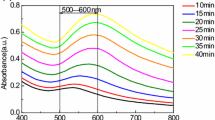
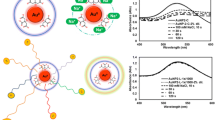
Abstract
The Turkevich method has been the preferred one for synthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), owing to its apparent simplicity and facility of replacing the citrate ions on the particle surface by molecules exhibiting different functionalities. Using the most common procedure labile spherical nanoparticles are usually obtained by this method. Here, by using factorial design of experiments, we demonstrated that gold nanodiscs (AuNDs) with short aspect ratio can be generated by the Turkevich method when Au:citrate ratio is 1:1. In comparison with the CTAB capped gold nanorods (AuNR), the citrate stabilized AuNDs exhibited a more labile character, allowing fast ligand exchange reactions and easy functionalization of the nanoparticle surface. In the presence of 4-mercaptopyridine (4-mpy), the surface enhancement Raman scattering effect was 100 and 1000 times higher than the one observed for CTAB-AuNR and spherical AuNPs, respectively, increasing the 4-mpy detection limit to 2.5 × 10−9 molL−1.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asadabad MA, Eskandari MJ (2016) Electron diffraction. In: Modern electron microscopy in physical and life sciences. InTech
Biggs S, Mulvaney P, Zukoski CF, Grieser F (1994) Study of anion adsorption at the gold-aqueous solution interface by atomic force microscopy. J Am Chem Soc 116(20):9150–9157
DuChene JS, Niu W, Abendroth JM, Sun Q, Zhao W, Huo F, Wei WD (2013) Halide anions as shape-directing agents for obtaining high-quality anisotropic gold nanostructures. Chem Mater 25(8):1392–1399
Elechiguerra JL, Reyes-Gasga J, Yacaman MJ (2006) The role of twinning in shape evolution of anisotropic noble metal nanostructures. J Mater Chem 16(40):3906–3919
Ermushev AV, Mchedlishvili BV, Olenĭkov VA, Petukhov AV (1993) Surface enhancement of local optical fields and the lightning-rod effect. Quantum Electronics 23(5):435–440
Frens G (1973) Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat Phys Sci 241(105):20–22
Gole A, Murphy CJ (2004) Seed-mediated synthesis of gold nanorods: role of the size and nature of the seed. Chem Mater 16(19):3633–3640
Grasseschi D, Zamarion VM, Araki K, Toma HE (2010) Surface enhanced raman scattering spot tests: a new insight on Feigl’s analysis using gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem 82(22):9146–9149
Grasseschi D, Parussulo ALA, Zamarion VM, Guimarães RR, Araki K, Toma HE (2013) How relevant can the SERS effect in isolated nanoparticles be? RSC Adv 3(46):24465–24472
Grasseschi D, Ando RA, Toma HE, Zamarion VM (2015a) Unraveling the nature of Turkevich gold nanoparticles: the unexpected role of the dicarboxyketone species. RSC Adv 5(8):5716–5724
Grasseschi D, Lima FS, Nakamura M, Toma HE (2015b) Hyperspectral dark-field microscopy of gold nanodisks. Micron 69:15–20
Grasseschi D, Lima FS, Chaimovich H, Toma HE (2016) A critical evaluation of the role of the precursor complex and counterions in synthesis of gold nanoparticles in micellar media. arXiv:1607.00530
Gunst RF, Myers RH, Montgomery DC (1996) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments. Technometrics 38(3):285
Hermoso W, Alves TV, de Oliveira CC, Moriya EG, Ornellas FR, Camargo PH (2013) Triangular metal nanoprisms of Ag, Au, and Cu: modeling the influence of size, composition, and excitation wavelength on the optical properties. Chem Phys 423:142–150
