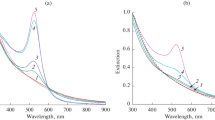
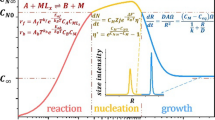
Abstract
The growth kinetics of nanosized ZnO was studied considering the influence of different parameters (mixing degree, temperature, alcohol chain length, reactant concentration and Zn/OH ratios) on the synthesis reaction and modelling the outputs using typical kinetic growth models, which were then evaluated by means of a sensitivity analysis. The Zn/OH ratio, the temperature and the alcohol chain length were found to be essential parameters to control the growth of ZnO nanoparticles, whereas zinc acetate concentration (for Zn/OH = 0.625) and the stirring during the ageing stage were shown to not have significant influence on the particle size growth. This last operational parameter was for the first time investigated for nanoparticles synthesized in 1-pentanol, and it is of outmost importance for the implementation of continuous industrial processes for mass production of nanosized ZnO and energy savings in the process. Concerning the nanoparticle growth modelling, the results show a different pattern from the more commonly accepted diffusion-limited Ostwald ripening process, i.e. the Lifshitz–Slyozov–Wagner (LSW) model. Indeed, this study shows that oriented attachment occurs during the early stages whereas for the later stages the particle growth is well represented by the LSW model. This conclusion contributes to clarify some controversy found in the literature regarding the kinetic model which better represents the ZnO NPs’ growth in alcoholic medium.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ameen S, Akhtar MS, Shin HS (2016) ZnO hollow nano-baskets for mineralization of cationic dye. Materials Letters 183:329–333. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2016.07.125
Arya SK, Saha S, Ramirez-Vick JE et al (2012) Recent advances in ZnO nanostructures and thin films for biosensor applications: review. Anal Chim Acta 737:1–21. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2012.05.048
Bahnemann DW, Kormann C, Hoffmann MR (1987) Preparation and characterization of quantum size zinc-oxide—a detailed spectroscopic study. J Phys Chem 91:3789–3798
Becheri A, Durr M, Lo Nostro P, Baglioni P (2008) Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles: application to textiles as UV-absorbers. J Nanopart Res 10:679–689. doi:10.1007/s11051-007-9318-3
Bell NS, Tallant DR (2009) Ripening and growth of zinc oxide nanorods from nanoparticles in 1,4 butanediol solvent. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 51:158–168. doi:10.1007/s10971-009-1967-5
Bhat SS, Qurashi A, Khanday FA (2017) ZnO nanostructures based biosensors for cancer and infectious disease applications: perspectives, prospects and promises. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 86:1–13. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2016.10.001
Brus L (1986) Electronic wave functions in semiconductor clusters: experiment and theory. J Phys Chem 90:2555–2560. doi:10.1021/j100403a003
Çınar S, Kaynar ÜH, Aydemir T et al (2017) An efficient removal of RB5 from aqueous solution by adsorption onto nano-ZnO/chitosan composite beads. Int J Biol Macromol 96:459–465. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.12.021
Dao DV, van den Bremt M, Koeller Z, Le TK (2016) Effect of metal ion doping on the optical properties and the deactivation of photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanopowder for application in sunscreens. Powder Technol 288:366–370. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2015.11.030
Derjaguin B V, Landau L (1941) Theory of the stability of strongly charged lyophobic sols and the adhesion of strongly charged particles in solution of electrolytes. Acta Physicochim USSR 14:633–662
Dhatshanamurthi P, Shanthi M, Swaminathan M (2017) An efficient pilot scale solar treatment method for dye industry effluent using nano-ZnO. J Water Process Eng 16:28–34. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.12.002
Fan Z, Lu JG (2005) Zinc oxide nanostructures: synthesis and properties. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 5:1561–1573
