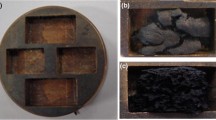
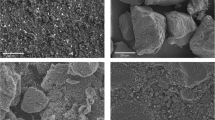
Abstract
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) as fillers in nanocomposites have attracted significant attention, and one of the applications is to use the CNTs as flame retardants. For such nanocomposites, possible release of CNTs at elevated temperatures after decomposition of the polymer matrix poses potential health threats. We investigated the airborne particle release from a decomposing multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)/epoxy nanocomposite in order to measure a possible release of MWCNTs. An experimental set-up was established that allows decomposing the samples in a furnace by exposure to increasing temperatures at a constant heating rate and under ambient air or nitrogen atmosphere. The particle analysis was performed by aerosol measurement devices and by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of collected particles. Further, by the application of a thermal denuder, it was also possible to measure non-volatile particles only. Characterization of the tested samples and the decomposition kinetics were determined by the usage of thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The particle release of different samples was investigated, of a neat epoxy, nanocomposites with 0.1 and 1 wt% MWCNTs, and nanocomposites with functionalized MWCNTs. The results showed that the added MWCNTs had little effect on the decomposition kinetics of the investigated samples, but the weight of the remaining residues after decomposition was influenced significantly. The measurements with decomposition in different atmospheres showed a release of a higher number of particles at temperatures below 300 °C when air was used. Analysis of collected particles by TEM revealed that no detectable amount of MWCNTs was released, but micrometer-sized fibrous particles were collected.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babrauskas V, Peacock RD (1992) Heat release rate: the single most important variable in fire hazard. Fire Saf J 18:255–272. doi:10.1016/0379-7112(92)90019-9
Bai JB, Allaoui A (2003) Effect of the length and the aggregate size of MWNTs on the improvement efficiency of the mechanical and electrical properties of nanocomposites—experimental investigation. Compos Part A 34:689–694. doi:10.1016/S1359-835X(03)00140-4
Bouillard J, R’Mili B, Moranviller D et al (2013) Nanosafety by design: risks from nanocomposite/nanowaste combustion. J Nanoparticle Res 15:1–11
Burtscher H, Baltensperger U, Bukowiecki N et al (2001) Separation of volatile and non-volatile aerosol fractions by thermodesorption: instrumental development and applications. J Aerosol Sci 32:427–442. doi:10.1016/S0021-8502(00)00089-6
Chatterjee S, Wang JW, Kuo WS et al (2012) Mechanical reinforcement and thermal conductivity in expanded graphene nanoplatelets reinforced epoxy composites. Chem Phys Lett 531:6–10. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2012.02.006
Christou A, Stec AA (2014) Characterising the release of carbon nanotubes from burning CNT-polymer composites. In: Nanosafe 2014, Grenoble. http://www.nanosafe.org/home/liblocal/docs/Nanosafe%202014/Session%206/06b-6%20-%20Antonis%20CHRISTOU.pdf.
