Abstract
Background
With increased urbanization and industrialization, modern life has led to an anthropogenic impact on the biosphere. Heavy metals pollution and pollutants from black liquor (BL) have caused severe effects on environment and living organisms. Bacterial biofilm has potential to remediate heavy metals and remove BL from the environment. Hence, this study was planned to investigate the potential of microbial biofilms for the bioremediation of heavy metals and BL polluted environments.
Methods and results
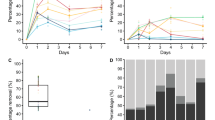
Eleven biofilm forming bacterial strains (SB1, SB2, SC1, AF1, 5A, BC-1, BC-2, BC-3, BC-4, BC-5 and BC-6) were isolated and identified upto species level via 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Biofilm strains belonging to Bacillus and Lysinibacillus sphaericus were used to remediate heavy metals (Pb, Ni, Mn, Zn, Cu, and Co). Atomic absorption spectroscopy showed significantly high (P ≤ 0.05) bioremediation potential by L. sphaericus biofilm (1462.0 ± 0.67 µgmL−1) against zinc (Zn). Similarly, Pseudomonas putida biofilm significantly (P ≤ 0.05) decolourized (65.1%) BL. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) analysis of treated heavy metals showed the shifting of major peaks (1637 & 1629–1647, 1633 & 1635–1643, and 1638–1633 cm−1) corresponding to specific amide groups due to C = O stretching.
Conclusion
The study suggested that biofilm of the microbial flora from tanneries and pulp paper effluents possesses a strong potential for heavy metals bioremediation and BL decolourization. To our knowledge, this is the first report showing promising biofilm remediation potential of bacterial flora of tanneries and pulp-paper effluent from Kasur and Sheikhupura, Punjab, Pakistan, against heavy metals and BL.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data related to article is available in manuscript.
Abbreviations
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared
- CRA:
-
Congo red assay
- BL:
-
Black liquor
- EPS:
-
Extra polysaccharide
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- rRNA:
-
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid
- OD:
-
Optical density
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
- U/µL:
-
Unit per microliter
- (cm− 1):
-
Reciprocal centimetre
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
- Rpm:
-
Revolution per minute
References
Mishra S, Huang Y, Li J, Wu X, Zhou Z, Lei Q, Bhatt P, Chen S (2022) Biofilm-mediated bioremediation is a powerful tool for the removal of environmental pollutants. Chemosphere 294:133609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133609
Jasu A, Ray RR (2021) Biofilm mediated strategies to mitigate heavy metal pollution: a critical review in metal bioremediation. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 37:102183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102183
Arora NK, Chauhan R (2021) Heavy metal toxicity and sustainable interventions for their decontamination. Springer, pp 1–3
Briffa J, Sinagra E, Blundell R (2020) Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 6:e04691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04691
Mishra S, Chen S, Saratale GD, Saratale RG, Romanholo Ferreira LF, Bilal M, Bharagava RN (2021) Reduction of hexavalent chromium by Microbacterium paraoxydans isolated from tannery wastewater and characterization of its reduced products. Water Process Eng 39:101748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101748
Hussain M, Liaqat I, Bukhari SM, Khan FS, Adalat R, Salman Shafique M, Azam SM, Ali A, Khalid M, Shahid Z, Iqbal MJ, Slahuddin EA (2023) The impact of cow dung augmentation on soil restoration and bio-accumulation of metals (Lead and Cadmium) in Pheretima posthuma (Annelida: Clitellata). Braz J Bio 83:e247562
Abinandan S, Subashchandrabose SR, Venkateswarlu K, Megharaj M (2018) Microalgae–bacteria biofilms: a sustainable synergistic approach in remediation of acid mine drainage. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:1131–1144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8693-7
Bhatt P, Bhatt K, Huang Y, Li J, Wu S, Chen S (2022) Biofilm formation in xenobiotic-degrading microorganisms. Crit Rev Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2022.2106417
Mohapatra RK, Behera SS, Patra JK, Thatoi H, Parhi PK (2020) Potential application of bacterial biofilm for bioremediation of toxic heavy metals and dye-contaminated environments. New and future developments in microbial biotechnology and bioengineering: microbial biofilms. Elsevier, pp 267–281
Meliani A, Bensoltane A (2016) Biofilm-mediated heavy metals bioremediation in PGPR Pseudomonas. J Bioremediat Biodegrad 7:2. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000370
