Abstract
Background
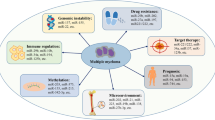
Circular RNA (circRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA that has recently attracted the attention of researchers. Multiple myeloma (MM) is a hematological malignancy with a dismal prognosis that indicates a pressing need for better treatment alternatives, particularly in terms of biological indicators. According to recent research findings, the presence of circRNA is also closely related to the incidence and progression of malignant hemopathy. There have been, however, only a few investigations of circRNA in MM.
Material and methods
This review will be on the biological properties and functions of circRNA in MM and a discussion of the clinical utility of circRNA in the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of MM.
Conclusions
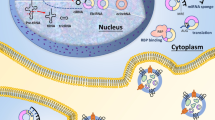
CircRNA is involved in gene transcription, translation, and epigenetic modification as well as the regulation of cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis, and hence, promotes or inhibits the occurrence and progression of MM. Therefore, circRNA holds promise as a potential future MM biomarker.
Graphical abstract


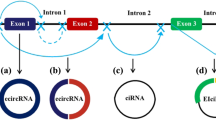
source of ciRNA by avoiding lariat debranching

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Abbreviations
- BTZ:
-
Bortezomib
- CDK2:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2
- ceRNA:
-
Competing endogenous RNA
- ciRNA:
-
Intronic circRNA
- CIN:
-
Chromosomal instability
- circRNA:
-
Circular RNA
- ecircRNA:
-
Exonic circRNA
- eicircRNA:
-
Exonic-intronic circRNA
- exo-circRNA:
-
Exosomal circular RNA
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- HD:
-
Healthy donor
- lncRNA:
-
Long noncoding RNA
- MM:
-
Multiple myeloma
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- MRE:
-
MiRNA response element
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- ncRNA:
-
Non-coding RNA
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PFS:
-
Progression-free surviva
- PN:
-
Peripheral neuropathy
- RBP:
-
RNA-binding protein
- snRNP:
-
Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein
- TLR4:
-
Toll-like receptor-4
- YAP:
-
Yes-associated protein
- YY1:
-
Yin Yang 1
References
Moreau P et al (2013) Multiple myeloma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 24(Suppl 6):vi133-7
Rajkumar SV et al (2014) International Myeloma Working Group updated criteria for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol 15(12):e538-48
Derman BA, Kosuri S, Jakubowiak A (2022) Knowing the unknowns in high risk multiple myeloma. Blood Rev 51:100887
Li J et al (2020) Roles of noncoding RNAs in drug resistance in multiple myeloma. J Cell Physiol 235(11):7681–7695
Lin Z et al (2020) The role of circular RNAs in hematological malignancies. Genomics 112(6):4000–4008
Tang X et al (2021) Review on circular RNAs and new insights into their roles in cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 19:910–928
Yang Q et al (2019) Emerging roles of noncoding RNAs in multiple myeloma: A review. J Cell Physiol 234(6):7957–7969
Zhang P, Wu W, Chen Q, Chen M (2019) Non-Coding RNAs and their Integrated Networks. J Integr Bioinform 16(3):20190027
Kapranov P et al (2007) RNA Maps Reveal New RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science 316(5830):1484–1488
Li L-J et al (2017) Translation of noncoding RNAs: focus on lncRNAs, pri-miRNAs, and circRNAs. Exp Cell Res 361(1):1–8
Han B, Chao J, Yao H (2018) Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: From the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol Ther 187:31–44
Cocquerelle C et al (1993) Mis-splicing yields circular RNA molecules. Faseb j 7(1):155–60
Jeck WR et al (2013) Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. Rna 19(2):141–57
Kristensen LS et al (2019) The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet 20(11):675–691
Memczak S et al (2013) Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 495(7441):333–8
