Abstract
Background
Helicobacter pylori infection is considered as the major risk factor for gastric adenocarcinoma. Today, the increasing emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains has drastically decreased the eradication rate of H. pylori infection. This study was aimed to investigate the inhibitory and modulatory effects of live and pasteurized Lactobacillus crispatus strain RIGLD-1 on H. pylori adhesion, invasion, and inflammatory response in AGS cell line.
Methods and results
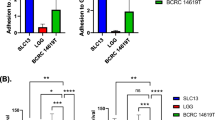
The probiotic potential and properties of L. crispatus were evaluated using several functional and safety tests. Cell viability of AGS cells exposed to varying concentrations of live and pasteurized L. crispatus was assessed by MTT assay. The adhesion and invasion abilities of H. pylori exposed to either live or pasteurized L. crispatus were examined by gentamycin protection assay. The mRNA expression of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, IL-10, and TGF-ß genes was determined by RT-qPCR from coinfected AGS cells. ELISA was used for the detection of IL-8 secretion from treated cells. Both live and pasteurized L. crispatus significantly decreased H. pylori adhesion/invasion to AGS cells. In addition, both live and pasteurized L. crispatus modulated H. pylori-induced inflammation by downregulating the mRNA expression of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α and upregulating the expression of IL-10, and TGF-ß cytokines in AGS cells. Furthermore, H. pylori-induced IL-8 production was dramatically decreased after treatment with live and pasteurized L. crispatus.
Conclusions
In conclusion, our findings demonstrated that live and pasteurized L. crispatus strain RIGLD-1 are safe, and could be suggested as a potential probiotic candidate against H. pylori colonization and inflammation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Charitos IA, D’Agostino D, Topi S, Bottalico L (2021) 40 years of Helicobacter pylori: a revolution in biomedical thought. Gastroenterol Insights 12(2):111–135. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent12020011
Fakharian F, Asgari B, Nabavi-Rad A, Sadeghi A, Soleimani N, Yadegar A et al (2022) The interplay between Helicobacter pylori and the gut microbiota: an emerging driver influencing the immune system homeostasis and gastric carcinogenesis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 1177. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.953718
Baj J, Forma A, Sitarz M, Portincasa P, Garruti G, Krasowska D et al (2020) Helicobacter pylori virulence factors—mechanisms of bacterial pathogenicity in the gastric microenvironment. Cells 10(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010027
Atrisco-Morales J, Ramírez M, Castañón-Sánchez CA, Román-Román A, Román-Fernández IV, Martínez-Carrillo DN et al (2022) In peripheral blood mononuclear cells Helicobacter pylori induces the secretion of Soluble and Exosomal Cytokines related to carcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 23(15):8801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158801
Chongruksut W, Limpakan S, Chakrabandhu B, Ruengorn C, Nanta S (2016) Correlation of Helicobacter pylori and interleukin-8 mRNA expression in high risk gastric cancer population prediction. World J Gastrointest Oncol 8(2):215. https://doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v8.i2.215
Wasielica-Berger J, Gugnacki P, Mlynarczyk M, Rogalski P, Swidnicka-Siergiejko A, Antonowicz S et al (2022) Comparative effectiveness of various eradication regimens for Helicobacter pylori infection in the northeastern region of Poland. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(11):6921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116921
Suzuki S, Gotoda T, Kusano C, Ikehara H, Ichijima R, Ohyauchi M et al (2020) Seven-day vonoprazan and low-dose amoxicillin dual therapy as first-line Helicobacter pylori treatment: a multicentre randomised trial in Japan. Gut 69(6):1019–1026. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319954
Farzi N, Yadegar A, Sadeghi A, Asadzadeh Aghdaei H, Marian Smith S, Raymond J et al (2019) High prevalence of antibiotic resistance in iranian Helicobacter pylori isolates: importance of functional and mutational analysis of resistance genes and virulence genotyping. JCM 8(11):2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8112004
Cremonini F, Di Caro S, Covino M, Armuzzi A, Gabrielli M, Santarelli L et al (2002) Effect of different probiotic preparations on anti-Helicobacter pylori therapy-related side effects: a parallel group, triple blind, placebo-controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol 97(11):2744–2749. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.07063.x
Binda S, Hill C, Johansen E, Obis D, Pot B, Sanders ME et al (2020) Criteria to qualify microorganisms as “probiotic” in foods and dietary supplements. Fron Microbiol 1662. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01662
Das TK, Pradhan S, Chakrabarti S, Mondal KC, Ghosh K (2022) Current status of probiotic and related health benefits. Appl Food Biotechnol 100185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.afres.2022.100185
Keshavarz Azizi Raftar S, Ashrafian F, Yadegar A, Lari A, Moradi HR, Shahriary A et al (2021) The protective effects of live and pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila and its extracellular vesicles against HFD/CCl4-induced liver Injury. Microbiol Spectr 9(2):e00484–e00421. https://doi.org/10.1128/Spectrum.00484-21
Lin C-C, Huang W-C, Su C-H, Lin W-D, Wu W-T, Yu B et al (2020) Effects of multi-strain probiotics on immune responses and metabolic balance in Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Nutrients 12(8):2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082476
