Abstract
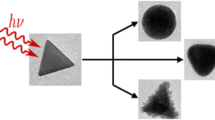
We investigate the photothermal conversion and transformation of gold nanoparticles with an initial dogbone shape after dispersion in hydrated chitosan films, which is a representative model of biological tissue, and excitation by a CW diode laser for 1 min. Gold nanodogbones are observed to undergo a distinct modification above a sharp threshold of ~11 W cm−2 and 110 °C. Surprisingly, the very same modification is achieved up to at least 36 W cm−2 and 250 °C. We use an analytical model derived from Gans theory to associate the change in color of the films with the change in shape statistics of these gold nanoparticles. This model proves both convenient and dependable. We interpret the photothermal transformation as a rearrangement of particles with a dogbone shape and an aspect ratio of 4.1 into rods with an aspect ratio of 2.5, where material from the end lobes of the dogbones may relocate to the waists of the rods. In turn, additional transitions to stable gold nanospheres may exhibit fairly slower kinetics.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkilany AM, Murphy CJ (2010) Toxicity and cellular uptake of gold nanoparticles: what we have learned so far? J Nanopart Res 12:2313–2333
Alpert J, Hamad-Schifferli K (2010) Effect of ligands on thermal dissipation from gold nanorods. Langmuir 26:3786–3789
Brioude A, Jiang XC, Pileni MP (2005) Optical properties of gold nanorods: DDA simulations supported by experiments. J Phys Chem B 109:13138–13142
Calandra P, Giordano C, Longo A, Turco Liveri V (2006) Physicochemical investigation of surfactant-coated gold nanoparticles synthesized in the confined space of dry reversed micelles. Mat Chem Phys 98:494–499
Chang SS, Shih CW, Chen CD, Lai WC, Wang CRC (1999) The shape transition of gold nanorods. Langmuir 15:701–709
Chen HJ, Kou XS, Yang Z, Ni WH, Wang JF (2008) Shape- and size-dependent refractive index sensitivity of gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 24:5233–5237
Chen LC, Wei CW, Souris JS, Cheng SH, Chen CT, Yang CS, Li PC, Lo LW (2010a) Enhanced photoacoustic stability of gold nanorods by silica matrix confinement. J Biomed Opt 15:016010
Chen YS, Frey W, Kim S, Homan K, Kruizinga P, Sokolov K, Emelianov S (2010b) Enhanced thermal stability of silica-coated gold nanorods for photoacoustic imaging and image-guided therapy. Opt Express 18:8867–8877
Di Martino A, Sittinger M, Risbud MV (2005) Chitosan: a versatile biopolymer for orthopaedic tissue-engineering. Biomaterials 26:5983–5990
Dong Y, Ruan Y, Wang H, Zhao Y, Bi D (2004) Studies on glass transition temperature of chitosan with four techniques. J Appl Polym Sci 93:1553–1558
Dos Santos DS, Goulet PJG, Pieczonka NPW, Oliveira ON, Aroca RF (2004) Gold nanoparticle embedded, self-sustained chitosan films as substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Langmuir 20:10273–10277
Eghtedari M, Oraevsky AA, Copland JA, Kotov NA, Conjusteau A, Motamedi M (2007) High sensitivity of in vivo detection of gold nanorods using a laser optoacoustic imaging system. Nano Lett 7:1914–1918
Eghtedari M, Liopo A, Copland JA, Oraevsky AA, Motamedi M (2009) Engineering of hetero-functional gold nanorods for the in vivo molecular targeting of breast cancer cells. Nano Lett 9:287–291
Etchegoin PG, Le Ru EC, Meyer M (2006) An analytic model for the optical properties of gold. J Chem Phys 125:164705
Eustis S, El-Sayed MA (2006) Determination of the aspect ratio statistical distribution of gold nanorods in solution from a theoretical fit of the observed inhomogeneously broadened longitudinal plasmon resonance absorption spectrum. J Appl Phys 100:044324
Fujie T, Matsutani N, Kinoshita M, Okamura Y, Saito A, Takeoka S (2009) Adhesive, flexible, and robust polysaccharide nanosheets integrated for tissue-defect repair. Adv Funct Mater 19:2560–2568
