Abstract
Background
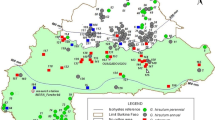
The semi-domesticated Brazilian perennial cotton (Gossypium spp.) germplasm is considered a source of variability for creating modern upland cotton varieties. Here we used Inter-simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) markers to detect intra and interspecific genetic polymorphism in Gossypium hirsutum L. r. marie-galante and Gossypium barbadense L. and to use molecular data to assessing genetic diversity and molecular discrimination of these species.
Methods and results
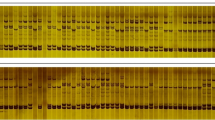
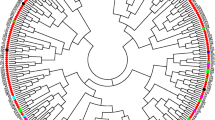
The sets contained 12 G. barbadense genotypes and 16 G. hirsutum genotypes from a Brazilian collection. The 11 ISSR primers were used for genotyping yielded 101 bands (polymorphism = 47.5%) and were classified as moderately informative (PIC = 0.304). The ISSR markers exposed a greater diversity in G. hirsutum (P = 24.72%; HE =0.071 and I = 0.111) as compared to G. barbadense (P = 17.98%, HE = 0.043 and I = 0.070). The AMOVA analysis showed that 89.47% of the genetic variation was partitioned within species which is supported by Nei’s genetic differentiation (Gst = 0.598) and gene flow (Nm = 0.338), suggesting that strong reproductive barriers between species. The UPGMA Cluster Analysis, Principal Coordinate Analysis and Bayesian Model-Based Structural Analysis divided the 28 genotypes into two main clades consistent with the taxonomical delimitation.
Conclusion
The ISSR marker system offers a new approach to determining molecular differences between two cotton species (G. hirsutum L. r. marie-galante and G. barbadense L.). This study can expand the molecular marker resources for the identification and improvement of our knowledge about the genetic diversity and relationships between perennial cotton genotypes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borém A, Freire EC, Penna JCV, Barroso PAV (2003) Considerations about cotton gene escape in Brazil: a review. Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol 3:315–332
Almeida VCD, Hoffmann LV, Yokomizo GKI, Costa JND, Giband M, Barroso PAV (2009) In situ and genetic characterization of Gossypium barbadense populations from the States of Pará and Amapá, Brazil. Pesquisa Agropecuaria Brasileira 44:719–725
Menezes IPP, Hoffmann LV, Lima TH, Silva AR, Lucena VS, Barroso PAV (2017) Genetic diversity of arboreal cotton populations of the brazilian semiarid: a remnant primary gene pool for cotton cultivars. Genet Mol Res 16:gmr16039659
Menezes IPP, Hoffmann LV, Silva JO, Barroso PAV (2018) Distribuição do modo de ocorrência no local de raças de algodoeiro Semiárido Brasileiro. Multi-Sci J 1:39–47
Hoffmann LV, Cardoso KCM, Rocha ASNC, Oliveira AID, Abreu AG, Pereira CCO, Malafaia G, Menezes IPP (2018) Genetic diversity of Gossypium barbadense from the central brazilian Amazon. Acta Amazonica 48:1–9
Rodrigues JIS, Carvalho LP, Farias FJC (2016) Comparison of wild accessions of Gossypium barbadense L. from Peru and Brazil via microsatellite markers. Bioscience J 32:1352–1363
Vasconcelos UAA, Cavalcanti JJV, Farias FJC, Vasconcelos WS, Santos RC (2018) Diallel analysis in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) for water stress tolerance. Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol 18:24–30
Albrana (2022) Algodões brasileiros nativos e naturalizados. CNPA Embrapa. http://www.cnpa.embrapa.br/albrana. Accessed 10 January 2022
Sabev P, Valkova N, Todorovska EG (2020) Molecular markers and their application in cotton breeding: progress and future perspectives. Bulgarian J Agricultural Sci 26:816–828
Marwal A, Gaur RK (2020) Molecular markers: tool for genetic analysis. In: Verma A, Singh A (eds) Animal biotechnology. Academic Press Elsevier, Cambridge, pp 353–372
Gemmill CE, Grierson ER (2021) Inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR), microsatellite-primed genomic profiling using universal primers. Mol Plant Taxonomy 2222:249–262
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) Isolatin of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3321–3323
McDermott JM, McDonald BA (1993) Gene flow in plant pathosystem. Annu Rev Phytopathol 31:353–373
Yeh FC, Boyle TYZ, Xiyan JM (1999) POPGENE: microsoft window-based freeware for population genetic analysis version 1.32. University of Alberta, Edmonton
Rohlf FJ (2000) NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 2.1. Exeter Software, New York
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Version 4.3. Palaeontol Electron 4:1–9
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2007) ARLEQUIN: a software for population data analysis. Version 3.1. University de Geneva, Geneva
Earl DA, Von-Holdt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing structure output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4:359–361
