Abstract
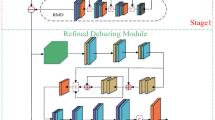
Single image dehazing, which is the process of removing haze from a single input image, is an important task in computer vision. This task is extremely challenging because it is massively ill-posed. In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end deep residual convolutional dehazing network (DRCDN) based on convolutional neural networks for single image dehazing, which consists of two subnetworks: one network is used for recovering a coarse clear image, and the other network is used to refine the result. The DRCDN firstly predicts the coarse clear image via a context aggregation subnetwork, which can capture global structure information. Subsequently, it adopts a novel hierarchical convolutional neural network to further refine the details of the clean image by integrating the local context information. The DRCDN is directly trained using complete images and the corresponding ground-truth haze-free images. Experimental results on synthetic datasets and natural hazy images demonstrate that the proposed method performs favorably against the state-of-the-art methods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Narasimhan, S.G., Nayar, S.K.: Vision and the atmosphere. Int. J. Comput. Vision 48(3), 233–254 (2002)
He, K., Sun, J., Tang, X.: Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33(12), 2341–2353 (2011)
Schechner, Y.Y., Narasimhan, S.G., Nayar, S.K : Instant dehazing of images using polarization. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol. 1, pp. 325–332 (2001)
Narasimhan, S.G., Nayar, S.K.: Contrast restoration of weather degraded images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 25(6), 713–724 (2003)
Shwartz, S., Namer, E., Schechner, Y.Y : Blind haze separation. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol. 2, pp. 1984–1991 (2006)
Kopf, J., Neubert, B., Chen, B., Cohen, M., Cohen-Or, D., Deussen, O., Uyttendaele, M., Lischinski, D.: Deep photo: model-based photograph enhancement and viewing. In: ACM transactions on graphics, vol. 27, Article No. 116 (2008)
Chen, X., He, F.: A matting method based on full feature coverage. Multimedia Tools Appl. 78(9), 11173–11201 (2019)
Yu, H., He, F.: A novel segmentation model for medical images with intensity inhomogeneity based on adaptive perturbation. Multimedia Tools Appl. 78(9), 11779–11798 (2019)
Haiping, Y., He, F., Pan, Y.: A novel region-based active contour model via local patch similarity measure for image segmentation. Multimedia Tools Appl. 77(18), 24097–24119 (2018)
Tan, R.T: Visibility in bad weather from a single image. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2008)
Fattal, R.: Single image dehazing. ACM Trans. Gr. 27(3), 72 (2008)
Meng, G., Wang, Y., Duan, J., Xiang, S., Pan, C.: Efficient image dehazing with boundary constraint and contextual regularization. In: International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 617–624 (2013)
Fattal, R.: Dehazing using color-lines. ACM Trans. Gr. 34(1), 13 (2014)
Zhu, Q., Mai, J., Shao, L.: A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(11), 3522–3533 (2015)
Berman, D., Avidan, S., et al.: Non-local image dehazing. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1674–1682 (2016)
Li, K., He, F., Haiping, Y., Chen, X.: A parallel and robust object tracking approach synthesizing adaptive bayesian learning and improved incremental subspace learning. Front. Comput. Sci. 13(5), 1116–1135 (2019)
Ren, W., Liu, S., Ma, L., Qianqian, X., Xiangyu, X., Cao, X., Junping, D., Yang, M.-H.: Low-light image enhancement via a deep hybrid network. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(9), 4364–4375 (2019)
Ren, W., Zhang, J., Ma, L., Pan, J., Cao, X., Zuo, W., Liu, W., Yang, M.-H.: Deep non-blind deconvolution via generalized low-rank approximation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 297–307 (2018)
Li, H., He, F., Yan, X.: IBEA-SVM an indicator-based evolutionary algorithm based on pre-selection with classification guided by SVM. Appl. Math.-A J. Chin. Univ. 34(1), 1–26 (2019)
Li, H., He, F., Liang, Y., Quan, Q.: A dividing-based many-objective evolutionary algorithm for large-scale feature selection. Soft Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04324-5
Yan, Y., Ren, W., Cao, X.: Recolored image detection via a deep discriminative model. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 14(1), 5–17 (2018)
Ding, B., Long, C., Zhang, L., Xiao, C.: ARGAN: attentive recurrent generative adversarial network for shadow detection and removal. In: International Conference on Computer Vision (2019)
Yong, J., He, F., Li, H., Zhou, W.: A novel bat algorithm based on cross boundary learning and uniform explosion strategy. Appl. Math.-A J. Chin. Univ. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11766-019-3714-1
Luo, J., He, F., Yong, J.: An efficient and robust bat algorithm with fusion of opposition-based learning and whale optimization algorithm. Intell. Data Anal. 24(3: to appear in this issue) (2020)
Zhang, W., Xiao, C: PCAN: 3D attention map learning using contextual information for point cloud based retrieval. In: the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 12436–12445 (2019)
Hou, N., He, F., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y.: An efficient GPU-based parallel tabu search algorithm for hardware/software co-design. Front. Comput. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-019-8184-3
Cai, B., Xiangmin, X., Jia, K., Qing, C., Tao, D.: Dehazenet: an end-to-end system for single image haze removal. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(11), 5187–5198 (2016)
Ren, W., Liu, S., Zhang, H., Pan, J., Cao, X., Yang, M.-H.: Single image dehazing via multi-scale convolutional neural networks. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 154–169 (2016)
Sulami, M., Glatzer, I., Fattal, R., Werman, M.: Automatic recovery of the atmospheric light in hazy images. In: IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography, pp. 1–11 (2014)