Hansen TB et al (2013) Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495(7441):384–8
Meng S et al (2019) Epigenetics in neurodevelopment: emerging role of circular RNA. Front Cell Neurosci 13:327
Cortés-López M et al (2018) Global accumulation of circRNAs during aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Genomics 19(1):8
Liang D et al (2017) The output of protein-coding genes shifts to circular RNAs when the pre-mRNA processing machinery is limiting. Mol Cell 68(5):940-954.e3
Zhang XO et al (2016) Diverse alternative back-splicing and alternative splicing landscape of circular RNAs. Genome Res 26(9):1277–87
Liu M et al (2019) Circbank: a comprehensive database for circRNA with standard nomenclature. RNA Biol 16(7):899–905
Lyu D, Huang S (2017) The emerging role and clinical implication of human exonic circular RNA. RNA Biol 14(8):1000–1006
Capel B et al (1993) Circular transcripts of the testis-determining gene Sry in adult mouse testis. Cell 73(5):1019–30
Hansen TB et al (2011) miRNA-dependent gene silencing involving Ago2-mediated cleavage of a circular antisense RNA. Embo j 30(21):4414–22
Hanan M, Soreq H, Kadener S (2017) CircRNAs in the brain. RNA Biol 14(8):1028–1034
Rybak-Wolf A et al (2015) Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant, conserved, and dynamically expressed. Mol Cell 58(5):870–85
Nair AA et al (2016) Circular RNAs and their associations with breast cancer subtypes. Oncotarget 7(49):80967–80979
Taheri M et al (2021) The role and clinical potentials of circular RNAs in prostate cancer. Front Oncol 11:781414
Werfel S et al (2016) Characterization of circular RNAs in human, mouse and rat hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol 98:103–7
Ruan H et al (2019) Comprehensive characterization of circular RNAs in ~ 1000 human cancer cell lines. Genome Med 11(1):55
Akhter R (2018) Circular RNA and alzheimer’s disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 1087:239–243
Huang Y et al (2021) Emerging important roles of circRNAs in human cancer and other diseases. Genes Dis 8(4):412–423
Li Z et al (2015) Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22(3):256–64
Wu TY et al (2014) MiR-19a is correlated with prognosis and apoptosis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating TIMP-2 expression. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(1):56–63
Zhang Y et al (2013) Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell 51(6):792–806
Lasda E, Parker R (2014) Circular RNAs: diversity of form and function. RNA 20(12):1829–42
Kelly S et al (2015) Exon skipping is correlated with exon circularization. J Mol Biol 427(15):2414–2417
Li Y et al (2017) CircHIPK3 sponges miR-558 to suppress heparanase expression in bladder cancer cells. EMBO Rep 18(9):1646–1659
Ashwal-Fluss R et al (2014) circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 56(1):55–66
Wang H et al (2022) Review: RNA-based diagnostic markers discovery and therapeutic targets development in cancer. Pharmacol Ther 234:108123
Piwecka M et al (2017) Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aam8526
Salzman J et al (2013) Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet 9(9):e1003777
Chen LL (2016) The biogenesis and emerging roles of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17(4):205–11
Shao Y, Chen Y (2016) Roles of circular RNAs in neurologic disease. Front Mol Neurosci 9:25
Li RC et al (2018) CiRS-7 promotes growth and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via regulation of miR-7/HOXB13. Cell Death Dis 9(8):838
Yang F et al (2019) Cis-acting circ-CTNNB1 promotes β-Catenin signaling and cancer progression via DDX3-mediated transactivation of YY1. Cancer Res 79(3):557–571
Du WW et al (2016) Foxo3 circular RNA retards cell cycle progression via forming ternary complexes with p21 and CDK2. Nucleic Acids Res 44(6):2846–58
