Hu Q, Sun W, Qian C, Wang C, Bomba HN, Gu Z (2015b) Anticancer platelet-mimicking nanovehicles. Adv Mater 27(44):7043–7050
Hwang H-Y, Kim I-S, Kwon IC, Kim Y-H (2008) Tumor target ability and antitumor effect of docetaxel-loaded hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles. J Control Release 128(1):23–31
Jeannot V, Gauche C, Mazzaferro S, Couvet M, Vanwonterghem L, Henry M, Didier C, Vollaire J, Josserand V, Coll J-L (2018) Anti-tumor efficacy of hyaluronan-based nanoparticles for the co-delivery of drugs in lung cancer. J Control Release 275:117–128
Lemjabbar-Alaoui H, Hassan OU, Yang Y-W, Buchanan P (2015) Lung cancer: biology and treatment options. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1856(2):189–210
Li B, Zhang X-X, Huang H-Y, Chen L-Q, Cui J-H, Liu Y, Jin H, Lee B-J, Cao Q-R (2018) Effective deactivation of A549 tumor cells in vitro and in vivo by RGD-decorated chitosan-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotube loading docetaxel. Int J Pharm 543(1–2):8–20
Liu Z, Cai W, He L, Nakayama N, Chen K, Sun X, Chen X, Dai H (2007) In vivo biodistribution and highly efficient tumour targeting of carbon nanotubes in mice. Nat Nanotechnol 2(1):47–52
Liu R, Li D, He B, Xu X, Sheng M, Lai Y, Wang G, Gu Z (2011) Anti-tumor drug delivery of pH-sensitive poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (L-histidine-)-poly (L-lactide) nanoparticles. J Control Release 152(1):49–56
Mittal V, El Rayes T, Narula N, et al (2016) The microenvironment of lung cancer and therapeutic implications[M]//Lung Cancer and Personalized Medicine: Novel Therapies and Clinical Management. Springer, Cham, pp 75–110
Moghimi SM, Hunter AC, Peer D (2016) Platelet mimicry: the emperor’s new clothes? Nanomedicine 12(1):245–248
Piao L, Li Y, Zhang H, Jiang J (2019) Stereocomplex micelle loaded with paclitaxel for enhanced therapy of breast cancer in an orthotopic mouse model. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed (just-accepted):1–12
Rao L, Bu LL, Meng QF, Cai B, Deng WW, Li A, Li K, Guo SS, Zhang WF, Liu W (2017) Antitumor platelet-mimicking magnetic nanoparticles. Adv Funct Mater 27(9):1604774
Tian W, Lu J, Jiao D (2019) Stem cell membrane vesicle–coated nanoparticles for efficient tumor-targeted therapy of orthotopic breast cancer. Polym Adv Technol 30:1051–1060
Wang L, Liu Z, Liu D, Liu C, Juan Z, Zhang N (2011a) Docetaxel-loaded-lipid-based-nanosuspensions (DTX-LNS): preparation, pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and antitumor activity. Int J Pharm 413(1–2):194–201
Wang H, Zhao Y, Wu Y, Hu Y-l, Nan K, Nie G, Chen H (2011b) Enhanced anti-tumor efficacy by co-delivery of doxorubicin and paclitaxel with amphiphilic methoxy PEG-PLGA copolymer nanoparticles. Biomaterials 32(32):8281–8290
Wilhelm S, Tavares AJ, Dai Q, Ohta S, Audet J, Dvorak HF, Chan WC (2016) Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours. Nat Rev Mater 1(5):16014
Xu L, Wu S, Zhou X (2018) Bioinspired nanocarriers for an effective chemotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Biomater Appl 33(1):72–81
Zolnik BS, Gonzalez-Fernandez A, Sadrieh N, Dobrovolskaia MA (2010) Minireview: nanoparticles and the immune system. Endocrinology 151(2):458–465
Funding
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81362305) was gratefully acknowledged for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chi, C., Li, F., Liu, H. et al. Docetaxel-loaded biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted lung cancer therapy in vivo. J Nanopart Res 21, 144 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4580-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4580-8