Gans R (1912) Uber die Form ultramikroskopischer Goldteilchen. Ann Phys 37:881–900
Gao J, Bender CM, Murphy CJ (2003) Dependence of the gold nanorod aspect ratio on the nature of the directing surfactant in aqueous solution. Langmuir 19:9065–9070
Goodrich GP, Bao L, Gill-Sharp K, Sang KL, Wang J, Payne JD (2010) Photothermal therapy in a murine colon cancer model using near-infrared absorbing gold nanorods. J Biomed Opt 15:018001
Gou L, Murphy CJ (2005) Fine-tuning the shape of gold nanorods. Chem Mater 17:3668–3672
Guo HY, Ruan FX, Lu LH, Hu JW, Pan JA, Yang ZL, Ren B (2009) Correlating the shape, surface plasmon resonance, and surface-enhanced Raman scattering of gold nanorods. J Phys Chem C 113:10459–10464
Horiguchi Y, Honda K, Kato Y, Nakashima N, Niidome Y (2008) Photothermal reshaping of gold nanorods depends on the passivating layers of the nanorod surfaces. Langmuir 24:12026–12031
Huang CJ, Chiu PH, Wang YH, Meen TH, Yang CF (2007) Synthesis and characterization of gold nanodogbones by the seeded mediated growth method. Nanotechnology 18:395603
Huang X, Jain PK, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2008) Plasmonic photothermal therapy using gold nanoparticles. Lasers Med Sci 23:217–228
Huang X, Neretina S, El-Sayed MA (2009) Gold nanorods: from synthesis and properties to biological and biomedical applications. Adv Mater 21:4880–4910
Huff TB, Tong L, Zhao Y, Hansen MN, Cheng JX, Wei A (2007) Hyperthermic effects of gold nanorods on tumor cells. Nanomedicine 2:125–132
Jain PK, Lee KS, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2006) Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J Phys Chem B 110:7238–7248
Jana NR, Gearheart L, Murphy CJ (2001) Wet chemical synthesis of high aspect ratio cylindrical gold nanorods. J Phys Chem B 105:4065–4067
Jiang XC, Pileni MP (2007) Gold nanorods: influence of various parameters as seeds, solvent, surfactant on shape control. Colloids Surf A 295:228–232
Jiang H, Su W, Caracci S, Bunning TJ, Cooper T, Adams WW (1996) Optical waveguiding and morphology of chitosan thin films. J Appl Polym Sci 61:1163–1171
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379
Jose J, Manohar S, Kolkman RGM, Steenbergen W, van Leeuwen TG (2009) Imaging of tumor vasculature using Twente photoacoustic systems. J Biophoton 2:707–717
Kaczmarek H, Zawadzkia J (2010) Chitosan pyrolysis and adsorption properties of chitosan and its carbonizate. Carbohydr Res 345:941–947
Kang H, Jia B, Li J, Morrish D, Gu M (2010) Enhanced photothermal therapy assisted with gold nanorods using a radially polarized beam. Appl Phys Lett 96:063702
Khlebtsov NG (2010) Anisotropic properties of plasmonic nanoparticles: depolarized light scattering, dichroism, and birefringence. J Nanophoton 4:041587
Khlebtsov NG, Dykman LA (2010) Optical properties and biomedical applications of plasmonic nanoparticles. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transfer 111:1–35
Khlebtsov BN, Khanadeev VA, Khlebtsov NG (2008) Observation of extra-high depolarized light scattering spectra from gold nanorods. J Phys Chem C 112:12760–12768
Khlebtsov B, Khanadeev V, Pylaev T, Khlebtsov N (2011) A new T-matrix solvable model for nanorods: TEM-based ensemble simulations supported by experiments. J Phys Chem C DOI:10.1021/jp2000078
Kuo WS, Chang CN, Chang YT, Yang MH, Chien YH, Chen SJ, Yeh CS (2010) Gold nanorods in photodynamic therapy, as hyperthermia agents, and in near-infrared optical imaging. Ang Chem Int Ed 49:2711–2715
Ladet S, David L, Domard A (2008) Multi-membrane hydrogels. Nature 452:76–79
Lapotko DO, Lukianova E, Oraevsky AA (2006) Selective laser nano-thermolysis of human leukemia cells with microbubbles generated around clusters of gold nanoparticles. Laser Surg Med 38:631–642