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software structure: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Khan MMH, Rafii MY, Ramlee SI, Jusoh M, Al Mamun M, Halidu J (2021) DNA fingerprinting, fixation-index (Fst), and admixture mapping of selected Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea [L.] Verdc.) Accessions using ISSR markers system. Sci Rep 1:1–23
Bilwal BB, Vadodariya KV, Rajkumar BK, Upadhyay AK, Lahane GR (2017) Genetic diversity of parents using RAPD, ISSR and SSR molecular markers in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Bull Environ Pharmacol Life Sci 6:51–57
Ghuge SB, Mehetre SS, Chimote VP, Pawar BD, Naik RM (2018) Molecular characterization of cotton genotypes using SSR, ISSR and RAPD markers in relation to fiber quality traits. J Cotton Res 32:1–12
Nimbal S, Kuldeep J, Pawan K (2020) Molecular diversity analysis among elite genotypes of american cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Pantnagar J Res 18:1–4
Tajik-Khaveh Z, Iranbakhsh A, Vafaie-Tabar M, Ebadi M (2020) Study of genetic variation among some Gossypium spp. genotypes available in Iran using ISSR molecular marker. Rostaniha 21:264–277
Şahin CB, İşler N, Rustamova V (2020) Characterization of some cotton varieties using ISSR markers. KSU J Agric Nat 23:108–116
Hocaoglu-Ozyigit A, Ucar B, Altay V, Ozyigit II (2020) Genetic diversity and phylogenetic analyses of turkish cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) lines using ISSR markers and chloroplast trnL-F regions. J Nat Fibers 17:1–14
Sevindik E, Çayir EM, Emrebaş T, Filiz E (2021) Assessment of phylogenetic relationships of some worldwide-cultivated cotton genotypes (Gossypium hirsutum L.) by using ISSR and RAPD markers. Biologica Nyssana 12:131–139
Mint Abdelaziz S, Medraoui L, Alami M, Pakhrou O, Makkaoui M, Boukhary AOMS, Filali–Maltouf A (2020) Inter simple sequence repeat markers to assess genetic diversity of the desert date (Balanites aegyptiaca Del.) for Sahelian ecosystem restoration. Sci Rep 10:14948
Noormohammadi Z, Taghavi E, Foroutanb M, Sheidai M, Alishah O (2013) Structure analysis of genetic diversity in tetraploid and diploid cotton genotypes. Int J Plant Anim Sci 3:79–90
Farahani F, Sheidai M, Koohdar F (2018) Impressão digital genética de cultivares de algodão por marcadores moleculares ISSR. Genetika 50:627–634
Hinze LL, Fang DD, Gore MA, Scheffler BE, Yu JZ, Frelichowski J, Percy RG (2015) Molecular characterization of the Gossypium diversity reference set of the US national cotton germplasm collection. Theor Appl Genet 128:313–327
Hinze LL, Gazave E, Gore MA, Fang DD, Scheffler BE, Yu JZ, Jones DC, Frelichowski J, Percy RG (2016) Genetic diversity of the two commercial tetraploid cotton species in the Gossypium diversity reference set. J Hered 107:274–286
Menezes I, Barroso P, Hoffmann L, Lucena V, Giband M (2010) Genetic diversity of mocó cotton (Gossypium hirsutum race marie-galante) from the northeast of Brazil: implications for conservation. Bot Botanique 88:765–773
Pereira GS, Sousa RL, Araújo RL, Hoffmann LV, Silva EF, Barroso PAV (2012) Selective fertilization in interspecific crosses of allotetraploid species. Botany 90:159–166
Embrapa (2001) BRS 200 marrom: cultivar de algodão de fibra colorida. Embrapa Algodão. https://www.embrapa.br/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/276144/brs-200-marrom--cultivar-de-algodao-de-fibra-colorida. Accessed 20 Jan 2022
Araújo FS, Arriel NHC, Medeiros EP, Lima LM, Souza MA, Andrade AP, Bruno RLA (2022) Multi-level characterization of perennial cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. race marie-galante Hutch.) Populations from the northeastern Brazil to the breeding and conservation of this germplasm. Genetic Resource Crop Evolution 69:1219–1227
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (Brazil) for funding scholarships (Finance Code 001); Brazilian Agricultural Research Agency (Embrapa Cotton) for providing the germplasm and institutional support; and Kyvia Pontes for statistic support and her help in creating the artwork (the figures).
Funding
This study was funded by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior, Brazil (Finance Code 001) and Brazilian Agricultural Research Agency (Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fernando dos Santos Araújo, Riselane de Lucena Alcântara Bruno, Nair Helena Castro Arriel and Everaldo Paulo de Medeiros contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Liziane Maria de Lima and Mayara Andrade de Souza. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Fernando dos Santos Araújo, Riselane de Lucena Alcântara Bruno, Nair Helena Castro Arriel and Alberício Pereira de Andrade. Francival Cardoso Felix, Richeliel Albert Rodrigues Silva and Karialane da Silva Belarmino commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Araújo, F.d.S., Bruno, R.d.L.A., Arriel, N.H.C. et al. Genetic polymorphism detection in brazilian perennial cottons (Gossypium spp.) using an ISSR marker system and its application for molecular interspecific differentiation. Mol Biol Rep 50, 3001–3009 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08165-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08165-8