Abstract
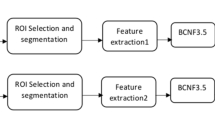
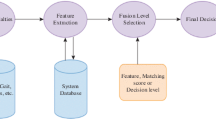
Multimodal biometric systems combine feature knowledge from multiple traits to overcome shortcomings of unimodal systems. However, most of the traditional biometric systems, during the last decade focused on use of handcrafted features for human recognition. The extraction of features is undoubtedly a critical step for the performance of these approaches, due to the difficulty in developing reliable features to deal with the changes in the given images. In this paper, we propose to develop a multimodal biometric system leveraging the power of convolutional neural network (CNN) for feature extraction. We use three pre trained networks for feature extraction: ResNet18, InceptionV3 and SqueezeNet. These CNN’s, before feature extraction, are first optimised by tuning the hyperparameters. Next, after optimisation, features are extracted from different network layers: convolutional layer in SqueezeNet and the average pooling layer in InceptionV3 and ResNet18. The dimensions of features are reduced using Principal Component Analysis and combined using concatenation. Finally, we used a wide array for classifiers i.e. Support vectors machine, K-Nearest Neighbour, Naïve Bayes, and Discriminant. The effectiveness of the proposed methodology was evaluated on three datasets: VIDTIMIT face dataset, AMI ear dataset and CASIA gait dataset, achieving accuracy of 100% with all three feature extraction mechanisms.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
There is no availability of data and material.
Code Availability
There is no code availability.
References
Jain, A., Hong, L., & Pankanti, S. (2000). Biometric identification. Communications of the ACM, 43(2), 90–98. https://doi.org/10.1145/328236.328110
Eskimez, S.E., Maddox, R.K., Xu, C., & Duan, Z. (2018) Generating Talking Face Landmarks from Speech. In: Deville, Y., Gannot, S., Mason, R., Plumbley, M.D., Ward, D. (eds.) Latent Variable Analysis and Signal Separation, Cham, pp. 372–381. Springer International Publishing.
Mo, H., Chen, B., & Luo, W. (2018). Fake Faces Identification via Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM Workshop on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security, Innsbruck, Austria, pp. 43–47. Association for Computing Machinery.
Li, S. Z., & Jain, A. K. (2011). Handbook of Face Recognition. Berlin: Springer.
Guo, Y., Lei, Y., Liu, L., Wang, Y., Bennamoun, M., & Sohel, F. (2016). EI3D: Expression-invariant 3D face recognition based on feature and shape matching. Pattern Recognition Letters, 83, 403–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2016.04.003
Mehraj, H., & Mir, AH. (2020). Human Recognition using Ear based Deep Learning Features. In 2020 International Conference on Emerging Smart Computing and Informatics (ESCI), 12–14 March 2020, pp. 357–360.
Liang, W., Huazhong, N., Tieniu, T., & Weiming, H. (2004). Fusion of static and dynamic body biometrics for gait recognition. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 14(2), 149–158. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2003.821972
Lowe, D. G. (2004). Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints. International Journal of Computer Vision, 60(2), 91–110. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94
Dalal, N., & Triggs, B. (2005). Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'05), 20–25 June 2005, pp. 886–893 vol. 881.
Kong, W. K., Zhang, D., & Li, W. (2003). Palmprint feature extraction using 2-D Gabor filters. Pattern Recognition, 36(10), 2339–2347. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3203(03)00121-3
Lai, J. H., Yuen, P. C., & Feng, G. C. (2001). Face recognition using holistic Fourier invariant features. Pattern Recognition, 34(1), 95–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3203(99)00200-9
Jin, A. T. B., Ling, D. N. C., & Song, O. T. (2004). An efficient fingerprint verification system using integrated wavelet and Fourier-Mellin invariant transform. Image and Vision Computing, 22(6), 503–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2003.12.002
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems - Volume 1, Lake Tahoe, Nevada,
Guo, Y., Liu, Y., Oerlemans, A., Lao, S., Wu, S., & Lew, M. S. (2016). Deep learning for visual understanding: A review. Neurocomputing, 187, 27–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.09.116
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., & Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learning. Nature, 521(7553), 436–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Sanderson, C., & Lovell, B.C. (2009). Multi-region probabilistic histograms for robust and scalable identity inference. In Tistarelli, M., Nixon, M.S. (eds.) Advances in Biometrics, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 199–208. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Gonzalez-Sanchez, E. (2008). Biometria de la oreja. P.hd Thesis, Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria.
