Abstract
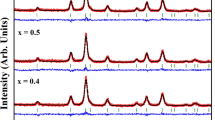
The effect of dipole–dipole and exchange interactions on dynamics of superspins in a system of MnFe2−x Ag x O4 (where x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.6) nanoparticles has been studied by Ac magnetic susceptibility measurements. Average crystallite size of samples was estimated to be ~7 to ~4 nm, with respect to the doping level of x = 0–0.6. It was found that the nanoparticles are superparamagnetic at room temperature with almost zero coercivity. Saturation magnetization of samples showed a remarkable reduction by increasing non-magnetic Ag doping level. By decreasing the temperature, a transition to frustrated superspin glass state was observed in all samples. Freezing temperatures of superspins were decreased by increasing the Ag content, as a result of decreasing size of crystallites, magnetization of nanoparticles, and consequently weakening of dipole–dipole interactions. The estimated values of zυ, τ 0, and T 0, using critical slowing down model, justify the observed variation of freezing temperatures. Furthermore it was realized that sensitivity of samples to the variation of applied frequency, an important parameter in hyperthermia based therapy, is affected by magnetic interactions between nanoparticles.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso J, Fdez-Gubieda ML, Barandiarán JM, Svalov A, Fernández Barquín L, Alba Venero D, Orue I (2010) Crossover from superspin glass to superferromagnet in Fe x Ag100−x nanostructured thin films (20 ≤ x ≤ 50). Phys Rev B 82:054406. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.82.054406
Ashiq MN, Saleem S, Malana MA, Anis UR (2009) Physical, electrical and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Zr–Ni doped Mn-ferrite synthesized by the co-precipitation method. J Alloy Compd 486:640–644. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.07.007
Aslibeiki B, Kameli P, Salamati H, Eshraghi M, Tahmasebi T (2010) Superspin glass state in MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 322:2929–2934. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.05.007
Aslibeiki B, Kameli P, Manouchehri I, Salamati H (2012a) Strongly interacting superspins in Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Curr Appl Phys 12:812–816. doi:10.1016/j.cap.2011.11.012
Aslibeiki B, Kameli P, Salamati H (2012b) The effect of grinding on magnetic properties of agglomereted MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 324:154–160. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.07.057
Chen M-L, Meng Z-D, Zhu L, Choi J-G, Park C-Y, Lee S-C, Hong D-S, Lee J-G, Jang W-K, Oh W-C (2011) Dispersion stability of metal (oxide)-graphene nanofluids with electrical and thermal properties. Sci Adv Mater 3:887–892. doi:10.1166/sam.2011.1213
Costa ACFM, Silva VJ, Cornejo DR, Morelli MR, Kiminami RHGA, Gama L (2008) Magnetic and structural properties of NiFe2O4 ferrite nanopowder doped with Zn2+. J Magn Magn Mater 320:e370–e372. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.02.159
Desautels RD, Skoropata E, Chen YY, Ouyang H, Freeland JW, van Lierop J (2011) Tuning the surface magnetism of gamma-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with a Cu shell. Appl Phys Lett 99:262501–262504. doi:10.1063/1.3671989
Desautels RD, Skoropata E, Chen YY, Ouyang H, Freeland JW, Lierop Jv (2012) Increased surface spin stability in γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with a Cu shell. J Phys Condens Matter 24:146001. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/24/14/146001
Fischer KH, Hertz J (1991) Spin glasses. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fita I, Markovich V, Mogilyansky D, Puzniak R, Wisniewski A, Titelman L, Vradman L, Herskowitz M, Varyukhin VN, Gorodetsky G (2008) Size- and pressure-controlled ferromagnetism in LaCoO3 nanoparticles. Phys Rev B 77:224421. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.77.224421
Goya GF, Lima E, Arelaro AD, Torres T, Rechenberg HR, Rossi L, Marquina C, Ibarra MR (2008) Magnetic hyperthermia with Fe3O4 nanoparticles: the influence of particle size on energy absorption. IEEE Trans Magn 44:4444–4447. doi:10.1109/TMAG.2008.2003508
Hiroi K, Komatsu K, Sato T (2011) Superspin glass originating from dipolar interaction with controlled interparticle distance among γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with silica shells. Phys Rev B 83:224423. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.83.224423