Gonfa BA, da Cunha AF, Timmons AB (2010) ZnO nanostructures for photovoltaic cells. Phys Status Solidi B-Basic Solid State Phys 247:1633–1636. doi:10.1002/pssb.200983684
Guo L, Yang SH, Yang CL et al (2000) Highly monodisperse polymer-capped ZnO nanoparticles: preparation and optical properties. Appl Phys Lett 76:2901–2903
Hosni M, Farhat S, Ben Amar M et al (2015) Mixing strategies for zinc oxide nanoparticle synthesis via a polyol process. AICHE J 61:1708–1721. doi:10.1002/aic.14737
Hu ZS, Oskam G, Searson PC (2003) Influence of solvent on the growth of ZnO nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 263:454–460. doi:10.1016/s0021-9797(03)00205-4
Hu Z, Herrera JF, Oskam G, Searson PC (2005a) Influence of the reactant concentrations on the synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 288:313–316. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2005.02.058
Hu ZS, Escamilla DJ, Heredia BE et al (2005b) Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles in 2-propanol by reaction with water. J Phys Chem B 109:11209–11214
Huang HC, Hsieh TE (2010) Highly stable precursor solution containing ZnO nanoparticles for the preparation of ZnO thin film transistors. Nanotechnology. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/21/29/295707
Huang, Zhang HZ, Banfield JF (2003) The role of oriented attachment crystal growth in hydrothermal coarsening of nanocrystalline ZnS. J Phys Chem B 107:10470–10475. doi:10.1021/Jp035518e
Keis K, Bauer C, Boschloo G et al (2002) Nanostructured ZnO electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cell applications. J Photochem Photobiol a-Chemistry 148:57–64
Kirchner H (1971) Coarsening of grain-boundary precipitates. Metall Mater Trans B Process Metall Mater Process Sci 2:2861–2864. doi:10.1007/bf02813264
Klingshirn C (1975) The luminescence of ZnO under high one- and two-quantum excitation. Phys Status Solidi 71:547–556. doi:10.1002/pssb.2220710216
Koch U, Fojtik A, Weller H, Henglein A (1985) Photochemistry of semiconductor colloids .13. Preparation of extremely small Zno particles, fluorescence phenomena and size quantization effects. Chem Phys Lett 122:507–510
Li S-C, Li Y-N (2010) Mechanical and antibacterial properties of modified nano-ZnO/high-density polyethylene composite films with a low doped content of nano-ZnO. J Appl Polym Sci 116:NA-NA. doi:10.1002/app.31802
Lifshitz IM, Slyozov VV (1961) The kinetics of precipitation from supersaturated solid solutions. J Phys Chem Solids 19:35–50
Mallakpour S, Behranvand V (2016) Nanocomposites based on biosafe nano ZnO and different polymeric matrixes for antibacterial, optical, thermal and mechanical applications. Eur Polym J 84:377–403. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2016.09.028
Meulenkamp EA (1998) Synthesis and growth of ZnO nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 102:5566–5572
Nain R, Yadav K, Jassal M, Agrawal AK (2015) Aligned ZnO nanorods as effective reinforcing material for obtaining high performance polyamide fibers. Compos Sci Technol 120:58–65. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2015.10.012
Ng HT, Chen B, Li J et al (2003) Optical properties of single-crystalline ZnO nanowires on m-sapphire. Appl Phys Lett 82:2023–2025
Nunes MI (2008) Micromixing in chemical reactors-test reactions. PhD thesis. Porto
Nunes MI, Santos RJ, Dias MM, Lopes JCB (2012) Micromixing assessment of confined impinging jet mixers used in RIM. Chem Eng Sci 74:276–286. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2012.02.054
Oskam G, Hu Z, Penn RL et al (2002) Coarsening of metal oxide nanoparticles. Phys Rev E 66:11403
Özgür Ü, Alivov YI, Liu C et al (2005) A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J Appl Phys 98:1–103
P MR, Muraleedaran K, VMA M (2015) Applications of chitosan powder with in situ synthesized nano ZnO particles as an antimicrobial agent. Int J Biol Macromol 77:266–272. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.03.058
Penn RL (2004) Kinetics of oriented aggregation. J Phys Chem B 108:12707–12712. doi:10.1021/Jp036490
Penn RL, Banfield JF (1998) Imperfect oriented attachment: dislocation generation in defect-free nanocrystals. Science (80-) 281:969–971