Zheng, S., Zhang, J., Huang, K., He, R., & Tan, T. (2011). Robust view transformation model for gait recognition. In 2011 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, 11–14 Sept. 2011, pp. 2073–2076.
Hong, L., Jain, A.K., & Pankanti, S. (1999). Can multibiometrics improve performance? In Proceedings AutoID, pp. 59–64. Citeseer.
Schiele, B. (2002). How many classifiers do I need? In Object recognition supported by user interaction for service robots, 11–15 Aug. 2002, pp. 176–179 vol.172.
Kyong, C., Bowyer, K. W., Sarkar, S., & Victor, B. (2003). Comparison and combination of ear and face images in appearance-based biometrics. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 25(9), 1160–1165.
Kale, A., Roychowdhury, A.K., & Chellappa, R. (2004). Fusion of gait and face for human identification. In 2004 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 17–21 May 2004, pp. V-901.
Xiao-na, X., & Zhi-chun, M. (2007). Multimodal recognition using ear and face profile based on CCA. APPLICATION RESEARCH OF COMPUTERS, 24(11), 312–314.
Zhou, X., & Bhanu, B. (2008). Feature fusion of side face and gait for video-based human identification. Pattern Recognition, 41(3), 778–795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2007.06.019
Chaudhary, S., & Nath, R. (2009). A Multimodal Biometric Recognition System Based on Fusion of Palmprint, Fingerprint and Face. In 2009 International Conference on Advances in Recent Technologies in Communication and Computing, 27–28 Oct. 2009, pp. 596–600.
Kisku, D. R., Gupta, P., Mehrotra, H., & Kanta, J. (2009). Sing: Multimodal Belief Fusion for Face and Ear Biometrics. Intelligent Information Management, 1, 166–171. https://doi.org/10.4236/iim.2009.13024
Yazdanpanah, A.P., Faez, K., & Amirfattahi, R. (2010). Multimodal biometric system using face, ear and gait biometrics. In 10th International Conference on Information Science, Signal Processing and their Applications (ISSPA 2010), 10–13 May 2010, pp. 251–254.
Razzak, M. I., Khan, M. K., Alghathbar, K., & Yusof, R. (2011). Multimodal biometric recognition based on fusion of low resolution face and finger veins. International Journal of Innovative Computing Information and Control, 7, 4679–4689.
Hossain, E., & Chetty, G. (2011). Person identity verification based on multimodal face-gait fusion. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, 11(6), 77–86.
Nadheen, M.F., & Poornima, S. (2013). Fusion in multimodal biometric using iris and ear. In 2013 IEEE Conference on Information & Communication Technologies, 11–12 April 2013, pp. 83–87.
Sim, H. M., Asmuni, H., Hassan, R., & Othman, R. M. (2014). Multimodal biometrics: Weighted score level fusion based on non-ideal iris and face images. Expert Systems with Applications, 41(11), 5390–5404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.02.051
Roy, K., Shelton, J., Connor, B. O., & Kamel, M. S. (2015). Multibiometric system using fuzzy level set, and genetic and evolutionary feature extraction. IET Biometrics, 4(3), 151–161.
Silva, P.H., Luz, E., Zanlorensi, L.A., Menotti, D., & Moreira, G. (2018). Multimodal feature level fusion based on particle swarm optimization with deep transfer learning. In 2018 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), 8–13 July 2018, pp. 1–8.
Kim, W., Song, J. M., & Park, K. R. (2018). Multimodal Biometric Recognition Based on Convolutional Neural Network by the Fusion of Finger-Vein and Finger Shape Using Near-Infrared (NIR) Camera Sensor. Sensors (Basel), 18(7), 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072296
Walia, G. S., Singh, T., Singh, K., & Verma, N. (2019). Robust multimodal biometric system based on optimal score level fusion model. Expert Systems with Applications, 116, 364–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.08.036
Regouid, M., Touahria, M., Benouis, M., & Costen, N. (2019). Multimodal biometric system for ECG, ear and iris recognition based on local descriptors. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 78(16), 22509–22535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-7467-x
Alay, N., & Al-Baity, H. (2019). A Multimodal Biometric System For Personal Verification Based On Different Level Fusion Of Iris And Face Traits. Bioscience Biotechnology Research Communications, 12, 565–576. https://doi.org/10.21786/bbrc/12.3/3
Cherrat, E.M., Alaoui, R., & Bouzahir, H. (2020). Convolutional neural networks approach for multimodal biometric identification system using the fusion of fingerprint, Finger-vein and Face images. PeerJ Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.248.
