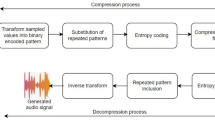
Abstract
In this paper, a lossless audio encoding technique has been proposed with the help of an optimized graph traversal and its performance is further enhanced by applying basic principles of Huffman encoding. Parsing each of the sampled values of input audio and representing each individual digit by the suitable path matching in the proposed weightage graph followed by a combination of dynamic bit sequence (directed graph traversal) produces the compressed audio format. Experimental results are incorporated with statistical parameters (compression ratio, SNR, PSNR) along with other parameters (Mean Opinion Score (MOS) and Entropy) and compared with existing lossless techniques for justifying its performance.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold M. (2000) Audio watermarking: features, applications and algorithms. In: 2000 IEEE International conference on multimedia and expo. ICME2000. Proceedings. Latest advances in the fast changing world of multimedia (cat. no. 00TH8532), vol 2. IEEE, pp 1013–1016
Concord A. (2010) Music of Canada edited by Frederick P. miller, Agnes F. Vandome, and John Mcbrewster. Musicological Explorations 11:136–139
Farzaneh M., Toroghi R. M., Asgari M. (2018) Audio compression using graph-based transform. In: 2018 9th International symposium on telecommunications (IST). IEEE, pp 410–415
Ghido F., Tabus I. (2012) Sparse modeling for lossless audio compression. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 21(1):14–28
Gunawan T. S., Zain M. K. M., Muin F. A., Kartiwi M. (2017) Investigation of lossless audio compression using ieee 1857.2 advanced audio coding. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 6(2):422–430
https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-450-principles-of-digitalcommunications-i-fall-2006/lecture-notes/book_3.pdf. Accessed: 28-10-2020
https://monkeysaudio.com/index.html. Accessed: 21-03-2021
http://www.wavpack.com. Accessed: 20-03-2021
https://xiph.org/flac/index.html. Accessed: 29-03-2021
http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs206/archive/f02/public/lec/lect20.pdf. Accessed: 29-09-2020
https://www.itu.int/dms_pubrec/itu-r/rec/bt/R-REC-BT.500-13-201201-I!!PDF-E.pdf. Accessed: 30-09-2020
Jiang X., Hadid A., Pang Y., Granger E., Feng X. (2019) Deep learning in object detection and recognition. Springer
Kotha H. D., Tummanapally M., Upadhyay V. K. (2019) Review on lossless compression techniques. J Phys: Conf Ser 1228:012007. IOP Publishing
Kutter M., Petitcolas F. A. (1999) Fair benchmark for image watermarking systems. In: Security and watermarking of multimedia contents, vol 3657. International Society for Optics and Photonics, pp 226–239
Li Z. N., Drew M. S., Liu J. (2014) Social media sharing. In: Fundamentals of multimedia. Springer, pp 617–643
Michalski P., Ruszczak B., Tomaszewski M. (2018) Convolutional neural networks implementations for computer vision. In: International scientific conference BCI 2018 Opole. Springer, pp 98–110
Moffat A. (2019) Huffman coding. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 52 (4):1–35
Mohdar F. J., Al-Otaibi M. S., Aboalsamh H. A. (2011) Audio compression testing tool for multimedia applications. In: Image processing and communications challenges 3. Springer, pp 409–418
Mondal U. K., Debnath A. (2020) Developing a dynamic cluster quantization based lossless audio compression (DCQLAC). Multimed Tools Appl 1–24
Mondal U. K., Debnath A., Mandal J. (2020) Deep learning-based lossless audio encoder (dllae). In: Intelligent computing: image processing based applications. Springer, pp 91–101
Nowak N., Zabierowski W. (2011) Methods of sound data compression–comparison of different standards (4)
Prasad B., Prasanna S. (2008) Speech, audio, image and biomedical signal processing using neural networks, vol 83. Springer Science & Business Media
Shannon C. E. (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J 27(3):379–423
Streijl R. C., Winkler S., Hands D. S. (2016) Mean opinion score (mos) revisited: methods and applications, limitations and alternatives. Multimed Syst 22(2):213–227
Ulacha G., Wernik C. (2019) A high efficiency multistage coder for lossless audio compression using ols+ and cdccr method. Appl Sci 9(23):5218
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal, U.K., Debnath, A. Designing a novel lossless audio compression technique with the help of optimized graph traversal (LACOGT). Multimed Tools Appl 81, 40385–40411 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12556-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12556-1