Abstract
Background
Bardet-Biedl Syndrome (BBS) is a rare (1:13,500-1-160,000) heterogeneous congenital disorder, characterized by postaxial polydactyly, obesity, hypogonadism, rod-cone dystrophy, cognitive impairment, and renal abnormalities (renal cystic dysplasia, anatomical malformation). To date about twenty-five genes have been identified to cause BBS, which accounts for about 80% of BBS diagnosis.
Methods
In the current study, we have performed mutational screening of four Pakistani consanguineous families (A-D) with clinical manifestation of BBS by microsatellite-based genotyping and whole exome sequencing.
Results
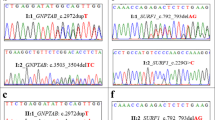
Analysis of the data revealed four variants, including a novel/unique inheritance pattern of compound heterozygous variants, p.(Ser40*) and p.(Thr259Leufs*21), in MKKS gene, novel homozygous variant, p.(Gly251Val)] in BBS7 gene and two previously reported p.(Thr259Leufs*21) in MKKS and p.(Met1Lys) in BBS5 gene. The variants were found segregated with the disorder within the families.
Conclusion
The study not only expanded mutations spectrum in the BBS genes, but this will facilitate diagnosis and genetic counselling of families carrying BBS related phenotypes in Pakistani population.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be available upon request.
References
Forsythe E, Beales PL (2013) Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 21:8–13
Putoux A, Attie-Bitach T, Martinovic J, Gubler MC (2012) Phenotypic variability of Bardet-Biedl syndrome: focusing on the kidney. Pediatr Nephrol 27:7–15
Dehani M, Zare-Abdollahi D, Bushehri A, Dehghani A, Effati J, Miratashi SAM, Khorshid HRK (2021) Identification of a Novel homozygous mutation in BBS10 gene in an iranian family with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol 13–230
Gupta N, D’Acierno M, Zona E, Capasso G, Zacchia M (2022) Bardet–Biedl syndrome: the pleiotropic role of the chaperonin-like BBS6, 10, and 12 proteins. Am J Med Genet Part C: Seminars Med Genet Vol 190(1):9–19
Wheway G, Lord J, Baralle D (2019) Splicing in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of ciliopathies. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul Mech 1862(11–12):194433
Umair M, Ahamd F, Bilal M, Asiri A, Younus M, Khan A (2019) A comprehensive review of genetic skeletal disorders reported from Pakistan: a brief commentary. Meta Gene 20:100559
Umair M, Hassan A, Jan A, Ahmad F et al (2016) Homozygous sequence variants in the FKBP10 gene underlie osteogenesis imperfecta in consanguineous families. J Hum Genet 61:207–213
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A et al (2010) The genome analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Gen Res 20:1297–1303
Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H (2010) ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucl Acid Res 38:164
Kowalski MH, Qian H, Hou Z, Rosen JD, Tapia AL, Shan Y et al (2019) Use of > 100,000 NHLBI Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine (TOPMed) Consortium whole genome sequences improves imputation quality and detection of rare variant associations in admixed african and Hispanic/Latino populations. PLOS Genet 15:e1008500
Karczewski KJ, Francioli LC, Tiao G, Cummings BB, Alföldi J, Wang Q et al (2020) The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 581:434–443
Lyles CR, Lunn MR, Obedin-Maliver J, Bibbins-Domingo K (2018) The new era of precision population health: insights for the all of us Research Program and beyond. J Transl Med 16:1–4
Abbas S, Khan H, Alam Q, Mahmood A, Umair M (2023) Genetic advances in skeletal Disorders: an overview. J Biochem Clin Genet 6:1–13
Ullah A, Umair M, Yousaf M, Khan SA, Shah K, Ahmad F, …, Ahmad W (2017) Sequence variants in four genes underlying Bardet-Biedl syndrome in consanguineous families. Mol Vis 23:482–494
Hayat A, Khan AA, Rauf A, Khan SU, Hussain S, Ullah A, Ahmad W, Shams S, Khan B (2020) A novel missense variant in the BBS7 gene underlying Bardet-Biedl syndrome in a consanguineous pakistani family. Clin Dysmorphol 29:17–23
Ullah A, Khalid M, Umair M, Khan SA, Bilal M, Khan S, Ahmad W (2018) Novel sequence variants in the MKKS gene cause Bardet-Biedl syndrome with intra- and inter-familial variable phenotypes. Congenit Anom 58:173–175
Fath MA, Mullins RF, Searby C, Nishimura DY et al (2005) Mkks-null mice have a phenotype resembling Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 14:1109–1118
