Abstract
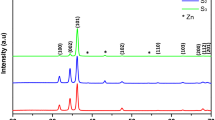
Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanowires (NWs) are exposed to energetic proton (H+), nitrogen (N+), phosphorus (P+), and argon (Ar+) ions to understand the radiation hardness and structural changes induced by these irradiations. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy is utilized to see the irradiation effects in NWs. Multiple doses and energies of radiation at different temperatures are used for different set of samples. The study reveals that wurtzite (crystalline)-structured ZnO NWs experience amorphization, degradation, and morphological changes after the irradiation. At room temperature, deterioration of the crystalline structure is observed under high fluence of H+, N+, and P+ ions. While for ZnO NWs, bombarded by Ar+ and P+ ions, nano-holes are produced. The ZnO NWs surfaces also show corrugated morphology full of nano-humps when irradiated by Ar+ ions at 400 °C. The corrugated surface could serve as tight-holding interface when interconnecting it with other NWs/nanotubes. These nano-humps may have the function of increasing the surface for surface-oriented sensing applications in the future.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad I, Dee CF, Husnain G, Rafique HM, Yan L, Naseem S (2012) Use of high-intensity electron beam to form nanohole, induce bending and fabricate nanocontact on a ZnO nanowire. Micro Nano Lett 7:122–124
Andrievski RA (2011) Behavior of radiation defects in nanomaterials. Rev Adv Mater Sci 29(2011):54–67
Bal AK, Singh R, Bedi RK (2012) Effect of Ni7+ ion irradiation on structure and ammonia sensing properties of thermally oxidized zinc and indium films. J Mater Sci Technol 28(8):700–706
Bai X-M, Voter AF et al (2010) Efficient annealing of radiation damage near grain boundaries via interstitial emission. Science 327:1631–1634
Bettge M, MacLaren S, Burdin S, Richard Haasch T, Abraham D, Petrov I, Yu MF, Sammann E (2012) Ion-induced surface relaxation: controlled bending and alignment of nanowire arrays. Nanotechnology 23:175302
Borschel C, Spindler S, Lerose D, Bochmann A, Silke Christiansen H, Nietzsche S, Oertel M, Ronning C (2011) Permanent bending and alignment of ZnO nanowires. Nanotechnology 22:185307
Dee CF, Majlis BY, Yahaya M, Salleh MM (2008) Electrical characterization of cross-linked ZnO nanostructures grown on Si and Si/SiO2 substrate. Sains Malaysiana 37:281–283
Dee CF, Ishaq A, Yan L, Xingtai Z, Majlis (2011a) Contact welding study of carbon nanotube with ZnO nanowire. Physica E 43:1857–1862
Dee CF, Ishaq A, Yan L, Xingtai Z, Majlis BY (2011b) Amorphization of ZnO nanowires by proton beam irradiation. NANO 6:259–263
Ishaq A, Yan L, Gong JL, Dezhang Z (2009) Graphite-to-amorphous structural transformation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes under proton beam Irradiation. Mater Lett 63:1505–1507
Ishaq A, Yan L, Husnain G, Bo L, Arshad M, Khalid A (2011) Tuning the optical properties of MWCNT thin films by N+ ion beam irradiation. NANO 6:357–362
Krasheninnikov AV, Banhart F (2007) Engineering of nanostructured carbon materials with electron or ion beams. Nat Mater 6:723–733
Krasheninnikov AV, Nordlund K (2010) Ion and electron irradiation-induced effects in nano-structured materials. J Appl Phys 107:071301–071370
Ni Z, Ishaq A, Yan L, Gong JL, Dezhang Z (2009) Enhanced electron field emission of carbon nanotubes by Si ion beam irradiation. J Phys D 42:075408
Shaw HC, Liu D, Jacobs BW, Ayres VM, Ronningen RM, Zeller AF, Crimp MA, Halpern J, He M-Q, Harris GL, Petkov MP (2005) Performance of nanomaterials and actively running nanocircuits during heavy ion irradiation. 12th NASA symposium on VLSI design, Coeur d’Alene, Idaho, USA, 4–5 Oct. 2005
Wang L, Kang Y, Liu X, Zhang S, Huang W, Wang S (2012) ZnO nanorod gas sensor for ethanol detection. Sens Actuators, B 162(1):20
Wang ZL (2004) Nanostructures of ZnO. Mater Today 7:26–33
Yan L, Guangying Z, Ishaq A, Xingtai Z (2011) Improving the electrical conductivity of multi-walled carbon nanotube networks by H ion beam irradiation. Carbon 49:2141–2144
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2010CB832903).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishaq, A., Usman, M., Dee, C.F. et al. Effect for hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorous, and argon ions irradiation on ZnO NWs. J Nanopart Res 15, 1467 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1467-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1467-y