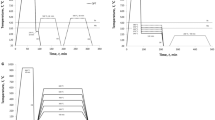
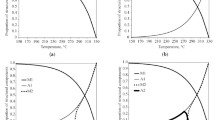
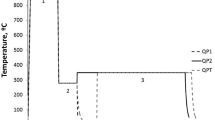
Steel 30Kh2GSN2VM (VL1) used in the aircraft industry for heavy-duty parts is studied. The temperature and time ranges of the transformation of supercooled austenite under continuous cooling from the temperature of complete austenitization are determined by the method of dilatometry. Different variants of interrupted and isothermal quenching are simulated to establish the special features of the transformations occurring in the steel in different stages of heat treatment. The mechanical properties are analyzed after isothermal and interrupted quenching and after oil quenching and tempering. It is shown that the isothermal quenching and the stage quenching (the quenching-partitioning technology) do not provide the expected stabilization of a considerable content of retained austenite and elevation of the mechanical properties of the steel.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Wang, B. Liu, Q. Pan, et al., “Effect of austempering on the mechanical properties of Nb/V microalloyed bainitic bearing steel,” Crystals, 12(7), 1001 (2022). DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12071001
A. Morri, L. Ceschini, M. Pellizzari, et al., “Effect of the austempering process on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 27MnCrB5-2 steel,” Arch. Metall. Mater., 62(2), 643 – 651 (2017). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/amm-2017-0094
J. Feng and M. Wettlaufer, “Plane-strain fracture toughness of AISI 4140 steel austempered below MS ,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 743, 494 – 499 (2019). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.11.122
M. V. Maisuradze, Yu. N. Yudin, and A. A. Kuklina, “Increase in impact strength during bainite structure formation in HY-TUF high-strength steel,” Metallurgist, 63(7 – 8), 8490858 (2019). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-019-00899-4
F.-C. An, S.-X. Zhao, X.-K. Xue, et al., “Incompleteness of bainitic transformation in quenched and tempered steel under continuous cooling conditions,” J. Mater. Res. Technol., 4, 8985 – 8996 (2020). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.06.039
Y. Onuki, K. Umemura, K. Fujiwara, et al., “Microstructure formation and carbon partitioning with austenite decomposition during isothermal heating process in Fe – Si – Mn – C steel monitored by in situ time-of-flight neutron diffraction,” Metals, 12, 957 (2022). DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/met12060957
S. Zhou, F. Hu, K. Wang, et al., “Nanomechanics of retained austenite in medium-carbon low-temperature bainitic steel: A critical analysis of a one-step treatment,” Materials, 15, 1996 (2022). DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15175996
D. R. Johnson and W. T. Becker, “Toughness of tempered upper and lower bainitic microstructures in a 4150 steel,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2(2), 255 – 263 (1993). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02660294
M. Azuma, N. Fujita, M. Takahashi, et al., “Modeling upper and lower bainite transformation in steels,” ISIJ Int., 45(2), 221 – 228 (2005). DOI: https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.45.221
J. G. Zhu, X. Sun, G. C. Barber, et al., “Bainite transformation-kinetics-microstructure characterization of austempered 4140 steel,” Metals, 10, 236 (2020). DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020236
A. Yu. Kaletin, Yu. V. Kaletina, and M. A. Ryzhkov, “Carbide-free bainite in low-carbon structural steels,” Pis’ma Mater., 10(3), 249 – 253 (2020).
C. M. Hasan, D. Chakrabarti, and S. B. Singh, “Thermomechanical treatment of steel with carbide-free bainite,” Metal-loved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 7,9– 18 (2021).