Ciecierska E, Boczkowska A, Kurzydlowski KJ et al (2013) The effect of carbon nanotubes on epoxy matrix nanocomposites. J Therm Anal Calorim 111:1019–1024. doi:10.1007/s10973-012-2506-0
Covaci A, Gerecke AC, Law RJ et al (2006) Hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) in the environment and humans: a review. Environ Sci Technol 40:3679–3688
Dittrich B, Wartig K-A, Hofmann D et al (2013) Carbon black, multiwall carbon nanotubes, expanded graphite and functionalized graphene flame retarded polypropylene nanocomposites. Polym Adv Technol 24:916–926
Du J, Wang S, You H, Zhao X (2013) Understanding the toxicity of carbon nanotubes in the environment is crucial to the control of nanomaterials in producing and processing and the assessment of health risk for human: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36:451–462. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2013.05.007
Erdely A, Dahm M, Chen BT et al (2013) Carbon nanotube dosimetry: from workplace exposure assessment to inhalation toxicology. Part Fibre Toxicol. doi:10.1186/1743-8977-10-53
Fu S, Song P, Yang H et al (2010) Effects of carbon nanotubes and its functionalization on the thermal and flammability properties of polypropylene/wood flour composites. J Mater Sci 45:3520–3528
Ging J, Tejerina-Anton R, Ramakrishnan G, Nielsen M, Murphy K, Gorham JM, Nguyen T, Orlov A (2014) Development of a conceptual framework for evaluation of nanomaterials release from nanocomposites: environmental and toxicological implications. Sci Total Environ 473–474:9–19
Hollertz R, Chatterjee S, Gutmann H et al (2011) Improvement of toughness and electrical properties of epoxy composites with carbon nanotubes prepared by industrially relevant processes. Nanotechnology 22:125702. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/22/12/125702
Huang H, Liu CH, Wu Y, Fan S (2005) Aligned carbon nanotube composite films for thermal management. Adv Mater 17:1652–1656. doi:10.1002/adma.200500467
Kaiser JP, Roesslein M, Buerki-Thurnherr T, Wick P (2011) Carbon nanotubes—curse or blessing. Curr Med Chem 18:2115–2128. doi:10.1007/s10101-010-0075-x
Kashiwagi T, Grulke E, Hilding J et al (2002) Thermal degradation and flammability properties of poly(propylene)/carbon nanotube composites. Macromol Rapid Commun 23:761–765
Kashiwagi T, Grulke E, Hilding J et al (2004) Thermal and flammability properties of polypropylene/carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Polymer 45:4227–4239
Kashiwagi T, Du F, Winey KI et al (2005a) Flammability properties of polymer nanocomposites with single-walled carbon nanotubes: effects of nanotube dispersion and concentration. Polymer 46:471–481
Kashiwagi T, Du FM, Douglas JF et al (2005b) Nanoparticle networks reduce the flammability of polymer nanocomposites. Nat Mater 4:928–933
Kashiwagi T, Mu M, Winey K et al (2008) Relation between the viscoelastic and flammability properties of polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 49:4358–4368
Kim JY, Park HS, Kim SH (2009) Thermal decomposition behavior of carbon-nanotube-reinforced poly(ethylene 2,6-naphthalate) nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 113:2008–2017
Lu L, Yu H, Wang S, Zhang Y (2009) Thermal degradation behavior of styrene-butadiene-styrene tri-block copolymer/multiwalled carbon nanotubes composites. J Appl Polym Sci 112:524–531. doi:10.1002/app.29414
Ma P-C, Mo S-Y, Tang B-Z, Kim J-K (2010a) Dispersion, interfacial interaction and re-agglomeration of functionalized carbon nanotubes in epoxy composites. Carbon 48:1824–1834. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2010.01.028
Ma PC, Siddiqui NA, Marom G, Kim JK (2010b) Dispersion and functionalization of carbon nanotubes for polymer-based nanocomposites: a review. Composites A 41:1345
Mouritz AP, Gibson AG (2006) Fire properties of polymer composite materials. Springer, New York
Mueller NC, Buha J, Wang J, Ulrich A, Nowack B (2013) Modeling the flows of engineered nanomaterials during waste handling. Environ Sci 15:251–259. doi:10.1039/c2em30761h
Neises B, Steglich W (1978) Simple method for esterification of carboxylic-acids. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 17:522–524
Nguyen T, Pellegrin B, Bernard C, Gu X, Gorham JM, Stutzman P, Stanley D, Shapiro A, Byrd E, Hettenhouser R, Chin J (2011) Fate of nanoparticles during life cycle of polymer nanocomposites. J Phys 304:12060
