Abstract
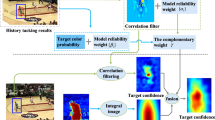
In recent years, the multi-expert collaborative tracking strategy has been introduced into visual tracking tasks and achieves impressive performance. Different from most existing multi-expert trackers that linearly fuse multiple tracking models, we propose a novel cascaded-parallel tracking algorithm (CPT) via adaptively selecting the suitable expert among multiple tracking models. And the CPT consists of cascaded and parallel tracking components. In the cascaded tracking component, we hierarchically implement two effective correlation filter models to coarse-to-fine locate the target. And in the parallel tracking component, a color tracking model is applied to locate the target to compensate for the demerit of the correlation filter models. With the proposed adaptive expert selection mechanism, the most reliable expert (i.e. tracking model) is selected for tracking in each frame. Extensive experimental results on OTB2013, OTB2015 and TempleColor128 datasets demonstrate that our proposed algorithm performs favorably against some state-of-the-art algorithms.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available from the corresponding author.
References
Avidan S (2007) Ensemble tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(2):261–271
Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Golodetz S et al (2016) Staple: complementary learners for real-time tracking. In: IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR), pp. 1401–1409
Bolme DS, Beveridge JR, Draper BA et al (2010) Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In: IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR), pp. 2544–2550
Boyd SP, Parikh N, Chu E et al (2011) Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found Trends Mach Learn 31(1):1–122
Collins RT, Liu Y, Leordeanu M (2005) Online selection of discriminative tracking features. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(10):1631–1643
Comaniciu D, Ramesh V, Meer P (2003) Kernel-based object tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(5):564–577
Danellgan M, Hager G, Khan FS et al (2014) Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking. In: British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), pp. 1–5
Danelljan M, Bhat G, Khan FS et al (2017) ECO: efficient convolution operators for tracking. In: IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR), pp. 6931–6939
Danelljan M, Robinson A, Khan FS et al (2016) Beyond correlation filters: learning continuous convolution operators for visual tracking. In: Eur Conf Comput Vis (ECCV), pp. 472–488
Danelljan M, Hager G, Khan FS et al (2015) Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In: IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis (ICCV), pp. 4310–4318
Danelljan M, Hager G, Khan FS et al (2016) Adaptive decontamination of the training set: a unified formulation for discriminative visual tracking. In: IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR), pp. 1430–1438
Danelljan M, Khan FS, Felsberg M et al (2014) Adaptive color attributes for real-time visual tracking. In: IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR) pp. 1090–1097
Danelljan M, Hager G, Khan FS et al (2017) Discriminative scale space tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(8):1561–1575
Dekel T, Oron S, Rubinstein M et al (2015) Best-buddies similarity for robust template matching. In: IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR), pp. 2021–2029
Duffner S, Garcia C (2013) PixelTrack: a fast adaptive algorithm for tracking non-rigid objects. In: IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis (ICCV), pp. 2480–2487
Fan H, Ling H (2017) Parallel tracking and verifying: a framework for real-time and high accuracy visual tracking. In: IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis (ICCV), pp. 5487–5495
Fang S, Ma Y, Li Z et al (2021) A visual tracking algorithm via confidence-based multi-feature correlation filtering. Multimed Tools Appl 80:23963–23982
Felzenszwalb PF, Girshick RB, McAllester D (2010) Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 32(9):1627–1645
Galoogahi HK, Fagg A, Lucey S (2017) Learning background-aware correlation filters for visual tracking. In: IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis (ICCV), pp. 1135–1143
Godec M, Roth PM, Bischof H (2013) Hough-based tracking of non-rigid objects. Comput Vis Image Underst 117(10):1245–1256
Hare S, Saffari A, Torr PHS (2011) Struck: structured output tracking with kernels. In: IEEE Int Conf Comput Visn (ICCV), pp. 263–270
Henriques JF, Caseiro R, Martins P et al (2012) Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels. In: Eur Conf Comput Vis (ECCV), pp. 702–715
Henriques JF, Caseiro R, Martins P et al (2015) High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(3):583–596
Kuai Y, Wen G, Li D (2018) Learning adaptively windowed correlation filters for robust tracking. J Vis Commun Image Represent 51:104–111
Li Y, Zhu J (2014) A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature integration. In: Eur Conf Comput Vis Workshops (ECCVW), pp. 254–265
Li F, Tian C, Zuo W et al (2018) Learning spatial-temporal regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In: IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR), pp. 4904–4913
Liang P, Blasch E, Ling H (2015) Encoding color information for visual tracking: algorithms and benchmark. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5630–5644
Liu S, Zhang T, Cao X et al (2016) Structural correlation filter for robust visual tracking. In: IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR), pp. 4312–4320
Lukezic A, Vojir T, Zajc LC et al (2018) Discriminative correlation filter tracker with channel and spatial reliability. Int J Comput Vis 126(7):671–688
Ma C, Huang JB, Yang X et al (2015) Hierarchical convolutional features for visual tracking. In: IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis (ICCV), pp. 3074–3082
Ma C, Huang JB, Yang X et al (2018) Adaptive correlation filters with long-term and short-term memory for object tracking. Int J Comput Vis 126(8):771–796
Possegger H, Mauthner T, Bischof H (2015) In defense of color-based model-free tracking. In: IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR), pp. 2113–2120
Qi Y, Zhang S, Qin L et al (2019) Hedging deep features for visual tracking. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(5):1116–1130
Wang N, Zhou W, Tian Q et al (2018) Multi-cue correlation filters for robust visual tracking. In: IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR) pp. 4844–4853
Wu Y, Lim J, Yang MH (2013) Online object tracking: a benchmark. In: IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit (CVPR), pp. 2411–2418
Wu Y, Lin J, Yang MH (2015) Object tracking benchmark. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(9):1834–1848
Yan J, Zhong L, Yao Y et al (2021) Dual-template adaptive correlation filter for real-time object tracking. Multimed Tools Appl 80:2355–2376
Zhang J, Ma S, Sclaroff S (2014) MEEM: robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization. In: Eur Conf Comput Vis (ECCV), pp. 188–203
Zhao D, Xiao L, Fu H et al (2019) Augmenting cascaded correlation filters with spatial-temporal saliency for visual tracking. Inf Sci 470:78–93
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 61972307].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare that they no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, Z., Liu, G., Zhang, H. et al. Robust cascaded-parallel visual tracking using collaborative color and correlation filter models. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 33–59 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15614-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15614-4