Abstract
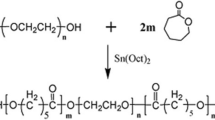
The fabrication of submicron size microsphere from 8-Phe-4 poly(ester amide) (PEA) using polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as the emulsion was reported. The biodegradable microspheres were prepared by an oil-in-water emulsion/solvent evaporation technique, and PVA was used as the emulsion. Furthermore, the emulsion PVA was electrospun into nanofibrous mats, and 8-Phe-4 PEA microspheres were entrapped in the resultant mats. The dual functions of PVA to fabricate ideal nanofibrous mats which can entrap microspheres in them and to obtain 8-Phe-4 microspheres as emulsion in their potential application were demonstrated. The anti-cancer drug doxorubicin (DOX) was encapsulated in the 8-Phe-4 amino acid-based PEA microspheres and the entrapment efficiency is almost 100 %. At the same time, the DOX can be controlled released in PBS solution and in α-chymotrypsin solution. The cytotoxicity of PVA, PVA mats-entrapped 8-Phe-4 microspheres and PVA mats-entrapped DOX-loaded 8-Phe-4 microspheres, was investigated. Hela cells were used to test the cytotoxicity of the DOX that released from the PVA mats-entrapped DOX-loaded 8-Phe-4 microspheres for 2 days, and the cell viability is below 30 % when the 8-Phe-4 microspheres concentration is 1 mg/mL. It demonstrated that the PVA mats-entrapped DOX-loaded 8-Phe-4 microspheres have a potential biomedical application.
Graphical Abstract
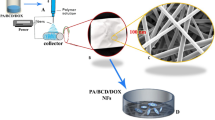
The table of contents: DOX-loaded microspheres can be encapsulated in the PVA fibers by electrospinning and the DOX can be controlled released from the PVA fibers-entrapped microspheres. MTT assay indicated that the more than 70 % Hela cells were killed by the DOX released from DOX-loaded microspheres encapsulated in the PVA after 48 h.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asin L, Armelin E, Montane J, Rodriguez-Galan A, Puiggali J (2001) Sequential poly(ester amide)s based on glycine, diols, and dicarboxylic acids: thermal polyesterification versus interfacial polyamidation. Characterization of polymers containing stiff units. J Polym Sci A 39(24):4283–4293. doi:10.1002/pola.10082
Chu CH, Wang YC, Huang HY, Wu LC, Yang CS (2011) Ultrafine PEG-coated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles formulated by hydrophobic surfactant-assisted one-pot synthesis for biomedical applications. Nanotechnology 22(18). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/22/18/185601
Feng SS, Huang GF (2001) Effects of emulsifiers on the controlled release of paclitaxel (Taxol (R)) from nanospheres of biodegradable polymers. J Control Release 71(1):53–69. doi:10.1016/s0168-3659(00)00364-3
Fong H, Chun I, Reneker DH (1999) Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer 40(16):4585–4592. doi:10.1016/s0032-3861(99)00068-3
Fong H, Liu WD, Wang CS, Vaia RA (2002) Generation of electrospun fibers of nylon 6 and nylon 6-montmorillonite nanocomposite. Polymer 43(3):775–780. doi:10.1016/s0032-3861(01)00665-6
Guo K, Chu CC (2007a) Controlled release of paclitaxel from biodegradable unsaturated poly(ester amide)s/poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate hydrogels. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 18(5):489–504. doi:10.1163/156856207780852569
Guo K, Chu CC (2007b) Synthesis, characterization, and biodegradation of novel poly(ether ester amide)s based on l-phenylalanine and oligoethylene glycol. Biomacromolecules 8(9):2851–2861. doi:10.1021/bm070158c
Guo K, Chu CC (2008) Copolymers of unsaturated and saturated poly(ether ester amide)s: synthesis, characterization, and biodegradation. J Appl Polym Sci 110(3):1858–1869. doi:10.1002/app.28826
Guo K, Chu CC (2009) Biodegradable and injectable paclitaxel-loaded poly(ester amide)s microspheres: fabrication and characterization. J Biomed Mater Res B 89B(2):491–500. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.31239
