Abstract
Background
The elevated drug efflux by ABC transports has been considered the primary mechanism of drug resistance in cancer. Recently, non-coding RNAs, such as pseudogenes, have been proposed to be involved in transporter-mediated drug resistance in cancer. The human genome has 22 ABC transporter pseudogenes. Among these pseudogenes, ABCC6P1 has co-expression with its ancestral gene in various human tissues. In the present study, we assessed the effect of ABCC6P1 pseudogene overexpression on ABCC6 expression and drug resistance.
Methods and results
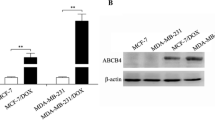
The ABCC6P1 was transfected into the MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. In ABCC6P1-overexpressing cells, the ABCC6 level significantly increased. The results of cell treatment with doxorubicin, 5-fluorouracil, cisplatin, and paclitaxel showed that the survival of ABCC6P1-overexpressing cells was higher than normal cells. Furthermore, uptake of doxorubicin was lower in ABCC6P1-overexpressing cells.
Conclusions
In conclusion, our results show that overexpression of ABCC6P1 pseudogene induces the drug resistance phenotype, possibly through activation of the ancestral gene.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE (2021) Jemal a cancer statistics. CA 71(1):7–33
Kern R, Correa SC, Scandolara TB, Carla da Silva J, Pires BR, Panis C (2020) Current advances in the diagnosis and personalized treatment of breast cancer: lessons from tumor biology. Pers Med 17(05):399–420
Bortolozzi R, Luraghi A, Mattiuzzo E, Sacchetti A, Silvani A, Viola G (2020) Ecdysteroid derivatives that reverse p-glycoprotein-mediated drug resistance. J Nat Prod 83(8):2434–2446
Liu X (2019) ABC family transporters. Adv Exp Med Biol 1141:13–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7647-4_2
Amawi H, Sim HM, Tiwari AK, Ambudkar SV, Shukla S (2019) ABC transporter-mediated multidrug-resistant cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 1141:549–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7647-4_12
Zheng Y, Ma L, Sun Q (2021) Clinically-relevant abc transporter for anti-cancer drug resistance. Front Pharmacol 12:705
He J, Fortunati E, Liu D-X, Li Y (2021) Pleiotropic roles of abc transporters in breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci 22(6):3199
Golalipour M, Mahjoubi F, Sanati MH, Alimoghaddam K (2007) Gene dosage is not responsible for the upregulation of MRP1 gene expression in adult leukemia patients. Arch Med Res 38(3):297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2006.10.016
Mahjoubi F, Golalipour M, Ghavamzadeh A, Alimoghaddam K (2008) Expression of MRP1 gene in acute leukemia. Sao Paulo Med J 126(3):172–179. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1516-31802008000300007
Wang Y, Wang Y, Qin Z (2021) The role of non-coding RNAs in ABC transporters regulation and their clinical implications of multidrug resistance in cancer. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 17(3):291–306. https://doi.org/10.1080/17425255.2021.1887139
Piehler AP, Hellum M, Wenzel JJ, Kaminski E, Haug KB, Kierulf P, Kaminski WE (2008) The human ABC transporter pseudogene family: Evidence for transcription and gene-pseudogene interference. BMC Genom 9:165. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-165
Xiao Y, Jiao C, Lin Y, Chen M, Zhang J, Wang J, Zhang Z (2017) lncRNA UCA1 contributes to imatinib resistance by acting as a cerna against miR-16 in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. DNA Cell Biol 36(1):18–25. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2016.3533
An Q, Zhou L, Xu N (2018) Long noncoding RNA FOXD2-AS1 accelerates the gemcitabine-resistance of bladder cancer by sponging miR-143. Biomed pharmacotherap 103:415–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.138
Kong J, Qiu Y, Li Y, Zhang H, Wang W (2019) TGF-β1 elevates P-gp and BCRP in hepatocellular carcinoma through HOTAIR/miR-145 axis. Biopharm Drug Dispos 40(2):70–80. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdd.2172
Han Z, Shi L (2018) Long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 modulates methotrexate resistance in osteosarcoma via miR-200c/ABCB1 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495(1):947–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.121
Wang R, Zhang T, Yang Z, Jiang C, Seng J (2018) Long non-coding RNA FTH1P3 activates paclitaxel resistance in breast cancer through miR-206/ABCB1. J Cell Mol 22(9):4068–4075. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13679
Gao R, Fang C, Xu J, Tan H, Li P, Ma L (2019) LncRNA CACS15 contributes to oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer by positively regulating ABCC1 through sponging miR-145. Arch Biochem Biophys 663:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2019.01.005
Hu H, Yang L, Li L, Zeng C (2018) Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 modulates oxaliplatin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma through miR-7-5p/ ABCC1 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503(4):2400–2406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.168
Huang H, Chen J, Ding CM, Jin X, Jia ZM, Peng J (2018) LncRNA NR2F1-AS1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma oxaliplatin resistance by targeting ABCC1 via miR-363. J Cell Mol 22(6):3238–3245. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13605
