Abstract
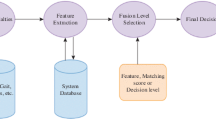
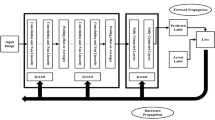
Deep networks have been successfully applied to unsupervised feature learning for single modalities such as Text, Image, or Audio. Here, we present the Deep Network that learns nonlinear transformations of two or more biometric modalities. The resultant representation is a combination of maximally correlated features of the input modalities. It can be viewed as a feature fusion technique with the nonlinear extension of the linear multiset canonical correlation analysis (MCCA). The Foundation of a multibiometric system is information fusion. Feature level fusion is an important area of research owing to the information richness of features. This Deep learning model outlines the integrated correlation among multiple feature vectors and forms a new fused feature vector. This paper presents the Deep Canonical Correlation Analysis (DCCA) for bimodal biometric system and Deep Multiset Canonical Correlation Analysis (DMCCA) framework for the multimodal biometric system outperforming the traditional CCA based fusion methods. Experiments are carried out with the SDUMLA-HMT multimodal dataset. Using the proposed DCCA method performance of a bi-modal biometric system with iris and fingerprint modalities in terms of EER (equal error rate) is 3.78% and 0.116% (single modality recognition). While for the multibiometric system with four modalities (iris, fingerprint, finger-vein, and face) with DMCCA, EER is 0.717%.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammour B, Boubchir L, Bouden T, Ramdani M (2020) Face–iris multimodal biometric identification system. Electron 9(1):85
An L, Yang S, Bhanu B (2015) Person re-identification by robust canonical correlation analysis. IEEE Signal Process Lett 22(8):1103–1107
Anderson TW (1958) An introduction to multivariate statistical analysis, vol 2. Wiley, New York
Andrew G, Arora R, Bilmes J, Livescu K (2013) Deep canonical correlation analysis. In: International conference on machine learning, PMLR, pp 1247–1255
Bach FR, Jordan MI (2005) A probabilistic interpretation of canonical correlation analysis
Belhumeur P, Hespanha J, Kriegman D (1997) Eigenfaces vs. fisherfaces: recognition using class specific linear projection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 19(7):711–720. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.598228
Bengio Y (2012) Practical recommendations for gradient-based training of deep architectures. In: Neural networks: Tricks of the trade, Springer, pp 437–478
Bilenko NY, Gallant JL (2016) Pyrcca: Regularized kernel canonical correlation analysis in python and its applications to neuroimaging. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics 10:49
Borga M, Knutsson H (2001) A canonical correlation approach to blind source separation. Report liu-IMT-EX-0062 Department of Biomedical Engineering Linkping University
Chakraborty S, Mitra M, Pal S (2016) Biometric analysis using fused feature set from side face texture and electrocardiogram. IET Sci, Meas Technol 11(2):226–233
Correa NM, Li YO, Adali T, Calhoun VD (2008) Canonical correlation analysis for feature-based fusion of biomedical imaging modalities and its application to detection of associative networks in schizophrenia. IEEE J Sel Top Sign Process 2(6):998–1007
Eskandari M, Toygar Ö. (2014) Fusion of face and iris biometrics using local and global feature extraction methods. Signal Image and Video Process 8 (6):995–1006
Gao X, Sun Q, Xu H (2017) Multiple-rank supervised canonical correlation analysis for feature extraction, fusion and recognition. Expert Syst Appl 84:171–185
Haghighat M, Abdel-Mottaleb M, Alhalabi W (2016) Discriminant correlation analysis: Real-time feature level fusion for multimodal biometric recognition. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 11(9):1984–1996
Hammad M, Liu Y, Wang K (2018) Multimodal biometric authentication systems using convolution neural network based on different level fusion of ecg and fingerprint. IEEE Access 7:26527–26542
Hardoon DR, Mourao-Miranda J, Brammer M, Shawe-Taylor J (2007) Unsupervised analysis of fmri data using kernel canonical correlation. NeuroImage 37(4):1250–1259
Hardoon DR, Szedmak S, Shawe-Taylor J (2004) Canonical correlation analysis: An overview with application to learning methods. Neural Comput 16 (12):2639–2664
Hel-Or Y (2004) The canonical correlations of color images and their use for demosaicing. HP Laboratories Israel, Tech. Rep HPL-2003-164r1