Keikha M, Karbalaei M (2021) Probiotics as the live microscopic fighters against Helicobacter pylori gastric infections. BMC Gastroenterol 21(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-021-01977-1
Han S, Lu Y, Xie J, Fei Y, Zheng G, Wang Z et al (2021) Probiotic gastrointestinal transit and colonization after oral administration: a long journey. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:609722. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.609722
Li T, Liu Z, Zhang X, Chen X, Wang S (2019) Local probiotic Lactobacillus crispatus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii exhibit strong antifungal effects against Vulvovaginal candidiasis in a rat model. Front Microbiol 10:1033
Yao-Jong Y, Ching-Chun C, Hsiao-Bai Y, Cheng-Chan L, Bor-Shyang S (2012) Lactobacillus acidophilus ameliorates H. pylori-induced gastric inflammation by inactivating the Smad7 and NFκB pathways. BMC Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-38
Pan M, Hidalgo-Cantabrana C, Goh YJ, Sanozky-Dawes R, Barrangou R (2020) Comparative analysis of Lactobacillus gasseri and Lactobacillus crispatus isolated from human urogenital and gastrointestinal tracts. Front Microbiol 10:3146. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.03146
Yarmohammadi M, Yadegar A, Ebrahimi MT, Zali MR (2021) Effects of a potential probiotic strain Lactobacillus gasseri ATCC 33323 on Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammatory response and gene expression in coinfected gastric epithelial cells. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 13(3):751–764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-020-09721-z
Salas-Jara M, Sanhueza E, Retamal-Díaz A, González C, Urrutia H, García A (2016) Probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum UCO-979 C biofilm formation on AGS and Caco-2 cells and Helicobacter pylori inhibition. Biofouling 32(10):1245–1257. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2016.1249367
Wayne P (2020) Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: 30th informational supplement. CLSI document M100
Mousavi E, Makvandi M, Teimoori A, Ataei A, Ghafari S, Samarbaf-Zadeh A (2018) Antiviral effects of Lactobacillus crispatus against HSV-2 in mammalian cell lines. J Chin Med Assoc 81(3):262–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcma.2017.07.010
Chen Y-H, Tsai W-H, Wu H-Y, Chen C-Y, Yeh W-L, Chen Y-H et al (2019) Probiotic Lactobacillus spp. act against Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation. J Clin Med 8(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8010090
Shan X, Zhang Y, Chen H, Dong L, Wu B, Xu T, Hu J, Liu Z, Wang W, Wu L, Feng Z (2017) Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor attenuates LPS-induced inflammation and acute lung injury in rats. Oncotarget 4(16):26648. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1501177
González-Domínguez É, Domínguez-Soto Á, Nieto C, Flores-Sevilla JL, Pacheco-Blanco M, Campos-Peña V, Meraz-Ríos MA, Vega MA, Corbí ÁL, Sánchez-Torres C (2016) Atypical activin A and IL-10 production impairs human CD16 + monocyte differentiation into anti-inflammatory macrophages. J Immunol 1327–1337. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1501177
Keshavarz Azizi Raftar S, Abdollahiyan S, Azimirad M, Yadegar A, Vaziri F, Moshiri A, Siadat SD, Zali MR (2021) The anti-fibrotic effects of heat-killed Akkermansia muciniphila MucT on liver fibrosis markers and activation of hepatic stellate cells. Probiotic Antimicrob Proteins 776–787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-020-09733-9
Chiang T-H, Chang W-J, Chen SL-S, Yen AM-F, Fann JC-Y, Chiu SY-H et al (2021) Mass eradication of Helicobacter pylori to reduce gastric cancer incidence and mortality: a long-term cohort study on Matsu Islands. Gut 70(2):243–250. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322200
Yang Y-J, Chuang C-C, Yang H-B, Lu C-C, Sheu B-S (2012) Lactobacillus acidophilus ameliorates H. pylori-induced gastric inflammation by inactivating the Smad7 and NFκB pathways. BMC Microbiol 12(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-38
Ji J, Yang H (2020) Using probiotics as supplementation for Helicobacter pylori antibiotic therapy. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031136
Sgouras D, Maragkoudakis P, Petraki K, Martinez-Gonzalez B, Eriotou E, Michopoulos S, et a (2004) In vitro and in vivo inhibition of Helicobacter pylori by Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(1):518–526. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.1.518-526.2004
Raheem A, Liang L, Zhang G, Cui S (2021) Modulatory effects of probiotics during pathogenic infections with emphasis on immune regulation. Front Immunol 12:616713. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.616713
Liévin-Le Moal V, Servin AL (2014) Anti-infective activities of Lactobacillus strains in the human intestinal microbiota: from probiotics to gastrointestinal anti-infectious biotherapeutic agents. Clin Microbiol rev 27(2):167–199. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00080-13
Kaur H, Kaur G, Ali SA (2022) Dairy-based probiotic-fermented Functional Foods: an update on their health-promoting Properties. Fermentation 8(9):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8090425
Barros CP, Guimaraes JT, Esmerino EA, Duarte MCK, Silva MC, Silva R et al (2020) Paraprobiotics and postbiotics: concepts and potential applications in dairy products. Curr Opin Food Sci 32:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2019.12.003