Han SI, Kim BS, Kang SW, Shirai H, Im SS (2003) Cellular interactions and degradation of aliphatic poly(ester amide)s derived from glycine and/or 4-amino butyric acid. Biomaterials 24(20):3453–3462. doi:10.1016/s0142-9612(03)00223-0
Hodge RM, Edward GH, Simon GP (1996) Water absorption and states of water in semicrystalline poly(vinyl alcohol) films. Polymer 37(8):1371–1376. doi:10.1016/0032-3861(96)81134-7
Katsarava R, Beridze V, Arabuli N, Kharadze D, Chu CC, Won CY (1999) Amino acid-based bioanalogous polymers. Synthesis, and study of regular poly(ester amide)s based on bis(alpha-amino acid) alpha, omega-alkylene diesters, and aliphatic dicarboxylic acids. J Polym Sci A 37(4):391–407. doi:10. 1002/(sici)1099-0518(19990215)37:4 < 391::aid-pola3 > 3.0.co;2-e
Krumova M, Lopez D, Benavente R, Mijangos C, Perena JM (2000) Effect of crosslinking on the mechanical and thermal properties of poly(vinyl alcohol). Polymer 41(26):9265–9272. doi:10.1016/s0032-3861(00)00287-1
Li L, Chu C-C (2009) Nitroxyl radical incorporated electrospun biodegradable poly(ester amide) nanofiber membranes. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 20(3):341–361. doi:10.1163/156856209x412209
Li R, Nie KM, Shen XF, Wang S (2007) Biodegradable polyester hybrid nanocomposites containing titanium dioxide network and poly(epsilon-caprolactone): synthesis and characterization. Mater Lett 61(6):1368–1371. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2006.07.032
Li N, Qin XH, Lin L, Wang SY (2008) The effects of spinning conditions on the morphology of electrospun jet and nonwoven membrane. Polym Eng Sci 48(12):2362–2366. doi:10.1002/pen.21188
Pant HR, Baek WI, Nam KT, Seo YA, Oh HJ, Kim HY (2011) Fabrication of polymeric microfibers containing rice-like oligomeric hydrogel nanoparticles on their surface: a novel strategy in the electrospinning process. Mater Lett 65(10):1441–1444. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2011.02.029
Paredes N, Rodriguez-Galan A, Puiggali J (1998) Synthesis and characterization of a family of biodegradable poly(ester amide)s derived from glycine. J Polym Sci A 36(8):1271–1282. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-0518(199806)36:8<1271:AID-POLA10>3.0.CO;2-3
Paredes N, Casas MT, Puiggali J (2000) Packing of sequential poly(ester amide)s derived from diols, dicarboxylic acids, and amino acids. Macromolecules 33(24):9090–9097. doi:10.1021/ma000649o
Qin XH (2010) Structure and property of electrospinning PAN nanofibers by different preoxidation temperature. J Therm Anal Calorim 99(2):571–575. doi:10.1007/s10973-009-0126-0
Qin XH (2011) Structure and property of electrospun PAN nanofibers by different pre-oxidated heating rates. J Ind Text 41(1):57–69. doi:10.1177/1528083710394889
Qin XH, Wu DQ (2012) Effect of different solvents on poly(caprolactone) (PCL) electrospun nonwoven membranes. J Therm Anal Calorim 107(3):1007–1013. doi:10.1007/s10973-011-1640-4
Qin XH, Xin DP (2010) The study on the air volume fraction of electrospun nanofiber nonwoven mats. Fibers Polym 11(4):632–637. doi:10.1007/s00000-010-0632-7
Qin XH, Jia L, Lu WY, Shou DH, Fan JT (2011) Stretching of the steady jet in electrospinning: theoretical analysis and experimental verification. Text Res J 81(4):388–397. doi:10.1177/0040517510392473
Reneker DH, Chun I (1996) Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 7(3):216–223. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/7/3/009
Scholes PD, Coombes AGA, Illum L, Davis SS, Watts JF, Ustariz C, Vert M, Davies MC (1999) Detection and determination of surface levels of poloxamer and PVA surfactant on biodegradable nanospheres using SSIMS and XPS. J Control Release 59(3):261–278. doi:10.1016/s0168-3659(98)00138-2
Sekiguchi T, Saika A, Nomura K, Watanabe T, Fujimoto Y, Enoki M, Sato T, Kato C, Kanehiro H (2011) Biodegradation of aliphatic polyesters soaked in deep seawaters and isolation of poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-degrading bacteria. Polym Degrad Stab 96(7):1397–1403. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.03.004