Sandhya M, Huang Y, Li J, Wu X, Zhou Z, Lei Q, Bhatt P, Chen S (2022) Biofilm-mediated bioremediation is a powerful tool for the removal of environmental pollutants. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133609
Uzor OS, Okpokwasili GC, Agbagwa EO (2020) Bacteriological and physicochemical profiles of soils in selected oil-contaminated sites in Yorla, Ogoni Land. Microbiol Res J Int 30:104–117. https://doi.org/10.9734/MRJI/2020/v30i830256
Liaqat I, Mirza SA, Iqbal R, Ali NM, Saleem G, Majid S, Shahid M (2018) Flagellar motility plays important role in Biofilm formation of Bacillus cereus and Yersinia enterocolitica. Pak J Pharm Sci 31:2047
Rathore DS, Sheikh MA, Gohel SD, Singh SP (2021) Genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity of the Nocardiopsis alba strains of seawater. Curr Microbiol 78:1377–1387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-021-02420-0
Liaqat I, Muhammad N, Mubin M, Arshad N, Iftikhar T, Sajjad S, Rashid F (2022) Antibacterial and larvicidal activity of ethyl acetate extract of actinomycetes from soil samples. Pak J Zool. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.pjz/20200526130518
Grujić S, Vasić S, Radojević I, Čomić L, Ostojić A (2017) Comparison of the Rhodotorula mucilaginosa biofilm and planktonic culture on heavy metal susceptibility and removal potential. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3259-y
Dutta S, Hossain M, Hassan M, Anwar M (2014) Decolourization of two industrial dyes by bacteria from paper and pulp mill effluents. Int Res J Biol Sci 3:51–55
Bhatt P, Bhandari G, Bhatt K, Maithani D, Mishra S, Gangola S, Bhatt R, Huang Y, Chen S (2021) Plasmid-mediated catabolism for the removal of xenobiotics from the environment. J Hazard Mater 420:126618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126618
Araújo AR, Araújo AC, Reis RL, Pires RA (2021) Vescalagin and castalagin present bactericidal activity toward methicillin-resistant bacteria. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 7:1022–1030. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c01698?ref=pdf
Nazli F, Jamil M, Hussain A, Hussain T (2020) Exopolysaccharides and indole-3-acetic acid producing Bacillus safensis strain FN13 potential candidate for phytostabilization of heavy metals. Environ Monit Assess 192:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08715-2
O’Toole GA (2016) Classic spotlight: how the gram stain works. J Bacteriol 198:3128. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00726-16
Hussain T, Roohi A, Munir S, Ahmed I, Khan J, Edel-Hermann V, Yong Kim K, Anees M (2013) Biochemical characterization and identification of bacterial strains isolated from drinking water sources of Kohat, Pakistan. Afr J Microbiol Res 7:1579–1590. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR12.2204
Ilesanmi OI, Adekunle AE, Omolaiye JA, Olorode EM, Ogunkanmi AL (2020) Isolation, optimization and molecular characterization of lipase producing bacteria from contaminated soil. Sci Afr 8:e00279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00279
Parker AD (2021) A Comparison of metagenomic sequencing using targeted 16S and whole genome shotgun NGS on microbial DNA samples. Montclair State University
Raag Harshavardhan P, Subbaiyan A, Vasavi U, Thirumoorthy P, Periyasamy M, Jesteena Johney J, Ragunathan R, Pichaipillai S, Velusamy S, Balamoorthy D (2022) Enhanced biodegradation of battery-contaminated soil using Bacillus sp. (mz959824) and its phytotoxicity study. Adv Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5697465
Idris MG, Umaru D, Aliyu AN, Musa IH (2022) Atomic absorption spectroscopy analysis of heavy metals in water at Daura Gypsum Mining Site, Yobe State, Nigeria. J Found Appli Phy 8:227–234
Marzan LW, Hossain M, Mina SA, Akter Y, Chowdhury AMA (2017) Isolation and biochemical characterization of heavy-metal resistant bacteria from tannery effluent in Chittagong city, Bangladesh: bioremediation viewpoint. Egypt J Aquat Res 43:65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2016.11.002
Kalaimurugan D, Balamuralikrishnan B, Durairaj K, Vasudhevan P, Shivakumar M, Kaul T, Chang S, Ravindran B, Venkatesan S (2020) Isolation and characterization of heavy-metal-resistant bacteria and their applications in environmental bioremediation. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:1455–1462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02563-5
Sedlakova-Kadukova J, Kopcakova A, Gresakova L, Godany A, Pristas P (2019) Bioaccumulation and biosorption of zinc by a novel Streptomyces K11 strain isolated from highly alkaline aluminium brown mud disposal site. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 167:204–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.123