Ma Y, Fan B, Ren Z, Liu B, Wang Y (2019) Long noncoding RNA DANCR contributes to docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer through targeting the miR-34a-5p/JAG1 pathway. Onco Targets Ther 12:5485–5497. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s197009
Song L, Zhou Z, Gan Y, Li P, Xu Y, Zhang Z, Luo F, Xu J, Zhou Q, Dai F (2019) Long noncoding RNA OIP5-AS1 causes cisplatin resistance in osteosarcoma through inducing the LPAATβ/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by sponging the miR-340-5p. J Cell Biochem 120(6):9656–9666. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28244
Zhang CL, Zhu KP, Ma XL (2017) Antisense lncRNA FOXC2-AS1 promotes doxorubicin resistance in osteosarcoma by increasing the expression of FOXC2. Cancer Lett 396:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.03.018
Fang Z, Chen W, Yuan Z, Liu X, Jiang H (2018) LncRNA-MALAT1 contributes to the cisplatin-resistance of lung cancer by upregulating MRP1 and MDR1 via STAT3 activation. Biomed pharmacother 101:536–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.130
Jiang B, Li Y, Qu X, Zhu H, Tan Y, Fan Q, Jiang Y, Liao M, Wu X (2018) Long noncoding RNA cancer susceptibility candidate 9 promotes doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer by binding to enhancer of zeste homolog 2. Int J Mol Med 42(5):2801–2810. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3812
Wang Y, Zhang D, Wu K, Zhao Q, Nie Y, Fan D (2014) Long noncoding RNA MRUL promotes ABCB1 expression in multidrug-resistant gastric cancer cell sublines. Mol Cell Biol 34(17):3182–3193. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.01580-13
Abdollahzadeh R, Daraei A (2019) Competing endogenous RNA (ceRN) cross talk and language in ceRNA regulatory networks: a new look at hallmarks of breast cancer. J Cell Physiol 234(7):10080–10100
Cheetham SW, Faulkner GJ (2020) Overcoming challenges and dogmas to understand the functions of pseudogenes. Nature Rev Genet. 21(3):191–201. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-019-0196-1
An Y, Furber KL, Ji S (2017) Pseudogenes regulate parental gene expression via ceRNA network. J Cell Mol Med 21(1):185–192. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12952
Kringen MK, Stormo C, Grimholt RM, Berg JP, Piehler AP (2012) Copy number variations of the ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCC6 gene and its pseudogenes. BMC Res Notes 5:425. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-5-425
Belinsky MG, Chen ZS, Shchaveleva I, Zeng H, Kruh GD (2002) Characterization of the drug resistance and transport properties of multidrug resistance protein 6 (MRP6, ABCC6). Can Res 62(21):6172–6177
Bisaccia F, Koshal P, Abruzzese V, Castiglione Morelli MA (2021) Structural and functional characterization of the abcc6 transporter in hepatic cells: role on PXE, cancer therapy and drug resistance. Int J Mol. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062858
Kringen MK, Stormo C, Berg JP, Terry SF, Vocke CM, Rizvi S, Hendig D, Piehler AP (2015) Copy number variation in the ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCC6 gene and ABCC6 pseudogenes in patients with pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Mol Genet Genomic Med 3(3):233–237. https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.137
Cai L, Lumsden A, Guenther UP, Neldner SA, Zäch S, Knoblauch H, Ramesar R, Hohl D, Callen DF, Neldner KH, Lindpaintner K, Richards RI, Struk B (2001) A novel Q378X mutation exists in the transmembrane transporter protein ABCC6 and its pseudogene: implications for mutation analysis in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. J Mol Med 79(9):536–546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001090100275
Guan Y, Li Y, Yang QB, Yu J, Qiao H (2021) LncRNA ABCC6P1 promotes proliferation and migration of papillary thyroid cancer cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Annals transl med 9(8):664. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-21-505
Ferrari P, Scatena C, Ghilli M et al (2022) Molecular mechanisms, biomarkers and emerging therapies for chemotherapy resistant TNBC. Int J Mol Sci 23:1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031665
Stewart PA, Luks J, Roycik MD et al (2013) Differentially expressed transcripts and dysregulated signaling pathways and networks in African American breast cancer. PLoS ONE 8:e82460. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082460
Soleymani Abyaneh H, Gupta N, Radziwon-Balicka A et al (2017) STAT3 but not HIF-1α is important in mediating hypoxia-induced chemoresistance in MDA-MB-231, a triple negative breast cancer cell line. Cancers 9:E137. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9100137
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Saeed Mohammadi for his helpful technical advice.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Golestan University of Medical Sciences (Grant Number 110477).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Research Ethics Committee at Golestan University of Medical Science (Ethics Number: IR.GOUMS.REC.1398.166).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemi, M., Golalipour, M. ABCC6P1 pseudogene induces ABCC6 upregulation and multidrug resistance in breast cancer. Mol Biol Rep 49, 9633–9639 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07872-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07872-6