Stone DL, Slavotinek A, Bouffard GG, Banerjee-Basu S, Baxevanis AD, Barr M, Biesecker LG (2000) Mutation of a gene encoding a putative chaperonin causes McKusick–Kaufman syndrome. Nat Genet 25:79–82
Huang L, Sun L, Wang Z, Li S, Chen C, Luo X, Ding X (2021) Novel compound heterozygous BBS2 and homozygous MKKS variants detected in chinese families with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome. J Ophthalmol 6751857
Dehghan R, Behnam M, Salehi M, Kelishadi R (2022) Novel mutations in the MKKS, BBS7, and ALMS1 genes in iranian children with clinically suspected Bardet-Biedl Syndrome. Case Rep Ophthalmol Med 21:6110775
Rao AR, Nazir A, Imtiaz S, Paracha SA et al (2023) Delineating the Spectrum of Genetic Variants Associated with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome in Consanguineous pakistani pedigrees. Genes 14:404
Nawaz H, Mujahid, Khan et al (2023) Biallelic variants in seven different genes Associated with clinically suspected Bardet–Biedl Syndrome. Genes 14:1113
Billingsley G, Bin J, Fieggen KJ et al (2010) Mutations in chaperonin-like BBS genes are a major contributor to disease development in a multiethnic bardet–biedl syndrome patient population. J Med Genet 47:453–463
Marion V, Stutzmann F, Gérard M et al (2012) Exome sequencing identifies mutations in LZTFL1, a BBSome and smoothened trafficking regulator, in a family with Bardet–Biedl syndrome with situs inversus and insertional polydactyly. J Med Genet 49:317–321
Zhang Q, Yu D, Seo S, Stone EM, Sheffield VC (2012) Intrinsic protein-protein interaction-mediated and chaperonin-assisted sequential assembly of stable bardet-biedl syndrome protein complex, the BBSome. J Biol Chem 287:20625–20635
Singh SK, Gui M, Koh F, Yip MC, Brown A (2020) Structure and activation mechanism of the BBSome membrane protein trafficking complex. Elife 15:9
Yuan Z, Li B, Xu M, Chang EY, Li H, Yang L et al (2017) The phenotypic variability of HK1-associated retinal dystrophy. Sci Rep 7:7051
Badano JL, Katsanis N (2002) Beyond Mendel: an evolving view of human genetic disease transmission. Nat Rev Genet 3:779–789
Klink BU, Gatsogiannis C, Hofnagel O, Wittinghofer A, Raunser S (2020) Structure of the human BBSome core complex. Elife 9:e53910
Pomeroy J, Krentz AD, Richardson JG, Berg RL, VanWormer JJ, Haws RM (2021) Bardet-Biedl syndrome: weight patterns and genetics in a rare obesity syndrome. Pediatr Obes 16:e12703
Hjortshoj TD, Gronskov K, Philp AR, Nishimura DY, Adeyemo A, Rotimi CN et al (2008) Novel mutations in BBS5 highlight the importance of this gene in non-caucasian Bardet-Biedl syndrome patients. Am J Med Genet Part A 146A:517–520
Meehan TF, Conte N, West DB, Jacobsen JO, Mason J, Warren J et al (2017) Disease model discovery from 3,328 gene knockouts by the International mouse phenotyping Consortium. Nat Genet 49:1231–1238
Khan S, Lin S, Harlalka GV, Ullah A, Shah K, Khalid S, Mehmood S, Hassan MJ, Ahmad W, Self JE, Crosby AH (2019) BBS5 and INPP5E mutations associated with ciliopathy disorders in families from Pakistan. Ann Hum Genet 83:477–482
Shao Y, An M, Shi X, Shao L (2022) Two novel variants in a Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 5 patient with severe renal phenotype. Nephrology 27:897–900
Funding
The authors (Muhammad Bilal and Abdullah) were supported by Indigenous PhD and IRSIP fellowships from Higher Education Commission (HEC), Islamabad, Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Amjad Ali, Abdullah and Muhammad Bilal collected blood samples, performed experimental work and prepared the manuscript. Emily Kathryn Mis helped in data analysis. Imran Ullah, Saquib Ali Lakhani and Wasim Ahmad designed the study, provided funds and finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
All the authors have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The research study was approved by Institutional Review Board (IRB), Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad, Pakistan under ethical committee approval number ‘IRB-QA-176’. Informed written consent was taken from participating members of families. Blood sampling from normal and affected individuals were carried out according to guidelines provided by Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, A., Abdullah, Bilal, M. et al. Sequence variants in different genes underlying Bardet-Biedl syndrome in four consanguineous families. Mol Biol Rep 50, 9963–9970 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08816-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08816-4