Shao CL, Kim HY, Gong J, Ding B, Lee DR, Park SJ (2003) Fiber mats of poly(vinyl alcohol)/silica composite via electrospinning. Mater Lett 57(9–10):1579–1584. doi:10.1016/s0167-577x(02)01036-4
Suh HR, Jeong BM, Rathi R, Kim SW (1998) Regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation using paclitaxel-loaded poly(ethylene oxide)–poly(lactide/glycolide) nanospheres. J Biomed Mater Res 42(2):331–338. doi:10.1002/(sici)1097-4636(199811)42:2<331:aid-jbm19>3.0.co;2-l
Tong R, Cheng JJ (2010) Controlled synthesis of camptothecin–polylactide conjugates and nanoconjugates. Bioconjug Chem 21(1):111–121. doi:10.1021/bc900356g
Tsitlanadze G, Machaidze M, Kviria T, Djavakhishvili N, Chu CC, Katsarava R (2004) Biodegradation of amino-acid-based poly(ester amide)s: in vitro weight loss and preliminary in vivo studies. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 15(1):1–24. doi:10.1163/156856204322752200
Wang YM, Sato H, Adachi I, Horikoshi I (1996) Preparation and characterization of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres for targeted delivery of a novel anticancer agent, Taxol. Chem Pharm Bull 44(10):1935–1940
Weng LH, Le HC, Lin JY, Golzarian J (2011) Doxorubicin loading and eluting characteristics of bioresorbable hydrogel microspheres: in vitro study. Int J Pharm 409(1–2):185–193. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.02.058
Wu DQ, Li ZY, Li C, Fan JJ, Lu B, Chang C, Cheng SX, Zhang XZ, Zhuo RX (2010) Porphyrin and galactosyl conjugated micelles for targeting photodynamic therapy. Pharm Res 27(1):187–199. doi:10.1007/s11095-009-9998-8
Yang XQ, Grailer JJ, Rowland IJ, Javadi A, Hurley SA, Matson VZ, Steeber DA, Gong SQ (2010) Multifunctional stable and pH-responsive polymer vesicles formed by heterofunctional triblock copolymer for targeted anticancer drug delivery and ultrasensitive MR imaging. ACS Nano 4(11):6805–6817. doi:10.1021/nn101670k
Ying XY, Cui D, Yu LA, Du YZ (2011) Solid lipid nanoparticles modified with chitosan oligosaccharides for the controlled release of doxorubicin. Carbohydr Polym 84(4):1357–1364. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.01.037
Yoshimoto H, Shin YM, Terai H, Vacanti JP (2003) A biodegradable nanofiber scaffold by electrospinning and its potential for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 24(12):2077–2082. doi:10.1016/s0142-9612(02)00635-x
Zhang HW, Bei JZ, Wang SG (2009) Multi-morphological biodegradable PLGE nanoparticles and their drug release behavior. Biomaterials 30(1):100–107. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.09.016
Zong XH, Kim K, Fang DF, Ran SF, Hsiao BS, Chu B (2002) Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes. Polymer 43(16):4403–4412 Piis0032-3861(02)00275-610.1016/s0032-3861(02)00275-6
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (50973014, 11172064 and 81101241), the Foundation for the Author of National Excellent Doctoral Dissertation of P. R. China (200961), and Shanghai Rising-Star Program in China (10QA1400100) and Fok Ying Tong Education Foundation (121071) to Prof. Xiao-Hong Qin and also Supported by Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-10-0322) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities as well as “Shu Guang” (11SG33) project supported by Shanghai Municipal Education Commission and Shanghai Education Development Foundation to her.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, XH., Wu, DQ. & Chu, CC. Dual functions of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA): fabricating particles and electrospinning nanofibers applied in controlled drug release. J Nanopart Res 15, 1395 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1395-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1395-2