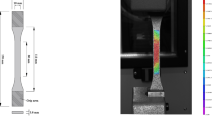
Abstract
In this research, the microscale strain rate sensitivity and high-temperature mechanical properties of cured isotropic conductive adhesive (ICA) were investigated using microindentation. The indentation modulus and hardness of cured ICA with high silver content are relatively large. The slopes of contact stiffness–depth curve, modulus and hardness increase with increasing loading strain rate. The elastic modulus, hardness and creep behaviour at high temperature were characterised on the basis of the “rapid loading–holding–rapid unloading” loading mode and the semiempirical method from the generalised Kelvin model. With increasing temperature, the elastic modulus and hardness of cured ICA decrease from 3000–7000 and 100–300 MPa in the glassy state to 6–200 and 1–10 MPa, respectively, in the rubbery state. Creep compliance, which is relatively high in the rubbery state, increases with increasing holding time. On the retardation spectrum, the widened retardation peaks reflect different retardation processes with increasing retardation time.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu Al-Rub, R.K., Faruk, A.N.M.: Prediction of micro and nano indentation size effects from spherical indenters. Mech. Adv. Mat. Struct. 19(1–3), 119–128 (2012)
Bhattacharyya, A.S., Mishra, S.K.: Micro/nanomechanical behavior of magnetron sputtered Si-C-N coatings through nanoindentation and scratch tests. J. Micromech. Microeng. 21(1), 015011 (2011)
Cheng, Y.T., Cheng, C.M.: Scaling, dimensional analysis, and indentation measurements. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 44, 91–149 (2004)
Chindam, C., Brown, N.R., Lakhtakia, A.: Temperature-dependent dynamic moduli of Parylene-C columnar microfibrous thin films. Polym. Test. 53, 89–97 (2016)
Feng, G., Ngan, A.H.W.: Effects of creep and thermal drift on modulus measurement using depth-sensing indentation. J. Mater. Res. 17(3), 660–668 (2002)
Ferry, J.D.: Viscoelastic Properties of Polymer, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York (1980)
Gao, L.L., Chen, X., Zhang, S.B., et al.: Mechanical properties of anisotropic conductive film with strain rate and temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 513–514, 216–221 (2009)
Gao, L.L., Chen, X., Gao, H.: Mechanical properties of anisotropic conductive adhesive film under hygrothermal aging and thermal cycling. J. Electron. Mater. 41(7), 2001–2009 (2012)
Gao, H., Zhang, W.G., Zhang, Z.: Study on fatigue life and electrical property of COG assembly under thermal–electric–mechanical coupled loads. Microelectron. Reliab. 56, 148–154 (2016)
Ji, X.K., Xiao, G.S., Jin, T., et al.: Shear properties of isotropic conductive adhesive joints under different loading rates. J. Adhes. 95(3), 204–217 (2019)
Jong, W.R., Peng, S.H., Tsai, H.C.: Characteristics of a new-type anisotropic conductive film joints during the bonding process. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 37(5), 506–513 (2010)
Lang, U., Naujoks, N., Dual, J.: Mechanical characterization of PEDOT: PSS thin films. Synth. Met. 159, 473–479 (2009)
Lau, J., Wong, C.P., Lee, N.C., et al.: Electronics Manufacturing: With Lead–Free, Halogen–Free, and Conductive Adhesive Materials. McGraw Hill, New York (2002)
Liu, J.: Conductive Adhesives for Electronics Packaging. Electrochemical Publications, London (1999)
Lucas, B.N., Oliver, W.C.: Indentation power-law creep of high-purity indium. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30(3), 601–610 (1999)
Ma, H., Qiu, H., Shuhua Qi, S.H.: Electrically conductive adhesives based on acrylate resin filled with silver-plated graphite nanosheets and carbon nanotubes. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 29(20), 2233–2244 (2015)
Marques, V.M.F., Johnston, C., Grant, P.S.: Nanomechanical characterization of Sn–Ag–Cu/Cu joints—Part 1: Young’s modulus, hardness and deformation mechanisms as a function of temperature. Acta Mater. 61, 2460–2470 (2013)
Marques, E.A.S., Da Silva, L.F.M., Banea, M.D., et al.: Adhesive joints for low- and high-temperature use: an overview. J. Adhes. 91, 556–585 (2015)
Ngan, A.H.W., Tang, B.: Viscoelastic effects during unloading in depth-sensing indentation. J. Mater. Res. 17(10), 2604–2610 (2002)
Oliver, W.C., Pethica, J.B.: U.S. Patent No. 4848141 (1989)
Oliver, W.C., Pharr, G.M.: Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: advance in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 19(1), 3–20 (2004)
Pedrazzoli, D., Dorigato, A., Pegoretti, A.: Monitoring the mechanical behavior under ramp and creep conditions of electrically conductive polymer composites. Composites, Part A 43, 1285–1292 (2012)
Pethica, J.B., Oliver, W.C.: Tip surface interaction in STM and AFM. Phys. Scr. 19, 61–68 (1987)
Pharr, G.M., Oliver, W.C., Brotzen, F.R.: On the generality of the relationship among contact stiffness, contact area, and elastic modulus during indentation. J. Mater. Res. 7(3), 613–617 (1992)
Pizzi, A., Mittal, K.L.: Handbook of Adhesive Technology. Springer, Berlin (2018)
Qiao, W.Y., Bao, H., Li, X.H., et al.: Research on electrical conductive adhesives filled with mixed filler. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 48, 159–163 (2014)
Shedbale, A.S., Singh, I.V., Mishra, B.K., et al.: Evaluation of mechanical properties using spherical ball indentation and coupled finite element-element-free Galerkin approach. Mech. Adv. Mat. Struct. 23(7), 832–843 (2016)
Staverman, A.J., Schwarzl, F.: The Physics of High Polymers. Springer, Berlin (1956)
Xiao, G.S., Yang, X.X., Yuan, G.Z., et al.: Mechanical properties of intermetallic compounds at the Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu/Cu joint interface using nanoindentation. Mater. Des. 88, 520–527 (2015)
Xiao, G.S., Liu, E.Q., Jin, T., et al.: Mechanical properties of cured isotropic conductive adhesive (ICA) under hygrothermal aging investigated by indentation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 122–123, 81–90 (2017)
Yang, S., Zhang, Y.W., Zeng, K.Y.: Analysis of nanoindentation creep for polymeric materials. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 3655–3666 (2004)
Yari, H., Mohseni, M., Ranjbar, Z., et al.: Novel toughened automotive clearcoats modified by a polyester-amide hyperbranched polymer: structural and mechanical aspects. Polym. Adv. Technol. 24(5), 495–502 (2013)
Zhou, Z.W., Ma, W., Zhang, S.J., et al.: Multiaxial creep of frozen loess. Mech. Mater. 95, 172–191 (2016)
Zhou, Z.W., Ma, W., Zhang, S.J., et al.: Effect of freeze-thaw cycles in mechanical behaviors of frozen loess. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 146, 9–18 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11802198, 11772217, 11702182), the Shanxi Province Program for Science and Technology innovation in Colleges and universities (Grant No. 2019L0303) and Natural Science Foundation for Young Scientists of Shanxi Province, China (Grant No. 201801D221026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, G., Li, Z., Liu, E. et al. Microscale mechanical properties dependent on the strain rate and temperature of cured isotropic conductive adhesive. Mech Time-Depend Mater 25, 249–264 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11043-019-09438-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11043-019-09438-9