Li PC, Huang SW, Wei CW, Chiou YC, Chen CD, Wang CRC (2005) Photoacoustic flow measurements by use of laser-induced shape transitions of gold nanorods. Opt Lett 30:3341–3343
Liao CK, Huang SW, Wei CW, Li PC (2007) Nanorod-based flow estimation using a high-frame-rate photoacoustic imaging system. J Biomed Opt 12:064006
Link S, El-Sayed MA (2000) Shape and size dependence of radiative, nonradiative, and photothermal properties of gold nanocrystals. Int Rev Phys Chem 19:409–453
Link S, Mohamed MB, El-Sayed MA (1999) Simulation of the optical absorption spectra of gold nanorods as a function of their aspect ratio and the effect of the medium dielectric constant. J Phys Chem B 103:3073–3077
Link S, Wang ZL, El-Sayed MA (2000a) How does a gold nanorod melt? J Phys Chem B 104:7867–7870
Link S, Burda C, Nikoobakht B, El-Sayed MA (2000b) Laser-induced shape changes of colloidal gold nanorods using femtosecond and nanosecond laser pulses. J Phys Chem B 104:6152–6163
Liu Y, Mills EN, Composto RJ (2009) Tuning optical properties of gold nanorods in polymer films through thermal reshaping. J Mat Chem 19:2704–2709
Matteini P, Ratto F, Rossi F, Centi S, Dei L, Pini R (2010a) Chitosan films doped with gold nanorods as laser-activatable hybrid bioadhesives. Adv Mater 22:4313–4316
Matteini P, Ratto F, Rossi F, Rossi G, Esposito G, Puca A, Albanese A, Maira A, Pini R (2010b) In vivo carotid artery closure by laser activation of hyaluronan-embedded gold nanorods. J Biomed Opt 15:041508
Mie G (1908) Beiträge zur Optik trüber Medien, speziell kolloidaler Metallösungen. Ann Phys 25:377–445
Mishchenko MI, Travis LD, Lacis AA (2002) Scattering, absorption, and emission of light by small particles. University Press, Cambridge, UK
Mishchenko MI, Zakharova NT, Videen G, Khlebtsov NG, Wriedt T (2010) Comprehensive T-matrix reference database: a 2007–2009 update. J Quantitat Spectrosc Radiat Transf 111:650–658
Mohamed MB, Volkov V, Link S, El-Sayed MA (2000) The ‘lightning’ gold nanorods: fluorescence enhancement of over a million compared to the gold metal. Chem Phys Lett 317:517–523
Mulvaney P, Perez-Juste J, Giersig M, Liz-Marzan LM, Pecharroman C (2006) Drastic surface plasmon mode shifts in gold nanorods due to electron charging. Plasmonics 1:61–66
Ni W, Kou X, Yang Z, Wang JF (2008) Tailoring longitudinal surface plasmon wavelengths, scattering and absorption cross sections of gold nanorods. ACS Nano 2:677–686
Niemz MH (2003) Laser-tissue interactions: fundamentals and applications. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, Germany
Niidome Y, Urakawa S, Kawahara M, Yamada S (2003) Dichroism of poly(vinylalcohol) films containing gold nanorods induced by polarized pulsed-laser irradiation. Jpn J Appl Phys 42:1749–1750
Nikoobakht B, El-Sayed MA (2003) Preparation and growth mechanism of gold nanorods (NRs) using seed-mediated growth method. Chem Mater 15:1957–1962
Park K, Koerner H, Vaia RA (2010) Depletion-induced shape and size selection of gold nanoparticles. Nano Lett 10:1433–1439
Perez-Juste J, Pastoriza-Santos I, Liz-Marzan LM, Mulvaney P (2005a) Gold nanorods: synthesis, characterization and applications. Coord Chem Rev 249:1870–1901
Perez-Juste J, Rodriguez-Gonzalez B, Mulvaney P, Liz-Marzan LM (2005b) Optical control and patterning of gold-nanorod–poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposite films. Adv Funct Mat 15:1065–1071
Petrova H, Perez-Juste J, Pastoriza-Santos I, Hartland GV, Liz-Marzan LM, Mulvaney P (2006) On the temperature stability of gold nanorods: comparison between thermal and ultrafast laser-induced heating. Phys Chem Chem Phys 8:814–821
Qiu L, Larson TA, Smith DK, Vitkin E, Zhang S, Modell MD, Itzkan I, Hanlon EB, Korgel BA, Sokolov KV, Perelman LT (2007) Single gold nanorod detection using confocal light absorption and scattering spectroscopy. IEEE J Sel Topics Quantum Electron 13:1730–1738
