Abstract
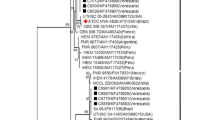
This report describes the first isolation of Sporothrix globosa from a Brazilian patient. A 77-year-old woman was examined for sporotrichosis infection. Histopathological examination of skin biopsy revealed chronic granulomatous infiltrate with microabcess. Furthermore, S. schenckii-like yeasts were evident as demonstrated by PAS and Grocott stains. The fungus was identified based on colony morphology on Sabouraud Dextrose Agar slants, Potato Dextrose Agar, and Corn Meal Agar, microscopic morphology on slides cultures, and assimilation of different carbon sources. The species confirmation was made by molecular methodology.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conti-Diaz IA. Epidemiology of sporotrichosis in Latin America. Mycopathologia. 1989;108:113–6.
Kovarik CL, Neyra E, Bustamante B. Evaluation of cats as the source of endemic sporotrichosis in Peru. Med Mycol. 2008;46:53–6.
Pappas PG, Tellez I, Deep AE, Nolasco D, Holgado W, Bustamanate B. Sporotrichosis in Peru: description of an area of hyperendemicity. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;30:65–70.
Carrada-Bravo T. New observations on the epidemiology and pathogenesis of sporotrichosis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1975;69:267–73.
Marimon R, Gené J, Cano J, Sutton DA, Trilles L, Dos Santos Lazéra M, et al. Molecular phylogeny of Sporothrix schenckii. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44(9):3251–6.
Marimon R, Cano J, Gené J, Sutton DA, Kawasaki M, Guarro J. Sporothrix brasiliensis, S. globosa, and S. mexicana, three new Sporothrix species of clinical interest. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45(10):3198–206.
Marimon R, Serena C, Gené J, Cano J, Guarro J. In vitro antifungal susceptibilities of five species of Sporothrix. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52(2):732–4.
Marimon R, Gené J, Cano J, Guarro J. Sporothrix luriei: rare fungus from clinical origin. Med Mycol. 2008;46(6):621–5.
Madrid H, Cano J, Gené J, Bonifaz A, Toriello C, Guarro J. Sporothrix globosa, a pathogenic fungus with widespread geographical distribution. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2009;26(3):218–22.
Dixon DM, Salkin IF, Duncan RA, Hurd NJ, Haines JH, Kemna ME, et al. Isolation and characterization of Sporothrix schenckii from clinical and environmental sources associated with the largest U.S. epidemic of sporotrichosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991;29:1106–13.
Woods JP, Kersulyte D, Goldman WE, Berg DE. Fast DNA isolation from Histoplasma capsulatum: methodology for arbitrary primer polymerase chain reaction-based epidemiological and clinical studies. J Clin Microbiol. 1993;31(2):463–4.
Susca A, Stea G, Mulé G, Perrone G. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) identification of Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus tubingensis based on the calmodulin gene. Food Addit Contam. 2007;24(10):1154–60.
O’Donnell K, Nirenberg HI, Aoki T, Cigelnik E. A multigene phylogeny of the Gibberella fujikuroi species complex: detection of additional phylogenetically distinct species. Mycoscience. 2000;41:61–78.
Otto TD, Vasconcellos EA, Gomes LHF, Moreira AS, Degrave WM, Mendonça-Lima L, et al. ChromaPipe: a pipeline for analysis, quality control and management for a DNA sequencing facility. Genet Mol Res. 2008;7(3):861–71.
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24(8):1596–9.
Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molec Biol and Evol. 1987;4:406–25.
Kimura M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of bases substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol. 1980;16(2):111–20.
Eck RV, Dayhoff MO. Atlas of protein sequence and structure. Silver Springs, Maryland: National Biomedical Research Foundation; 1966.
Nei M, Kumar S. Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford University, NY: Oxford University Press; 2000.
Felsenstein J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution. 1985;39:783–91.
Barros MBL, Schubach AO, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC, Schubach TMP, Reis RS, Conceição MJ, et al. Sporotrichosis with widespread cutaneous lesions: report of 24 cases related to transmission by domestic cats in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:677–81.
Mesa-Arango AC, Reyes-Montes MR, Pérez-Mejía A, Navarro-Barranco H, Souza V, Zúñiga G, et al. Phenotyping and genotyping of Sporothrix schenckii isolates according to geographic origin and clinical form of sporotrichosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40:3004–11.
Dixon DM, Duncan RA, Hurd NJ. Use of a mouse model to evaluate clinical and environmental isolates of Sporothrix spp. from the largest U.S. epidemic of sporotrichosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992;30:951–4.
Arrillaga-Moncrieff I, Capilla E, Mayayo E, Marimon R, Mariné M, Gené J, et al. Different virulence levels of the species of Sporothrix in a murine model. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009;15(7):651–5.
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this work was provided by FAPERJ (Grant Proc. E-26/111.619/2008). R. M. Z. O. is in part supported by CNPq 350338/2000-0. Automated sequencing was done using the Genomic Platform-DNA Sequencing Platform at Fundação Oswaldo Cruz—PDTIS/FIOCRUZ (RPT01A), Brazil
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, M.M.E., de Almeida-Paes, R., de Medeiros Muniz, M. et al. Sporotrichosis Caused By Sporothrix globosa in Rio De Janeiro, Brazil: Case Report. Mycopathologia 169, 359–363 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-010-9276-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-010-9276-7