Jana NLGCMR, Gearheart L, Murphy CJ (2001a) Seed-mediated growth approach for shape-controlled synthesis of spheroidal and rod-like gold nanoparticles using a surfactant template. Adv Mater 13(18):1389–1393
Jana NR, Gearheart L, Murphy CJ (2001b) Wet chemical synthesis of high aspect ratio cylindrical gold nanorods. J Phys Chem B 105(19):4065–4067
Ji X, Song X, Li J, Bai Y, Yang W, Peng X (2007) Size control of gold nanocrystals in citrate reduction: the third role of citrate. J Am Chem Soc 129(45):13939–13948
Jung HS, Kim K, Kim MS (1997) Raman spectroscopic investigation of the adsorption of 4-mercaptopyridine on a silver-sol surface. J Mol Struct 407(2-3):139–147
Kim F, Connor S, Song H, Kuykendall T, Yang P (2004) Platonic gold nanocrystals. Angew Chem (International ed. in English) 43(28):3673–3677
Kim J, Hong S, Jang H-J, Choi Y, Park S (2013) Influence of iodide ions on morphology of silver growth on gold hexagonal nanoplates. J Colloid Interface Sci 389(1): 71–76
Kimling J, Maier M, Okenve B, Kotaidis V, Ballot H, Plech A (2006) Turkevich method for gold nanoparticle synthesis revisited. J Phys Chem B 110(32):15700–15707
Klopman G (1968) Chemical reactivity and the concept of charge- and frontier-controlled reactions. J Am Chem Soc 90(2):223–234
Leite ER, Ribeiro C (2012) Crystallization and growth of colloidal nanocrystals. SpringerBriefs in Materials. Springer, New York
Lim B, Camargo PHC, Xia Y (2008) Mechanistic study of the synthesis of Au nanotadpoles, nanokites, and microplates by reducing aqueous HAuCl4 with poly(vinyl pyrrolidone). Langmuir: the ACS Journal of Surfaces and Colloids 24(18):10437–10442
Liu MZ, Guyot-Sionnest P (2005) Mechanism of silver(I)-assisted growth of gold nanorods and bipyramids. J Phys Chem B 109(47):22192–22200
Liu B, Xie J, Lee JY, Ting YP, Chen JP (2005) Optimization of high-yield biological synthesis of single-crystalline gold nanoplates. J Phys Chem B 109(32):15256–15263
Liu Z, Zu Y, Guo S (2009) Synthesis of micron-scale gold nanochains by a modified citrate reduction method. Appl Surf Sci 255(11):5827–5830
Lohse SE, Murphy CJ (2013) The quest for shape control: a history of gold nanorod synthesis. Chem Mater 25(8):1250–1261
Lohse SE, Burrows ND, Scarabelli L, Liz-Marzán LM, Murphy CJ (2014) Anisotropic noble metal nanocrystal growth: the role of halides. Chem Mater 26(1):34–43
Mezni A, Dammak T, Fkiri A, Mlayah A, Abid Y, Smiri LS (2014) Photochemistry at the surface of gold nanoprisms from surface-enhanced raman scattering blinking. J Phys Chem C 118 (31):17956–17967
Murphy CJ, Jana NR (2002) Controlling the aspect ratio of inorganic nanorods and nanowires. Adv Mater 14(1):80– 82
Nikoobakht B, El-Sayed MA (2003) Preparation and growth mechanism of gold nanorods (NRs) using seed-mediated growth method. Chem Mater 15(10):1957–1962
Nunes FS, Bonifácio LDS, Araki K, Toma HE (2006) Interaction of 2- and 4-Mercaptopyridine with Pentacyanoferrates and gold nanoparticles. Inorg Chem 45(1):94–101
Ogi T, Saitoh N, Nomura T, Konishi Y (2009) Room-temperature synthesis of gold nanoparticles and nanoplates using Shewanella algae cell extract. J Nanopart Res 12(7): 2531–2539
Ojea-Jiménez I, Campanera JM (2012) Molecular modeling of the reduction mechanism in the citrate-mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 116(44):23682–23691
Pan H, Low S, Weerasuriya N, Shon Y-S (2015) Graphene oxide-promoted reshaping and coarsening of gold nanorods and nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(5):3406–3413
Pastoriza-Santos I, Liz-Marzan LM (2008) Colloidal silver nanoplates. State of the art and future challenges. J Mater Chem 18(15):1724
