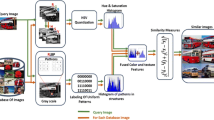
Abstract
Over the last decades, hand-crafted feature extractors have been used to encode image visual properties into feature vectors. Recently, data-driven feature learning approaches have been successfully explored as alternatives for producing more representative visual features. In this work, we combine both research venues, focusing on the color quantization problem. We propose two data-driven approaches to learn image representations through the search for optimized quantization schemes, which lead to more effective feature extraction algorithms and compact representations. Our strategy employs Genetic Algorithm, a soft-computing apparatus successfully utilized in Information-retrieval-related optimization problems. We hypothesize that changing the quantization affects the quality of image description approaches, leading to effective and efficient representations. We evaluate our approaches in content-based image retrieval tasks, considering eight well-known datasets with different visual properties. Results indicate that the approach focused on representation effectiveness outperformed baselines in all tested scenarios. The other approach, which also considers the size of created representations, produced competitive results keeping or even reducing the dimensionality of feature vectors up to 25%.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baeza-Yates RA, Ribeiro-Neto B (1999) Modern information retrieval. Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co. Inc., Boston
Bengio Y, Courville A, Vincent P (2013) Representation learning: a review and new perspectives. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(8):1798–1828
Bharti V, Biswas B, Shukla KK (2020) Recent trends in nature inspired computation with applications to deep learning. In: 2020 10th International conference on cloud computing, data science & engineering (confluence). IEEE, pp 294–299
Bhunia AK, Bhattacharyya A, Banerjee P, Roy PP, Murala S (2020) A novel feature descriptor for image retrieval by combining modified color histogram and diagonally symmetric co-occurrence texture pattern. Pattern Anal Applic 23:703–723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-019-00827-x
Bo L, Ren X, Fox D (2011) Hierarchical matching pursuit for image classification: architecture and fast algorithms. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 2115–2123
Bukh PND (1992) The art of computer systems performance analysis, techniques for experimental design, measurement, simulation and modeling. JSTOR
Coates A, Ng AY (2011) The importance of encoding versus training with sparse coding and vector quantization. In: Proceedings of the 28th international conference on machine learning (ICML-11). pp 921–928
Criminisi A (2004) Microsoft research Cambridge object recognition image database. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/project/image-understanding/
da S Torres R, Falcão AX (2006) Content-based image retrieval: theory and applications. Rev Inform Teór Apl (RITA) 13(2):161–185
da S Torres R, Falcão AX, Gonçalves MA, Papa JP, Zhang B, Fan W, Fox EA (2009) A genetic programming framework for content-based image retrieval. Pattern Recognit 42(2):283–292
Davis L (1991) Handbook of genetic algorithms. Van Nostrand Reinhold. https://books.google.com.br/books?id=Kl7vAAAAMAAJ
Davis SM, Landgrebe DA, Phillips TL, Swain PH, Hoffer RM, Lindenlaub JC, Silva LF (1978) Remote sensing: the quantitative approach, vol 1978. McGraw-Hill International Book Co, New York, p 405
dos Santos JA, Penatti OAB, da Silva Torres R (2010) Evaluating the potential of texture and color descriptors for remote sensing image retrieval and classification. VISAPP (2)203–208
Fan W, Fox EA, Pathak P, Wu H (2004) The effects of fitness functions on genetic programming-based ranking discovery for web search. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 55(7):628–636
García-Lamont F, Cervantes J, López-Chau A, Ruiz-Castilla S (2020) Color image segmentation using saturated RGB colors and decoupling the intensity from the hue. Multimed Tools Appl 79(1-2):1555–1584
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization, and machine learning. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Hinton GE, Zemel RS (1994) Autoencoders, minimum description length and helmholtz free energy. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 3–10
Hinton GE, Osindero S, Teh YW (2006) A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput 18(7):1527–1554
Khaldi B, Aiadi O, Kherfi ML (2019) Combining colour and grey-level co-occurrence matrix features: a comparative study. IET Image Process 13(9):1401–1410
Kim TK (2015) T test as a parametric statistic. Korean J Anesthesiol 68(6):540–546
Kingma DP, Welling M (2013) Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv:13126114
Krizhevsky A, Hinton G et al (2009) Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. Master’s thesis, University of Tront
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 1097–1105
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521(7553):436–444
Leibe B, Schiele B (2003) Analyzing appearance and contour based methods for object categorization. In: Proceedings 2003 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol 2, pp II–409
Li Y (2005) Object and concept recognition for content-based image retrieval. PhD thesis, University of Washington, Seattle
Li Y, Shapiro LG (2002) Consistent line clusters for building recognition in cbir. In: Proceedings of the international conference on pattern recognition
Li T, Leng J, Kong L, Guo S, Bai G, Wang K (2019) DCNR: deep cube CNN with random forest for hyperspectral image classification. Multimed Tools Appl 78(3):3411–3433
Li X, Li D, Peng L, Zhou H, Chen D, Zhang Y, Xie L (2019) Color and depth image registration algorithm based on multi-vector-fields constraints. Multimedia Tools Appl 78(17):24:301–24:319
Lu D, Weng Q (2007) A survey of image classification methods and techniques for improving classification performance. Int J Remote Sens 28(5):823–870
Luccheseyz L, Mitray S (2001) Color image segmentation: a state-of-the-art survey. Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad (INSA-A) 67(2):207–221
Makhzani A, Frey B (2013) K-sparse autoencoders. arXiv:13125663