Hotelling H (1992) Relations between two sets of variates. In: Breakthroughs in statistics, Springer, pp 162–190
Hsieh WW (2000) Nonlinear canonical correlation analysis by neural networks. Neural Netw 13(10):1095–1105
Huo G, Liu Y, Zhu X, Dong H, He F (2015) Face–iris multimodal biometric scheme based on feature level fusion. J Electron Imaging 24 (6):063020
Jain A, Nandakumar K, Ross A (2005) Score normalization in multimodal biometric systems. Pattern Recogn 38(12):2270–2285
Kettenring JR (1971) Canonical analysis of several sets of variables. Biometrika 58(3):433–451
Kim TK, Kittler J (2005) Locally linear discriminant analysis for multimodally distributed classes for face recognition with a single model image. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(3):318–327
Kim TK, Kittler J, Cipolla R (2007) Discriminative learning and recognition of image set classes using canonical correlations. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(6):1005–1018
Lai PL, Fyfe C (2000) Kernel and nonlinear canonical correlation analysis. Int J Neural Syst 10(05):365–377
Li YO, Adali T, Wang W, Calhoun VD (2009) Joint blind source separation by multiset canonical correlation analysis. IEEE Trans Signal Process 57 (10):3918–3929
Loog M, van Ginneken B, Duin RP (2005) Dimensionality reduction of image features using the canonical contextual correlation projection. Pattern Recogn 38(12):2409–2418
Nielsen AA (2002) Multiset canonical correlations analysis and multispectral, truly multitemporal remote sensing data. IEEE Trans Image Process 11 (3):293–305
Regouid M, Touahria M, Benouis M, Costen N (2019) Multimodal biometric system for ecg, ear and iris recognition based on local descriptors. Multimed Tools Appl 78(16):22509–22535
Ross A, Jain A (2003) Information fusion in biometrics. Pattern Recogn Lett 24(13):2115–2125
Ross A, Jain AK (2004) Multimodal biometrics: An overview. In: 2004 12Th european signal processing conference, IEEE, pp 1221–1224
Ross A, Poh N (2009) Multibiometric systems: Overview, case studies, and open issues. Handbook of Remote Biometrics, pp 273–292
Ross AA, Nandakumar K, Jain AK (2006) Handbook of multibiometrics, vol 6, Springer Science & Business Media
Sun QS, Liu ZD, Heng PA, Xia DS (2005) A theorem on the generalized canonical projective vectors. Pattern Recogn 38(3):449–452
Sun QS, Zeng SG, Heng PA, Xia DS (2004) Feature fusion method based on canonical correlation analysis and handwritten character recognition. In: ICARCV 2004 8Th control, automation, robotics and vision conference, 2004, vol 2, IEEE, pp 1547–1552
Sun QS, Zeng SG, Liu Y, Heng PA, Xia DS (2005) A new method of feature fusion and its application in image recognition. Pattern Recogn 38(12):2437–2448
Sun T, Chen S (2007) Locality preserving cca with applications to data visualization and pose estimation. Image Vis Comput 25(5):531–543
Turk M, Pentland A (1991) Eigenfaces for recognition. J Cogn Neurosci 3(1):71–86
Vía J, Santamaría I, Pérez J (2007) A learning algorithm for adaptive canonical correlation analysis of several data sets. Neural Netw 20(1):139–152
Wang L, Xiao L, Wei Z (2015) Image dehazing using two-dimensional canonical correlation analysis. IET Comput Vis 9(6):903–913
Xing X, Wang K, Yan T, Lv Z (2016) Complete canonical correlation analysis with application to multi-view gait recognition. Pattern Recogn 50:107–117
Yang J, Yang JY, Zhang D, Lu JF (2003) Feature fusion: Parallel strategy vs. serial strategy. Pattern Recogn 36(6):1369–1381
Yin Y, Liu L, Sun X (2011) Sdumla-hmt: A multimodal biometric database. In: Chinese conference on biometric recognition, Springer, pp 260–268
Yuan YH, Shen X, Li Y, Li B, Gou J, Qiang J, Zhang X, Sun QS (2019) Composite nonlinear multiset canonical correlation analysis for multiview feature learning and recognition. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, pp e5476
Yuan YH, Sun QS, Zhou Q, Xia DS (2011) A novel multiset integrated canonical correlation analysis framework and its application in feature fusion. Pattern Recogn 44(5):1031–1040
Zheng W, Zhou X, Zou C, Zhao L (2006) Facial expression recognition using kernel canonical correlation analysis (kcca). IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17 (1):233–238
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deshmukh, S., Abhyankar, A. & Kelkar, S. DCCA and DMCCA framework for multimodal biometric system. Multimed Tools Appl 81, 24477–24491 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12435-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12435-9