Forough S, Kumarss A, Azam H, Mohaddeseh L (2022) Application of Saccharomyces cerevisiae isolated from industrial effluent for zinc biosorption and zinc-enriched SCP production for human and animal. Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1590/fst.82021
Mishra S, Lin Z, Pang S, Zhang Y, Bhatt P, Chen S (2021) Biosurfactant is a powerful tool for the bioremediation of heavy metals from contaminated soils. J Hazard Mater 418:126253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126253
Chellaiah ER (2018) Cadmium (heavy metals) bioremediation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a minireview. Appl Water Sci 8:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0796-5
Fathollahi A, Khasteganan N, Coupe SJ, Newman AP (2021) A meta-analysis of metal biosorption by suspended bacteria from three phyla. Chemosphere 268:129290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129290
Tan H, Wang C, Zeng G, Luo Y, Li H, Xu H (2020) Bioreduction and biosorption of Cr (VI) by a novel Bacillus sp. CRB-B1 strain. J Hazard Mater 386:121628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121628
Princy S, Prabagaran SR (2022) Reduction of Cr (VI) by Bacillus species isolated from tannery effluent contaminated sites of Tamil Nadu, India. Mater Today Proc 48:148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.850
Huang F, Wang ZH, Cai YX, Chen SH, Tian JH, Cai KZ (2018) Heavy metal bioaccumulation and cation release by growing Bacillus cereus RC-1 under culture conditions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 157:216–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.077
Kumar A, Chandra R (2021) Biodegradation and toxicity reduction of pulp paper mill wastewater by isolated laccase producing Bacillus cereus AKRC03. Chem Eng Technol 4:100193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2021.100193
Wang Y, Chen X, Wu B, Ma T, Jiang H, Mi Y, Jiang C, Zang H, Zhao X, Li C (2022) Potential and mechanism for bioremediation of papermaking black liquor by a psychrotrophic lignin-degrading bacterium, Arthrobacter sp. C2. J Hazard Mater 439:129534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129534
Raj A, Kumar S, Haq I, Singh SK (2014) Bioremediation and toxicity reduction in pulp and paper mill effluent by newly isolated ligninolytic Paenibacillus sp. Ecol Eng 71:355–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.07.002
Arusha PN, Kiran RK, Shanti GG, Arun SK (2016) Optimization of cellulase production for Bacillus sp. and Pseudomonas sp. soil isolates. Afr J Microbiol Res 10:410–419. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR2016.7954
An X, Zhong B, Chen G, An W, Xia X, Li H, Lai F, Zhang Q (2021) Evaluation of bioremediation and detoxification potentiality for papermaking black liquor by a new isolated thermophilic and alkali-tolerant Serratia sp. AXJ-M. J Hazard Mater 406:124285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124285
Shabbir S, Faheem M, Ali N, Kerr PG, Wu Y (2017) Periphyton biofilms: a novel and natural biological system for the effective removal of sulphonated azo dye methyl orange by synergistic mechanism. Chemosphere 167:236–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.002
Díaz A, Marrero J, Cabrera G, Coto O, Gómez J (2022) Biosorption of nickel, cobalt, zinc and copper ions by Serratia marcescens strain 16 in mono and multimetallic systems. Biodegradation 33:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-021-09964-9
Rodríguez-Sánchez V, Guzmán-Moreno J, Rodríguez-González V, Flores-de la Torre JA, Ramírez-Santoyo RM, Vidales-Rodríguez LE (2017) Biosorption of lead phosphates by lead-tolerant bacteria as a mechanism for lead immobilization. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2314-6
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: [IL]; Methodology [NM]; Formal analysis and investigation: [IL, CA, MA, CR, MNA]; Writing—original draft preparation: [IL, NM] Writing—review and editing: [IL, UH, SA, MM, MNA]; Supervision: [IL].
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
All authors declare no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Consent for publications
Not applicable.
Research involving human and animals participants
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liaqat, I., Muhammad, N., Ara, C. et al. Bioremediation of heavy metals polluted environment and decolourization of black liquor using microbial biofilms. Mol Biol Rep 50, 3985–3997 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08334-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08334-3