Makhzani A, Frey BJ (2015) Winner-take-all autoencoders. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. pp 2791–2799
Mohseni SA, Wu HR, Thom JA, Bab-Hadiashar A (2020) Recognizing induced emotions with only one feature: a novel color histogram-based system. IEEE Access 8:37:173–37:190
Nakamura R, Fonseca L, dos Santos JA, Torres RDS, Yang XS, Papa JP (2014) Nature-inspired framework for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 52(4):2126–2137
Nayar SK, Nene SA, Murase H (1996) Real-time 100 object recognition system. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, vol 3, pp 2321–2325
Ng A, et al. (2011) Sparse autoencoder. In: CS294A lecture notes, vol 72, pp 1–19
Nogueira K, Penatti OA, dos Santos JA (2017) Towards better exploiting convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification. Pattern Recognit 61:539–556
Oh IS, Lee JS, Moon BR (2004) Hybrid genetic algorithms for feature selection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell (11):1424–1437
Omran MG, Engelbrecht AP, Salman A (2005) A color image quantization algorithm based on particle swarm optimization. Informatica 29(3):261–269
Penatti OAB, Torres RDS (2008) Color descriptors for web image retrieval: a comparative study. In: 2008 XXI Brazilian symposium on computer graphics and image processing. pp 163–170
Penatti OAB, Valle E, Torres RDS (2012) Comparative study of global color and texture descriptors for web image retrieval. J Vis Commun Image Representat 23(2):359–380
Pérez-Delgado M L (2019) The color quantization problem solved by swarm-based operations. Appl Intell 49(7):2482–2514
Ponti M, Nazaré TS, Thumé GS (2016) Image quantization as a dimensionality reduction procedure in color and texture feature extraction. Neurocomputing 173:385–396
Ranzato M, Poultney C, Chopra S, Cun YL (2007) Efficient learning of sparse representations with an energy-based model. In: Schölkopf B, Platt J, Hoffman T (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems, vol 19. MIT Press, pp 1137–1144
Rifai S, Vincent P, Muller X, Glorot X, Bengio Y (2011) Contractive auto-encoders: explicit invariance during feature extraction
Rocha A, Hauagge DC, Wainer J, Goldenstein S (2010) Automatic fruit and vegetable classification from images. Comput Electron Agric 70(1):96–104
Rodriguez-Coayahuitl L, Morales-Reyes A, Escalante HJ (2019) Evolving autoencoding structures through genetic programming. Genet Progr Evolvable Mach 20(3):413–440
Salakhutdinov R, Hinton G (2009) Deep boltzmann machines. In: Artificial intelligence and statistics. pp 448–455
Scheunders P (1996) A genetic lloyd-max image quantization algorithm. Pattern Recognit Lett 17(5):547–556
Sheng T, Feng C, Zhuo S, Zhang X, Shen L, Aleksic M (2018) A quantization-friendly separable convolution for mobilenets. In: 2018 1st Workshop on energy efficient machine learning and cognitive computing for embedded applications (EMC2). IEEE, pp 14–18
Smeulders AW, Worring M, Santini S, Gupta A, Jain R (2000) Content-based image retrieval at the end of the early years. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22(12):1349–1380
Stehling RO, Nascimento MA, Falcão AX (2002) A compact and efficient image retrieval approach based on border/interior pixel classification. In: International conference on information and knowledge management. pp 102–109
Suganuma M, Shirakawa S, Nagao T (2017) A genetic programming approach to designing convolutional neural network architectures. In: Proceedings of the genetic and evolutionary computation conference. pp 497–504
Swain MJ, Ballard DH (1991) Color indexing. Int J Comput Vis 7(1):11–32
Vincent P, Larochelle H, Bengio Y, Manzagol PA (2008) Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders. In: Proceedings of the 25th international conference on machine learning. pp 1096–1103
Vincent P, Larochelle H, Lajoie I, Bengio Y, Manzagol PA (2010) Stacked denoising autoencoders: learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. J Mach Learn Res 11:3371–3408
Wang JZ, Li J, Wiederhold G (2001) Simplicity: semantics-sensitive integrated matching for picture libraries. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23 (9):947–963
Wold S, Esbensen K, Geladi P (1987) Principal component analysis. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 2(1–3):37–52
Xie L, Yuille A (2017) Genetic cnn. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV). pp 1388–1397
Yang Y, Newsam S (2010) Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification. In: Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL international conference on advances in geographic information systems. pp 270–279
Yilmaz A, Javed O, Shah M (2006) Object tracking: a survey. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 38(4):13
Yu K, Lin Y, Lafferty J (2011) Learning image representations from the pixel level via hierarchical sparse coding. In: 2011 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). pp 1713–1720
Zeng S, Huang R, Wang H, Kang Z (2016) Image retrieval using spatiograms of colors quantized by gaussian mixture models. Neurocomputing 171:673–684
Zhang S, He F (2020) DRCDN: learning deep residual convolutional dehazing networks. Visual Comput 36(9):1797–1808
Zhang X, Zhou X, Lin M, Sun J (2018) Shufflenet: an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 6848–6856
Acknowledgments
This study was financed in part by: the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001; the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq)—grants #424700/2018-2 and #311395/2018-0; and the Minas Gerais Research Foundation (FAPEMIG)—grant APQ-00449-17. Authors are also grateful to CAPES (grant #88881.145912/2017-01), São Paulo Research Foundation—FAPESP (grants #2014/12236-1, #2015/24494-8, #2016/50250-1, and #2017/20945-0) and the FAPESP—Microsoft Virtual Institute (grants #2013/50155-0, #2013/50169-1, and #2014/50715-9).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, E.M., Torres, R.d.S. & dos Santos, J.A. A genetic algorithm approach for image representation learning through color quantization. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 15315–15350 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10194-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10194-z