Abstract
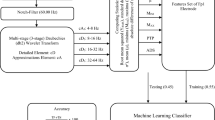
This paper focuses on EEG (Electroencephalography) signals as a robust method for emotion recognition. In emotion recognition, researchers usually use features such as eye pupil diameter, facial features, EEG signals and physiological signals like: respiration amplitude, heart rate, skin temperature, blood volume pulse, respiration rate etc. In this paper we use just EEG signals as we believe that a human being may suffer from some physical disabilities and impairments like visual disorders, motor impairment or some other common disorders. So, the use of EEG signal, in some aspects, can be more useful and utilizable in real life. In this paper, we use a combination of some existent techniques on this theme, such as wavelet coefficients and an 8-number electrode configuration, which makes our approach really convenient and comfortable to use, and some other methods that may seem minor; But the way we employ and combine them, make a novel, productive, high efficient and reliable algorithm that highly can help people with some special disorders. To have a brief overview of the results of our work: the average Arousal F-Score and Valence F-Score for our algorithm are, respectively, 0.73 and 0.77. These values for a corresponding work are, 0.60 and 0.50, respectively. As it is seen the results have improved by 0.13 and 0.27. The results of our EEG-based algorithm are even better than the fusion of facial and EEG signals or physiological signals presented in the corresponding works. Beside this better performance, the ease and comfort that our method provides for users, is far beyond description.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coan J, Allen J (2007) Handbook of emotion elicitation and assessment. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Erwin R, Gur R, Gur R, Skolnick B, Mawhinney-Hee M, Smailis J (1992) Facial emotion discrimination: I. Task construction and behavioral findings in normal subjects. Psychiatry Res 42(3):231–240
Fontaine J, Scherer K, Roesch E, Ellsworth P (2007) The World of Emotions is not Two-Dimensional. Psychol Sci 18(12):1050–1057
Graimann B, Allison B, Pfurtscheller G (2010) Brain-computer interfaces. Springer, Heidelberg
Hoffmann U, Ebrahimi T, Vesin J (2007) Bayesian machine learning applied in a brain-computer interface for disabled users. EPFL, Lausanne
Hoffmann U, Vesin J, Ebrahimi T, Diserens K (2008) An efficient P300-based brain–computer interface for disabled subjects. J Neurosci Methods 167(1):115–125
Isbister K, Höök K (2007) Evaluating affective interactions. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies 65(4):273–274
Khemri N (2012) P300 wave detection using a commercial non-invasive EEG sensor: reliability and performance in control applications. Master Thesis, Oklahoma State University
Khosrowabadi R, Quek C, Ang KK, Wahab A (2014) ERNN: A Biologically Inspired Feedforward Neural Network to Discriminate Emotion From EEG Signal. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 25(3):609–620
Lantz G, Grave de Peralta R, Spinelli L, Seeck M, Michel C (2003) Epileptic source localization with high density EEG: how many electrodes are needed? Clin Neurophysiol 114(1):63–69
Lee G, Kwon M, Kavuri Sri S, Lee M (2014) Emotion recognition based on 3D fuzzy visual and EEG features in movie clips. Neurocomputing 144:560–568
Lin YP, Wang CH, Wu TL, Jeng SK, Chen J H (2007) Multilayer perceptron for EEG signal classification during listening to emotional music. In: TENCON 2007-2007 IEEE Region 10 Conference. IEEE, Taipei, pp 1–3
Lin Y-P, Wang C-H, Jung T-P, Wu T-L, Jeng S-K, Duann J-R, Chen J-H (2010) EEG-Based Emotion Recognition in Music Listening. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(7):1798–1806
Mitra S, Liu Y (2004) Local facial asymmetry for expression classification. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2:II
Mohammadi Z, Frounchi J, Amiri M (2016) Wavelet-based emotion recognition system using EEG signal. Neural Comput & Applic 28(8):1985–1990
Momennezhad A, Shamsi M, Ebrahimnezhad H, Saberkari H (2014) Classification of EEG-P300 Signals Extracted From Brain Activities In Bci Systems Using Ν-SVM and BLDA algorithms. Applied Medical Informatics 34(2):23–35
Momennezhad A, Ebrahimnezhad H, Shamsi M, Asgharian L (2014) Brain Activity EEG-P300 Signal Categorization from LPC based Estimation of Signal using Fisher Linear Discriminant Analysis. International Journal of Intelligent Computing in Medical Sciences & Image Processing 6(1):17–26
Nguyen T, Hwang D, Jung J (2017) Handling imbalanced classification problem: A case study on social media datasets. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 32(2):1437–1448
Petrantonakis P, Hadjileontiadis L (2011) A Novel Emotion Elicitation Index Using Frontal Brain Asymmetry for Enhanced EEG-Based Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 15(5):737–746
Petrantonakis P, Hadjileontiadis L (2012) Adaptive Emotional Information Retrieval From EEG Signals in the Time-Frequency Domain. IEEE Trans Signal Process 60(5):2604–2616
Russell J (1991) Culture and the categorization of emotions. Psychol Bull 110(3):426–450
Russell J, Mehrabian A (1977) Evidence for a three-factor theory of emotions. J Res Pers 11(3):273–294
Scherer K (1993) Studying the emotion-antecedent appraisal process: An expert system approach. Cognit Emot 7(3-4):325–355
Shui-Hua W, Yang W, Dong Z, Phillips P, Zhang Y (2017) Facial emotion recognition via discrete wavelet transform, principal component analysis, and cat swarm optimization. In: International Conference on Intelligent Science and Big Data Engineering. Springer, Cham, pp 203–214
Soleymani M, Pantic M, Pun T (2012) Multimodal Emotion Recognition in Response to Videos. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 3(2):211–223
Soleymani M, Lichtenauer J, Pun T, Pantic M (2012) A Multimodal Database for Affect Recognition and Implicit Tagging. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 3(1):42–55
Soleymani M, Asghari-Esfeden S, Fu Y, Pantic M (2016) Analysis of EEG Signals and Facial Expressions for Continuous Emotion Detection. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 7(1):17–28
Subramanian R, Wache J, Abadi M, Vieriu R, Winkler S, Sebe N (2006) ASCERTAIN: Emotion and Personality Recognition using Commercial Sensors. IEEE Trans Affect Comput. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAFFC.2016.2625250
Wang Y, Gao X, Hong B, Jia C, Gao S (2008) Brain-Computer Interfaces Based on Visual Evoked Potentials. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine 27(5):64–71
Yoon H, Chung S (2013) EEG-based emotion estimation using Bayesian weighted-log-posterior function and perceptron convergence algorithm. Comput Biol Med 43(12):2230–2237
Zheng Z, Wu X, Srihari R (2004) Feature selection for text categorization on imbalanced data. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter 6(1):80
Acknowledgments
We thank Mohammad Soleymani and his colleagues for their generosity in accommodating us with their valuable dataset entitled “MAHNOB-HCI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Momennezhad, A. EEG-based emotion recognition utilizing wavelet coefficients. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 27089–27106 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-5906-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-5906-8