C. Hofer, H. Leitner, F. Winkelhofer, et al., “Structural characterization of “carbide-free” bainite in a Fe – 0.2C – 1.5Si – 2.5Mn steel,” Mater. Charact., 102, 85 – 91 (2015). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2015.02.020
M. Soliman and H. Palkowski, “Microstructure development and mechanical properties of medium carbon carbide-free bainite steels,” Procedia Eng., 81, 1306 – 1311 (2014). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.10.148
B. He, “On the factors governing austenite stability: Intrinsic versus extrinsic,” Materials, 13, 3440 (2020). DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153440
F. Zhao, P. Chen, B. Xu, et al., “Martensite transformation of retained austenite with diverse stability and strain partitioning during tensile deformation of a carbide-free bainitic steel,” Mater. Charact., 179, 111327 (2021). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2021.111327
J. Mola, E. J. Seo, and L. Cho, “Correlation between mechanical stability and hardness of austenite in martensite/austenite mixtures,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 822, 141687 (2021). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141687
S. Kang, K. Kim, Y. Son, and S.-J. Lee, “Application of the quenching and partitioning (Q&P) process to D6AC steel,” ISIJ Int., 56, 2057 – 2061 (2016). DOI: https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational. ISIJINT-2016-257
J. Sun and H. Yu, “Microstructure development and mechanical properties of quenching and partitioning (Q&P) steel and an incorporation of hot-dipping galvanization during Q&P process,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 586, 100 – 107 (2013). DOI: 10.1016/ j.msea.2013.08.021
H. Y. Li, X. W. Lu, X. C. Wu, et al., “Bainitic transformation during the two-step quenching and partitioning process in a medium carbon steel containing silicon,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527, 6255 – 6259 (2010). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.06.045
Y. Takahama, M. J. Santofimia, M. G. Mecozzi, et al., “Phase field simulation of the carbon redistribution during the quenching and partitioning process of a low-carbon steel,” Acta Mater., 60(6 – 7), 2916 – 2926 (2012) *
Y. Xu, F. Chen, Z. Li, et al., “Kinetics of carbon partitioning of Q&P steel: Considering the morphology of retained austenite,” Metals, 12, 344 (2022). DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020344
L. Wang and J. G. Speer, “Quenching and partitioning steel heat treatment,” Metallogr., Microstr., Anal., 2, 268 – 281 (2013). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-013-0082-8
B. C. De Cooman and J. G. Speer, “Quench and partitioning steel: A new AHSS concept for automotive anti-intrusion applications,” Steel Res. Int., 77(9 – 10), 634 – 640 (2006). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.200606441
E. De Moor and J. G. Speer, “Bainitic and quenching and partitioning steels,” in: Automotive Steels. Design, Metallurgy, Processing and Applications, Woodhead Publ., UK (2017), pp. 289 – 316. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100638-2.00010-9
A. B. Dobuzhskaya, G. A. Galitsyn, N. V. Mukhranov, et al., “A study of structural and phase transformations under cooling of rail steels,” Stal’, No. 11, 86 – 91 (2015).
B. Adamczyk-Cieslak, M. Koralnik, R. Kuziak, et al., “Studies of bainitic steel for rail applications based on carbide-free, low-alloy steel,” Metall. Mater. Tans. A, 52, 5429 – 5442 (2021). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-021-06480-6
M. N. Georgiev and T. V. Semenova, “Railroad rails from bainitic steel,” Metal. Sci. Heat Treat., 60, 464 – 470 (2018). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-018-0302-6
H. Y. Li, X. W. Lu, X. C. Wu, et al., “Bainitic transformation during two-step quenching and partitioning process in a medium carbon steel containing silicon,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527(23), 6255 – 6259 (2010). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.06.045
M. V. Maisuradze and M. A. Ryzhkov, “Thermal stabilization of austenite during quenching and partitioning of austenite for automotive steels,” Metallurgist, 62(3 – 4), 337 – 347 (2018). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-018-0666-2
V. C. Igwemezie and P. C. Agu, “Development of bainitic steels for engineering applications,” Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol., 3(2), 2698 – 2711 (2014). DOI: https://doi.org/10.17577/IJERTV3IS20656
A. T. Tumanov (ed.), Aviation Materials. Vol. 1. Structural Steels [in Russian], ONTI, Moscow (1975), 429 p.
M. V. Maisuradze, M. A. Ryzhkov, Yu. V. Yudin, and A. A. Kuklina, “Transformations of supercooled austenite in a promising high-strength steel grade under continuous cooling conditions,” Metal Sci. Heat Treat., 59(7 – 8), 486 – 490 (2017). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-017-0176-z
T. A. Kop, J. Sietsma, and S. Van Der Zwaag, “Dilatometric analysis of phase transformations in hypo-eutectoid steels,” J. Mater. Sci., 36, 519 – 526 (2001). DOI: 10.1023/ A:1004805402404
D. P. Koistinen and R. E. Marburger, “A general equation prescribing the extent of the austenite-martensite transformation in pure iron-carbon alloys and plain carbon steels,” Acta Metall., 7, 59 – 60 (1959). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(59)90170-1
D. V. Edmomds, K. He, F. C. Rizzo, et al., “Quenching and partitioning martensite — A novel steel heat treatment,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 438 – 440, 25 – 34 (2006). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.02.133
M. V. Maisuradze, A. A. Kuklina, D. I. Lebedev, et al., “Microstructure and mechanical properties of aircraft steel 30Kh2GSN2VM,” Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 8, 48 – 56 (2022).
J. B. Austin and R. L. Rickett, “Kinetics of the decomposition of austenite at constant temperature,” Trans. Amer. Inst. Mining Metall. Eng., 964,1– 20 (1939).
M. J. Starink, “Kinetic equations for diffusion-controlled precipitation reactions,” J. Mater. Sci., 32, 4061 – 4070 (1997). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018649823542
H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia and R. Honeycombe, Steels: Microstructure and Properties, Elsevier Ltd., Oxford (2017), 488 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 4, pp. 21 – 33, April, 2023.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Maisuradze, M.V., Ryzhkov, M.A. & Nazarova, V.V. Dilatometric Study of Structure Formation in Steel 30Kh2GSN2VM Under Quenching-Partitioning and Austempering. Met Sci Heat Treat 65, 209–220 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-023-00916-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-023-00916-z