Berman, D., Treibitz, T., Avidan, S.: Air-light estimation using haze-lines. In: IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography, pp. 1–9 (2017)
Li, B., Peng, X., Wang, Z., Xu, J., Feng, D.: Aod-net: all-in-one dehazing network. In: International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4770–4778 (2017)
Ren, W., Ma, L., Zhang, J., Pan, J., Cao, X., Liu, W., Yang, M.-H.: Gated fusion network for single image dehazing. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3253–3261 (2018)
Zhang, S., Ren, W., Yao, J.: Feed-net: Fully end-to-end dehazing. In: IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, pp. 1–6 (2018)
Zhang, H., Patel, V.M.: Densely connected pyramid dehazing network. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3194–3203 (2018)
Ancuti, C.O., Ancuti, C.: Single image dehazing by multi-scale fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(8), 3271–3282 (2013)
Tarel, J.-P., Hautiere, N.: Fast visibility restoration from a single color or gray level image. In: International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2201–2208 (2009)
Tang, K., Yang, J., Wang, J.: Investigating haze-relevant features in a learning framework for image dehazing. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2995–3000 (2014)
Pan, Y., He, F., Yu, H.: A correlative denoising autoencoder to model social influence for top-n recommender system. Front. Comput. Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-019-8123-3
Pan, Y., He, F., Yu, H.: Learning adaptive trust strength with user roles of truster and trustee for trust-aware recommender systems. Appl. Intell. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-019-01542-0
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1097–1105 (2012)
Szegedy, C., Toshev, A., Erhan, D.: Deep neural networks for object detection. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2553–2561 (2013)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 91–99 (2015)
Yu, J., Jiang, Y., Wang, Z., Cao, Z., Huang, T.: Unitbox: an advanced object detection network. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM on Multimedia Conference, pp. 516–520 (2016)
Xie, J., Xu, L., Chen, E.: Image denoising and inpainting with deep neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 341–349 (2012)
Dong, C., Loy, C.C., He, K., Tang, X.: Xiaoou: image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(2), 295–307 (2016)
Kim, J., Kwon Lee, J., Mu Lee, K.: Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1646–1654 (2016)
Liu, D., Wen, B., Liu, X., Huang, T.S.: When image denoising meets high-level vision tasks: a deep learning approach. In: International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 842–848 (2017)
Zhang, S., He, F., Ren, W., Yao, J.: Joint learning of image detail and transmission map for single image dehazing. Vis. Comput. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-018-1612-9
Yu, F., Koltun, V., Funkhouser, T.A: Dilated residual networks. In:Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol. 2, p. 3 (2017)
Fu, X., Huang, J., Zeng, D., Huang, Y., Ding, X., Paisley, J.: Removing rain from single images via a deep detail network. In:Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3855–3863 (2017)
Mehta, S., Rastegari, M., Caspi, A., Shapiro, L., Hajishirzi, H.: Espnet: efficient spatial pyramid of dilated convolutions for semantic segmentation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 552–568 (2018)
Yu, Fi., Koltun, V.: Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2016). arXiv:1511.07122
Johnson, J., Alahi, A., Fei-Fei, L.: Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 694–711 (2016)
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Hao, S., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., Huang, Z., Karpathy, A., Khosla, A., Bernstein, M.: Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vision 115(3), 211–252 (2015)
Zhang, Y., Ding, L., Sharma, G.: Hazerd: an outdoor scene dataset and benchmark for single image dehazing. In: International Conference on Image Processing, pp. 3205–3209 (2017)
Li, K., He, F., Yu, H.: Robust visual tracking based on convolutional features with illumination and occlusion handing. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 33(1), 223–236 (2018)
Mbelwa, J.T., Zhao, Q., Wang, F.: Visual tracking tracker via object proposals and co-trained kernelized correlation filters. Vis. Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01727-1
Pan, Y., He, F., Haiping, Y.: A novel enhanced collaborative autoencoder with knowledge distillation for top-n recommender systems. Neurocomputing 332, 137–148 (2019)
Liu, F., Shen, C., Lin, G., Reid, I.: Learning depth from single monocular images using deep convolutional neural fields. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(10), 2024–2039 (2016)
Li, B., Ren, W., Fu, D., Tao, D., Feng, D., Zeng, W., Wang, Z.: Benchmarking single image dehazing and beyond. In: IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, pp. 492–505 (2018)
Yang, D., Sun, J.: Proximal dehaze-net: A prior learning-based deep network for single image dehazing. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 702–717 (2018)
FazlErsi, E., Kazemi Nooghabi, M.: Revisiting correlation based filters for low-resolution and long-term visual tracking. Vis. Comput. 35(10), 1447–1459 (2019)
Doyle, L., David Mould, D.: Augmenting photographs with textures using the laplacian pyramid. Vis. Comput. 35(10), 1489–1500 (2019)
Umer, S., Dhara, B.C., Chanda, B.: NIR and VW iris image recognition using ensemble of patch statistics features. Vis. Comput. 35(9), 1327–1344 (2019)
Acknowledgements
We thank anonymous reviewers very much for their suggestive comments. This work is partially supported by the NSFC (No. 61472289, 41571436).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., He, F. DRCDN: learning deep residual convolutional dehazing networks. Vis Comput 36, 1797–1808 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01774-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01774-8