Nowack B, David RM, Fissan H et al (2013) Potential release scenarios for carbon nanotubes used in composites. Environ Int 59:1–11. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2013.04.003
Nyden MR, Harris RH, Kim YS et al (2010) Characterizing particle emissions from burning polymer nanocomposites. In: Technical proceedings o f the 2010 NSTI nanotechnology conference expo, p 717–719
Ozawa T (1965) A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 38:1881–1886. doi:10.1246/bcsj.38.1881
Pinto F, Costa P, Gulyurtlu I, Cabrita I (1999) Pyrolysis of plastic wastes. 1. Effect of plastic waste composition on product yield. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 51:39–55. doi:10.1016/S0165-2370(99)00007-8
Qu Z, Wang G (2012) A comparative study on the properties of the different amino-functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes reinforced epoxy resin composites. J Appl Polym Sci 124:403–411. doi:10.1002/app
Rahatekar SS, Zammarano M, Matko S et al (2010) Effect of carbon nanotubes and montmorillonite on the flammability of epoxy nanocomposites. Polym Degrad Stab 95:870–879. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.01.003
Ribeiro B, Nohara L, Oishi S et al (2012) Nonoxidative thermal degradation kinetic of polyamide 6,6 reinforced with carbon nanotubes. J Thermoplast Compos Mater 26:1317–1331. doi:10.1177/0892705712439566
Schartel B, Pötschke P, Knoll U, Abdel-Goad M (2005) Fire behaviour of polyamide 6/multiwall carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 41:1061–1070
Schlagenhauf L, Chu BTT, Buha J et al (2012) Release of carbon nanotubes from an epoxy-based nanocomposite during an abrasion process. Environ Sci Technol 46:7366–7372. doi:10.1021/es300320y
Seo M-K, Park S-J (2004) A kinetic study on the thermal degradation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes-reinforced poly(propylene) composites. Macromol Mater Eng 289:368–374. doi:10.1002/mame.200300303
Shariati J, Saadatabadi AR, Khorasheh F (2012) Thermal degradation behavior and kinetic analysis of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene based multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposites prepared via in-situ polymerization. J Macromol Sci Part A 49:749–757. doi:10.1080/10601325.2012.703520
Uddin N, Nyden MR, Davis RD (2011) Characterization of nanoparticle release from polymer nanocomposites due to fire. In: Nanotech 2011 conference and expo, p 1–4
Verdejo R, Barroso-Bujans F, Rodriguez-Perez MA et al (2008) Carbon nanotubes provide self-extinguishing grade to silicone-based foams. J Mater Chem 18:3933–3939
Vogt J (1985) Thermal analysis of epoxy-resins: identification of decomposition products. Thermochim Acta 85:411–414. doi:10.1016/0040-6031(85)85611-2
Wang J, Asbach C, Fissan H, Hülser T, Kuhlbusch TAJ, Thompson D, Pui DYH (2011) How can nanobiotechnology oversight advance science and industry: examples from environmental, health and safety studies of nanoparticles (nano-EHS). J Nanopart Res 13:1373–1387. doi:10.1007/s11051-011-0236-z
Willis J (2012) Proposal to amend Annex A to the Stockholm Convention to be discussed at the sixth meeting of the Conference of the Parties
Wu Q, Zhu W, Zhang C et al (2010) Study of fire retardant behavior of carbon nanotube membranes and carbon nanofiber paper in carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Carbon 48:1799–1806
Zammarano M, Krämer RH, Harris R et al (2008) Flammability reduction of flexible polyurethane foams via carbon nanofiber network formation. Polym Adv Technol 19:588–595. doi:10.1002/pat
Zybex technologies (2014) Safety Data Sheet ZNT-boost (Solid). Retrieved from http://www.zyvextech.com/assets/pdf/ZNT-bOOST-SOLID-Resin-Linear-Polymer-20032514-3.pdf
Acknowledgments
This study was financed by the Swiss National Science Foundation (NFP 64), “Evaluation platform for safety and environment risks of carbon nanotube reinforced nanocomposites,” 406440_131286.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlagenhauf, L., Kuo, YY., Bahk, Y.K. et al. Decomposition and particle release of a carbon nanotube/epoxy nanocomposite at elevated temperatures. J Nanopart Res 17, 440 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3245-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3245-5