Verstraelen H, Verhelst R, Claeys G, De Backer E, Temmerman M, Vaneechoutte M (2009) Longitudinal analysis of the vaginal microflora in pregnancy suggests that L. crispatus and/or L. iners are more conductive to the occurrence of abnormal vaginal microflora. BMC Microbiol 9:116. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-9-116
Wang S, Zhang M, Yu L, Tian F, Lu W, Wang G et al (2022) Evaluation of the Potential Protective Effects of Lactobacillus Strains against Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol 2022. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6432750
Wang N, Mao F-y, Huang W-w, Kong H, Shi Y, Yang Z-b et al (2019) Resistant gastric environment of Lactobacillus crispatus from stomach inhibits Helicobacter pylori colonization and attenuates gastric inflammation. Res Sq. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.2.9712/v1
Prasad J, Gill H, Smart J, Gopal PK (1998) Selection and characterisation of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains for use as probiotics. Int Dairy J 8(12):993–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-6946(99)00024-240
Ruiz L, Margolles A, Sánchez B (2013) Bile resistance mechanisms in Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Front Microbiol 4:396. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2013.00396
de Klerk N, Maudsdotter L, Gebreegziabher H, Saroj SD, Eriksson B, Eriksson OS et al (2016) Lactobacilli reduce Helicobacter pylori attachment to host gastric epithelial cells by inhibiting adhesion gene expression. Infect Immun 84(5):1526–1535. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00163-16
Jan I, Rather RA, Mushtaq I, Malik AA, Besina S, Baba AB et al (2021) Helicobacter pylori subdues Cytokine Signaling to alter mucosal inflammation via hypermethylation of suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 gene during gastric carcinogenesis. Front oncol 10:604747. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.604747
Yamada S, Kato S, Matsuhisa T, Makonkawkeyoon L, Yoshida M, Chakrabandhu T et al (2013) Predominant mucosal IL-8 mRNA expression in non-caga Thais is risk for gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 19(19):2941–2949. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i19.2941
Song H, Zhou L, Liu D, Ge L, Li Y (2019) Probiotic effect on Helicobacter pylori attachment and inhibition of inflammation in human gastric epithelial cells. Exp Ther Med 18(3):1551–1562. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7742
García A, Navarro K, Sanhueza E, Pineda S, Pastene E, Quezada M et al (2017) Characterization of Lactobacillus fermentum UCO-979 C, a probiotic strain with a potent anti-Helicobacter pylori activity. Electron J Biotechnol 25:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2016.11.008
Cristofori F, Dargenio VN, Dargenio C, Miniello VL, Barone M, Francavilla R (2021) Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of probiotics in gut inflammation: a door to the body. Front Immunol 12:178. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.578386
Shi M, Yue Y, Ma C, Dong L, Chen F (2022) Pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila ameliorate the LPS-Induced Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction via modulating AMPK and NF-κB through TLR2 in Caco-2 cells. Nutrients 14(4):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040764
Gotteland M, Brunser O, Cruchet S (2006) Systematic review: are probiotics useful in controlling gastric colonization by Helicobacter pylori? Aliment Pharmacol ther 23(8):1077–1086. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.02868.x
Plovier H, Everard A, Druart C, Depommier C, Van Hul M, Geurts L et al (2017) A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat Med 23(1):107–113. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4236
Feng C, Zhang W, Zhang T, Li B, He Q, Kwok L-Y et al (2022) Oral administration of pasteurized probiotic fermented milk alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced inflammatory bowel disease in rats. J Funct Foods 94:105140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2022.105140
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank laboratory staff of the Foodborne and Waterborne Diseases Research Center, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. We also are grateful to the staff of the Department of Microbiology and Microbial Biotechnology, Faculty of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Shahid Beheshti University, Tehran, Iran.
Funding
The study was funded by a research grant (Project No: RIGLD 1128) from the Foodborne and Waterborne Diseases Research Center, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FF performed microbiological experiments, cell culture, RT-qPCR, data analysis, and wrote the manuscript draft; AY designed the study, participated in data analysis, conceptualization, writing and editing, and project administration; AY, AS, FP and NS critically revised the manuscript. All authors read the final version of the manuscript and approved the list of authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This work does not contain any studies related with human participants or animals. The study was approved by the Institutional Ethical Review Committee of the Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran (Project No. IR.SBMU.RIGLD.REC.1399.046).
Consent for participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fakharian, F., Sadeghi, A., Pouresmaeili, F. et al. Immunomodulatory effects of live and pasteurized Lactobacillus crispatus strain RIGLD-1 on Helicobacter pylori-triggered inflammation in gastric epithelial cells in vitro. Mol Biol Rep 50, 6795–6805 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08596-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08596-x