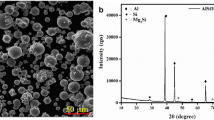
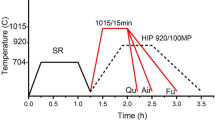
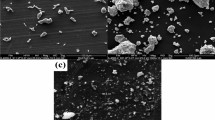
We study the microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir processed AZ91D cast magnesium alloy under various conditions of heat treatment. It is shown that, in the initial as-cast state, the structure of the alloy contained a continuously networked β-phase with an average grain size of 150 μm. The friction stir processed (FSP) specimens had an average grain size of 12 μm and smooth grain boundaries. The subsequent heat treatment of the FSP specimens at various temperatures between 150°C and 250°C led to the appearance of numerous particles of the β-phase. The FSP specimens heat-treated at 200°C had finer grains, a larger number of fine particles of the β-phase, and better mechanical properties than any other specimens.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. A. Luo, “Applications: aerospace, automotive and other structural applications of magnesium,” in: Fundamentals of Magnesium Alloy Metallurgy, Woodhead Publ., (2013), p. 266 – 316.
Y. Estrin, S. S. Nene, B. P. Kashyap, N. Prabhu, and T. Al-Samman, Mater. Lett., 173 (2016) 252 – 256.
M. K. Kulekci, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 39, 851 – 865 (2008).
A. Luo, J. Renaud, I. Nakatsugawa, and J. Plourde, JOM, 47, 28 – 31 (1995).
M. Easton, A. Beer, M. Barnett, C. Davies, G. Dunlop, Y. Durandet, S. Blacket, T. Hilditch, and P. Beggs, J. Minerals, Metals & Mater. Soc., 60, 57 – 62 (2008).
A. A. Luo and A. K. Sachdev, “Applications of magnesium alloys in automotive engineering,” in: Advances in Wrought Magnesium Alloys, Woodhead Publ. (2012), pp. 393 – 426.
S. Shrestha, A. Sturgeon, P. Shashkov, and A. Shatrov, “Improved corrosion performance of AZ91D magnesium alloy coated with the Keronite™_process,” in: Essential Readings in Magnesium Technology, Springer (2016), pp. 603 – 607.
R. S. Mishra and Z. Y. Ma, Mater. Sci. Eng. R: Reports, 50, 1 – 78 (2005).
J. D. Robson, S. Cui, and Z. W. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 527, 7299 – 7304 (2010).
F. Chai, D. Zhang,W. Zhang, and Y. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 590, 80 – 87 (2014).
D. Ni, D. Wang, A. Feng, G. Yao, and Z. Ma, Scr. Mater., 61, 568 – 571 (2009).
P. Cavaliere and P. P. De Marco, J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 184, 77 – 83 (2007).
A. H. Feng and Z. Y. Ma, Scr. Mater., 56, 397 – 400 (2007).
W. H. Loke, R. Ibrahim, and S. Lathabai, “Improving the microstructure and mechanical properties of a cast Mg – 9Al –1Zn alloy using friction stir processing,” Mater. Sci. Forum, 838 – 839, 214 – 219 (2016).
Z. Lu and D. Zhang, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of a fine-grained AZ91 magnesium alloy prepared by multipass friction stir processing,” Mater. Sci. Forum, 850, 778 – 783 (2016).
R. S. Mishra, P. S. De, and N. Kumar, “Fundamental physical metallurgy background for FSW/P,” in: Friction Stir Welding and Processing: Science and Engineering, Springer: Cham. (2014) p. 59 – 93.
R. Vaira Vignesh and R. Padmanaban, Trans. Indian Inst. Metals, 1 – 15 (2017); https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-017-1110-1.
R. Vaira Vignesh, R. Padmanaban, M. Arivarasu, S. Thirumalini, J. Gokulachandran, and R. Mutyala Sesha Satya Sai, IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng., 149, 012208 (2016).
S. Mohan Kumar, R. Pramod, M. E. Shashi Kumar, and H. K. Govindaraju, Proc. Eng., 19, 178 – 185 (2014).
M. Arivarasu, P. Roshith, R. Padmanaban, S. Thirumalini, K. V. Phani Prabhakar, and G. Padmanabham, Canad. Metallurg. Quart., 56, 232 – 244 (2017).
T. Regułaa, E. Czekaja, A. Fajkiela, K. Saja, M. Lech-Gregab, and M. Bronickic, Arch. Foundry Eng., 10, 141 – 146 (2010).
F. Vesling and T. Ryspaev, Russ. J. Non-Ferrous Met., 48, 57 – 62 (2007).
Y. Wang, G. Liu, and Z. Fan, Acta Mater., 54, 689 – 699 (2006).
J. Liao, M. Hotta, K. Kaneko, and K. Kondoh, Scr. Mater., 61, 208 – 211 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 5, pp. 46 – 52, May, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Govindaraju, M., Vignesh, R.V. & Padmanaban, R. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Friction Stir Processed AZ91D Magnesium Alloy. Met Sci Heat Treat 61, 311–317 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-019-00422-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-019-00422-1