Pearson RG (1963) Hard and soft acids and bases. J Am Chem Soc 85(22):3533–3539
Pei L, Mori K, Adachi M (2004) Formation process of two-dimensional networked gold nanowires by citrate reduction of AuCl4- and the shape stabilization. Langmuir 20(18):7837–7843
Personick MLM, Mirkin CCA (2013) Making sense of the mayhem behind shape control in the synthesis of gold nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 135(49):18238–47
Pong B-K, Elim HI, Chong J-X, Ji W, Trout BL, Lee J-Y (2007) New insights on the nanoparticle growth mechanism in the citrate reduction of gold(III) salt: formation of the Au nanowire intermediate and its nonlinear optical properties. J Phys Chem C 111(17):6281–6287
Shankar SS, Rai A, Ankamwar B, Singh A, Ahmad A, Sastry M (2004) Biological synthesis of triangular gold nanoprisms. Nat Mater 3(7):482–488
Shankar SS, Rai A, Ahmad A, Sastry M (2005) Controlling the optical properties of lemongrass extract synthesized gold nanotriangles and potential application in infrared-absorbing optical coatings. Chem Mater 17(3):566–572
Stewart ME, Anderton CR, Thompson LB, Maria J, Gray SK, Rogers JA, Nuzzo RG (2008) Nanostructured plasmonic sensors. Chem Rev 108(2):494–521
Toma HE, Zamarion VM, Toma SH, Araki K (2010) The coordination chemistry at gold nanoparticles. J Braz Chem Soc 21(7):1158–1176
Turkevich J (1985a) Colloidal gold. Part I. Gold Bull 18:86–91
Turkevich J (1985b) Colloidal gold. Part II. Gold Bull 18:125–131
Turkevich J, Stevenson PPC, Hillier J (1951) A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss Faraday Soc 11:55–75
Turkevich J, Stevenson PC, Hillier J (1953) The formation of colloidal gold. J Phys Chem 57 (7):670–673
Vainrub A, Pustovyy O, Vodyanoy V (2006) Resolution of 90 nm (λ/5) in an optical transmission microscope with an annular condenser. Opt Lett 31(19):2855
Vianna PG, Grasseschi D, Costa GKB, Carvalho ICS, Domingues SH, Fontana J, de Matos CJS (2016) Graphene oxide/gold nanorod nanocomposite for stable surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. ACS Photonics 3(6):1027–1035
Wang Z, Ma L (2009) Gold nanoparticle probes. Coord Chem Rev 253(11-12):1607–1618
Wuithschick M, Birnbaum A, Witte S, Sztucki M, Vainio U, Pinna N, Rademann K, Emmerling F, Kraehnert R, Polte J (2015) Turkevich in new robes: key questions answered for the most common gold nanoparticle synthesis. ACS Nano 9(7):7052–7071
Xiong Y, Washio I, Chen J, Cai H, Li Z-Y, Xia Y (2006) Poly(vinyl pyrrolidone): a dual functional reductant and stabilizer for the facile synthesis of noble metal nanoplates in aqueous solutions. Langmuir 22(20):8563–8570
Yu HZ, Xia N, Liu ZF (1999) SERS titration of 4-Mercaptopyridine self-assembled monolayers at aqueous buffer/gold interfaces. Anal Chem 71(7):1354–8
Zamarion VM, Timm RA, Araki K, Toma HE (2008) Ultrasensitive SERS nanoprobes for hazardous metal ions based on trimercaptotriazine-modified gold nanoparticles. Inorg Chem 47(8):2934–2936
Acknowledgments
FAPESP, CNPq, NAP-NN, and PETROBRAS are gratefully acknowledged. We especially thanks Professor Thiago Paixão for the help with factorial design, Professor Pedro H. C. Camargo for the discussions, and Dr. Kazunori Fujisawa for the help with the TEM measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grasseschi, D., de O. Pereira, M.L., Shinohara, J.S. et al. Facile synthesis of labile gold nanodiscs by the Turkevich method. J Nanopart Res 20, 35 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4149-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4149-y