Mehraj, H., & Mir, A. H. (2020). Feature vector extraction and optimization for multimodal biometrics employing face, ear and gait utilizing artificial neural networks. International Journal of Cloud Computing, 9(2/3), 131–149.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 27–30 June 2016, pp. 770–778.
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., & Wojna, Z. (2016). Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 27–30 June 2016, pp. 2818–2826.
Iandola, F.N., Moskewicz, M.W., Ashraf, K., Han, S., Dally, W., & Keutzer, K. (2017). SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <1MB model size. arXiv:1602.07360.
Bengio, Y. (2012). Practical recommendations for gradient-based training of deep architectures. In G. Montavon, G. B. Orr, & K.-R. Müller (Eds.), Neural networks: Tricks of the trade (2nd ed., pp. 437–478). Berlin: Springer.
Kingma, D.P., & Ba, J. (2015). Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. CoRR arXiv:abs/1412.6980.
Ross, A. (2009). Fusion, Feature-Level. In S. Z. Li & A. Jain (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Biometrics (pp. 597–602). Berlin: Springer.
Ramon, M. M., Nan, X., & Christodoulou, C. G. (2005). Beamforming using support vector machines. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 4, 439–442.
Tharwat, A., Gaber, T., Ibrahim, A., & Hassanien, A. E. (2017). Linear discriminant analysis: A detailed tutorial. Ai Communications, 30, 169–190. https://doi.org/10.3233/AIC-170729
Friedman, J. H. (1989). Regularized Discriminant Analysis. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 84(405), 165–175. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1989.10478752
Carpita, M., Sandri, M., Simonetto, A., & Zuccolotto, P. (2014). Chapter 14 - Football Mining with R. In Y. Zhao & Y. Cen (Eds.), Data mining applications with R (pp. 397–433). Cambridge: Academic Press.
Li, Y.-X., Tan, C. L., Ding, X., & Liu, C. (2004). Contextual post-processing based on the confusion matrix in offline handwritten Chinese script recognition. Pattern Recognition, 37(9), 1901–1912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2004.03.002
Yang, W., Wang, S., Shahzad, M., & Zhou, W. (2021). A cancelable biometric authentication system based on feature-adaptive random projection. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 58, 102704.
Maharjan, P., Shrestha, K., Bhatta, T., Cho, H., Park, C., Salauddin, M., ...& Park, J. Y. (2021). Keystroke Dynamics based Hybrid Nanogenerators for Biometric Authentication and Identification using Artificial Intelligence. Advanced Science, 2100711.
Varshini, S. A., & Aravinth, J. (2021). Hybrid Level Fusion Schemes for Multimodal Biometric Authentication System Based on Matcher Performance. In Computational Vision and Bio-Inspired Computing (pp. 431–447). Springer, Singapore.
Kohlakala, A., & Coetzer, J. (2021). Ear-based biometric authentication through the detection of prominent contours. SAIEE Africa Research Journal, 112(2), 89–98.
Premanand, R. P., & Rajaram, A. (2020). Enhanced data accuracy based PATH discovery using backing route selection algorithm in MANET. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl., 13, 2089–2098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-019-00824-1
Rajaram, A., & Dr. S. Palaniswami (2010). Malicious node detection system for mobile ad hoc networks. (IJCSIT) International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies, 1(2), 77–85.
Dr.S.Palaniswami, Ayyasamy Rajaram. An Enhanced Distributed Certificate Authority Scheme for Authentication in Mobile Ad hoc Networks. The International Arab Journal of Information Technology (IAJIT). 9 (3), 291–298.
Funding
There is no funding information.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
There is no author’s contribution.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehraj, H., Mir, A.H. Robust Multimodal Biometric System Based on Feature Level Fusion of Optimiseddeepnet Features. Wireless Pers Commun 127, 2461–2482 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09075-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09075-x