Jiang Y, Song W, Xie C, Wang A, Zeng D, Hu M (2006) Electrical conductivity and gas sensitivity to VOCs of V-doped ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Mater Lett 60:1374–1378. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2005.11.032
Komorida Y, Mito M, Deguchi H, Takagi S, Millan A, Silva NJO, Palacio F (2009) Surface and core magnetic anisotropy in maghemite nanoparticles determined by pressure experiments. Appl Phys Lett 94:202503. doi:10.1063/1.3131782
Kumar L, Kar M (2011) Influence of Al3+ ion concentration on the crystal structure and magnetic anisotropy of nanocrystalline spinel cobalt ferrite. J Magn Magn Mater 323:2042–2048. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.03.010
Mahmoudi M, Sant S, Wang B, Laurent S, Sen T (2011) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63:24–46. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2010.05.006
Millan A, Urtizberea A, Silva NJO, Palacio F, Amaral VS, Snoeck E, Serin V (2007) Surface effects in maghemite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 312:L5–L9. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.09.011
Msomi JZ, Moyo T, Abdallah HMI, Strydom AM, Britz D (2011) XRD, magnetic and Mössbauer spectral studies of Ag x Ni1−x Fe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles. J Supercond Novel Magn 24:711–715. doi:10.1007/s10948-010-0942-2
Mujasambatoo K, Kumar S, Ansari MS (2011) Ferrimagnetic ordering of Ti4+ doped Mn1+x Fe2−2x O4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.5) ferrites at room temperature. Sci Adv Mater 3:120–126. doi:10.1166/sam.2011.1143
Mydosh JA (1993) Spin glasses: an experimental introduction. Taylor & Francis, London
Natividad E, Castro M, Mediano A (2011) Adiabatic magnetothermia makes possible the study of the temperature dependence of the heat dissipated by magnetic nanoparticles under alternating magnetic fields. Appl Phys Lett 98:243113–243119. doi:10.1063/1.3600633
O’Handley RC (2000) Modern magnetic materials: principles and applications. Wiley, New York
Pandey BK, Shahi AK, Swarnkar RK, Gopal R (2012) Magnetic property of novel cobalt sulfate nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation. Sci Adv Mater 4:537–543. doi:10.1166/sam.2012.1315
Pankhurst QA, Connolly J, Jones SK, Dobson J (2003) Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J Phys D 36:R167. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/36/13/201
Qin GW, Pei WL, Ren YP, Shimada Y, Endo Y, Yamaguchi M, Okamoto S, Kitakami O (2011) Effect of annealing on magnetic properties of Ni80Fe20 permalloy nanoparticles prepared by polyol method. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11:10796–10799. doi:10.1166/jnn.2011.3981
Rudolf H, Silvio D, Robert M, Matthias Z (2006) Magnetic particle hyperthermia: nanoparticle magnetism and materials development for cancer therapy. J Phys Condens Matter 18:S2919. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/18/38/S26
Soundararajan D, Mangalaraj D, Nataraj D, Dorosinskii L, Santoyo-Salazar J, Senthil K, Ko JM (2011) Structural, compositional and magnetic studies on Zn1−x Cr x Te (x = 0.05, 0.15) films grown on GaAs (100) substrates. Sci Adv Mater 3:80–88. doi:10.1166/sam.2011.1134
Subhankar B, Wolfgang K (2009) Supermagnetism. J Phys D 42:013001. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/42/1/013001
Suzuki M, Fullem SI, Suzuki IS, Wang L, Zhong C-J (2009) Observation of superspin-glass behavior in Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Phys Rev B 79:024418. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.79.024418
Vargas JM, Srivastava A, Yourdkhani A, Zaldivar L, Caruntu G, Spinu L (2011) Tuning the thermal relaxation of transition-metal ferrite nanoparticles through their intrinsic magnetocrystalline anisotropy. J Appl Phys 110:064304–064306. doi:10.1063/1.3638053
Vázquez-Vázquez C, López-Quintela MA, Buján-Núñez MC, Rivas J (2011) Finite size and surface effects on the magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 13:1663–1676. doi:10.1007/s11051-010-9920-7
Wu J, Xue D (2011) Progress of science and technology of ZnO as advanced material. Sci Adv Mater 3:127–149. doi:10.1166/sam.2011.1144
Xia C, Hu C, Tian Y, Wan B, Chen P, Xu J (2011) Magnetic and optical properties of Mn doped ZnO nanocrystalline films. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11:10506–10510. doi:10.1166/jnn.2011.4049
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aslibeiki, B., Kameli, P. & Salamati, H. The role of Ag on dynamics of superspins in MnFe2−x Ag x O4 nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 15, 1430 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1430-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1430-y