Penn R, Tanaka K, Erbs J (2007) Size dependent kinetics of oriented aggregation. J Cryst Growth 309:97–102. doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2007.09.011
Pesika NS, Hu ZS, Stebe KJ, Searson PC (2002) Quenching of growth of ZnO nanoparticles by adsorption of octanethiol. J Phys Chem B 106:6985–6990. doi:10.1021/jp0144606
Pesika NS, Stebe KJ, Searson PC (2003) Relationship between absorbance spectra and particle size distributions for quantum-sized nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B 107:10412–10415
Ratkovich AS, Penn RL (2007) Controlling nanosized ZnO growth kinetics using various Zn : OH concentration ratios. J Phys Chem C 111:14098–14104. doi:10.1021/jp071500i
Ribeiro C, Lee EJH, Longo E, Leite ER (2005) A kinetic model to describe nanocrystal growth by the oriented attachment mechanism. ChemPhysChem 6:690–696. doi:10.1002/cphc.200400505
Santra PK, Mukherjee S, Sarma DD (2010) Growth kinetics of ZnO nanocrystals in the presence of a base: effect of the size of the alkali cation. J Phys Chem C 114:22113–22118. doi:10.1021/Jp108613f
Sikora B, Fronc K, Kaminska I et al (2012) The growth kinetics of colloidal ZnO nanoparticles in alcohols. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 61:197–205. doi:10.1007/s10971-011-2614-5
Spanhel L, Anderson MA (1991) Semiconductor clusters in the sol-gel process: quantized aggregation, gelation, and crystal growth in concentrated zinc oxide colloids. J Am Chem Soc 113:2826–2833
Speight MV (1968) Growth kinetics of grain-boundary precipitates. Acta Metall 16:133–135. doi:10.1016/0001-6160(68)90081-3
Stokes RJ, Evans DF (1997) Fundamentals of interfacial engineering. CH Publishers, New York
Talapin DV, Rogach AL, Haase M, Weller H (2001) Evolution of an ensemble of nanoparticles in a colloidal solution: theoretical study. J Phys Chem B 105:12278–12285. doi:10.1021/Jp012229m
Verwey EJ, Overbeek JTG (1948) Theory of the stability of lyophobic colloids. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Viswanatha R, Sarma DD (2006) Study of the growth of capped ZnO nanocrystals: a route to rational synthesis. Chemistry 12:180–186. doi:10.1002/chem.200500632
Viswanatha R, Sapra S, Sen Gupta S et al (2004) Synthesis and characterization of Mn-doped ZnO nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B 108:6303–6310. doi:10.1021/jp049960o
Viswanatha R, Amenitsch H, Sarma DD (2007a) Growth kinetics of ZnO nanocrystals: a few surprises. J Am Chem Soc 129:4470–4475. doi:10.1021/ja068161b
Viswanatha R, Santra PK, Dasgupta C, Sarma DD (2007b) Growth mechanism of nanocrystals in solution: ZnO, a case study. Phys Rev Lett 98:20
Voigt M, Klaumünzer M, Thiem H, Peukert W (2010) Detailed analysis of the growth kinetics of ZnO nanorods in methanol. J Phys Chem C 114:6243–6249. doi:10.1021/jp911258d
Wagner C (1961) Theorie Der Alterung Von Niederschlagen Durch Umlosen (Ostwald-Reifung). Zeitschrift Fur Elektrochemie 65:581–591
Wong EM, Bonevich JE, Searson PC (1998) Growth kinetics of nanocrystalline ZnO particles from colloidal suspensions. J Phys Chem B 102:7770–7775. doi:10.1021/jp982397n
Yang ZX, Zhong W, Du X et al (2011) The synthesis of novel ZnO microcrystals through a simple solvothermal method and their optical properties. J Alloys Compd 509:3403–3408. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.12.089
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by national research grants PTDC/EQU-EQU/098617/2008, PTDC/QEQ-FTT/0041/2014 and POCI-01-0145-FEDER, by project POCI-01-0145-FEDER-006984—Associate Laboratory LSRE-LCM funded by FEDER through COMPETE2020—Programa Operacional Competitividade e Internacionalização (POCI) and by FCT—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary material
(DOCX 4895 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fonseca, A.S., Figueira, P.A., Pereira, A.S. et al. Parametric analysis of the growth of colloidal ZnO nanoparticles synthesized in alcoholic medium. J Nanopart Res 19, 75 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3774-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-017-3774-1