Qiu L, Larson TA, Vitkin E, Guo L, Hanlon EB, Itzkan I, Sokolov KV, Perelman LT (2010) Gold nanorod light scattering labels for biomedical imaging. Biomed Opt Exp 1:135–142
Ratto F, Locatelli A, Fontana S, Kharrazi S, Ashtaputre S, Kulkarni SK, Heun S, Rosei F (2006) Diffusion dynamics during the nucleation and growth of Ge/Si nanostructures on Si(111). Phys Rev Lett 96:096103
Ratto F, Johnston TW, Heun S, Rosei F (2008) A numerical approach to quantify self-ordering among self-organized nanostructures. Surf Sci 602:249–258
Ratto F, Matteini P, Rossi F, Menabuoni L, Tiwari N, Kulkarni SK, Pini R (2009) Photothermal effects in connective tissues mediated by laser-activated gold nanorods. Nanomedicine 5:143–151
Ratto F, Matteini P, Rossi F, Pini R (2010) Size and shape control in the overgrowth of gold nanorods. J Nanopart Res 12:2029–2036
Ratto F, Matteini P, Centi S, Rossi F, Pini R (2011) Gold nanorods as new nanochromophores for photothermal therapies. J Biophotonics 4:64–73
Rossi F, Matteini P, Ratto F, Menabuoni L, Lenzetti I, Pini R (2008) Laser tissue welding in ophthalmic surgery. J Biophoton 1:331–342
Sprunken DP, Omi H, Furukawa K, Nakashima H, Sychugov I, Kobayashi Y, Torimitsu K (2007) Influence of the local environment on determining aspect-ratio distributions of gold nanorods in solution using gans theory. J Phys Chem C 111:14299–14306
Takahashi H, Niidome T, Nariai A, Niidome Y, Yamada S (2006) Photothermal reshaping of gold nanorods prevents further cell death. Nanotechnology 17:4431–4435
Tao J, Lu YH, Zheng RS, Lin KQ, Xie ZG, Luo ZF, Li SL, Wang P, Ming H (2008) Effect of aspect ratio distribution on localized surface plasmon resonance extinction spectrum of gold nanorods. Chin Phys Lett 25:4459–4462
Thomsen S (1991) Pathologic analysis of photothermal and photomechanical effects of laser–tissue interactions. Photochem Photobiol 53:825–835
Tollan CM, Marcilla R, Pomposo JA, Rodriguez J, Aizpurua J, Molina J, Mecerreyes D (2009) Irreversible thermochromic behavior in gold and silver nanorod/polymeric ionic liquid nanocomposite films. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1:348–352
Ungureanu C, Amelink A, Rayavarapu RG, Sterenborg HJCM, Manohar S, van Leeuwen TG (2010) Differential pathlength spectroscopy for the quantitation of optical properties of gold nanoparticles. ACS Nano 4:4081–4089
Von Maltzahn G, Park JH, Agrawal A, Kishor Bandaru N, Das SK, Sailor MJ, Bhatia SN (2009) Computationally guided photothermal tumor therapy using long-circulating gold nanorod antennas. Cancer Res 69:3892–3900
Wang YT, Teitel S, Dellago C (2005) Surface-driven bulk reorganization of gold nanorods. Nano Lett 5:2174–2178
Wijaya A, Schaffer SB, Pallares IG, Hamad-Schifferli K (2009) Selective release of multiple DNA oligonucleotides from gold nanorods. ACS Nano 3:80–86
Xu XD, Cortie MB (2006) Shape change and color gamut in gold nanorods, dumbbells, and dog bones. Adv Funct Mat 16:2170–2176
Zijlstra P, Chon JWM, Gu M (2009) Five-dimensional optical recording mediated by surface plasmons in gold nanorods. Nature 459:410–413
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Cosimo Trono for the refractometry measurements and Prof. Stefano Cavalieri for useful discussions. This work was supported by the NANO-TREAT and NANO-CHROM projects of the Health Board of Tuscany and the FP7 NoE Photonics 4 Life.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ratto, F., Matteini, P., Cini, A. et al. CW laser-induced photothermal conversion and shape transformation of gold nanodogbones in hydrated chitosan films. J Nanopart Res 13, 4337–4348 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0380-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0380-5