Abdelmohsen K et al (2017) Identification of HuR target circular RNAs uncovers suppression of PABPN1 translation by CircPABPN1. RNA Biol 14(3):361–369
Liang WC et al (2019) Translation of the circular RNA circβ-catenin promotes liver cancer cell growth through activation of the Wnt pathway. Genome Biol 20(1):84
Xia X et al (2019) A novel tumor suppressor protein encoded by circular AKT3 RNA inhibits glioblastoma tumorigenicity by competing with active phosphoinositide-dependent Kinase-1. Mol Cancer 18(1):131
Zhang M et al (2018) A novel protein encoded by the circular form of the SHPRH gene suppresses glioma tumorigenesis. Oncogene 37(13):1805–1814
Yang Y et al (2018) Novel role of FBXW7 circular RNA in repressing glioma tumorigenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst 110(3):304–15
Legnini I et al (2017) Circ-ZNF609 is a circular RNA that can be translated and functions in myogenesis. Mol Cell 66(1):22-37.e9
Yang Y et al (2017) Extensive translation of circular RNAs driven by N(6)-methyladenosine. Cell Res 27(5):626–641
Qin M, Wei G, Sun X (2018) Circ-UBR5: an exonic circular RNA and novel small nuclear RNA involved in RNA splicing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503(2):1027–1034
Chen LL (2020) The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21(8):475–490
Lin H et al (2021) Novel insights into exosomal circular RNAs: redefining intercellular communication in cancer biology. Clin Transl Med 11(12):e636
Liu L, Zhang F, Li J (2021) CircRNA circ_0001821 predicts an unfavorable prognosis and promotes the proliferation of multiple myeloma. Hematology 26(1):716–723
Zhou F et al (2021) Circular RNA protein tyrosine kinase 2 promotes cell proliferation, migration and suppresses apoptosis via activating microRNA-638 mediated MEK/ERK, WNT/β-Catenin signaling pathways in multiple myeloma. Front Oncol 11:648189
Tang X et al (2021) BUB1B and circBUB1B_544aa aggravate multiple myeloma malignancy through evoking chromosomal instability. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6(1):361
Tian FQ et al (2021) Inhibition of hsa_circ_0003489 shifts balance from autophagy to apoptosis and sensitizes multiple myeloma cells to bortezomib via miR-874–3p/HDAC1 axis. J Gene Med 23(9):e3329
Chen F et al (2020) Effect of the up-regulation of circular RNA Hsa_circ_0069767 derived from C-KIT on the biological behavior of multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Manag Res 12:11321–11331
White ME, Fenger JM, Carson WE 3rd (2019) Emerging roles of and therapeutic strategies targeting BRD4 in cancer. Cell Immunol 337:48–53
Wang Y et al (2020) Circ_0007841 promotes the progression of multiple myeloma through targeting miR-338–3p/BRD4 signaling cascade. Cancer Cell Int 20:383
Song Y et al (2020) Hsa_Circ_0007841 enhances multiple myeloma chemotherapy resistance through upregulating ABCG2. Technol Cancer Res Treat 19:1533033820928371
Gao M et al (2019) hsa_circ_0007841: a novel potential biomarker and drug resistance for multiple myeloma. Front Oncol 9:1261
Wang Y et al (2020) Depletion of circ_0007841 inhibits multiple myeloma development and BTZ resistance via miR-129–5p/JAG1 axis. Cell Cycle 19(23):3289–3302
Yu S et al (2021) circRNA circ-MYBL2 is a novel tumor suppressor and potential biomarker in multiple myeloma. Hum Cell 34(1):219–228
Liu F et al (2021) Upregulation of circ_0000142 promotes multiple myeloma progression by adsorbing miR-610 and upregulating AKT3 expression. J Biochem 169(3):327–336
Chen F et al (2020) Circular RNA circ-CDYL sponges miR-1180 to elevate yes-associated protein in multiple myeloma. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 245(11):925–932
Houshmand M et al (2018) Long non-coding RNA PVT1 as a novel candidate for targeted therapy in hematologic malignancies. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 98:54–64
Ghetti M et al (2020) Linear and circular PVT1 in hematological malignancies and immune response: two faces of the same coin. Mol Cancer 19(1):69
Yang M et al (2018) Down-regulation of miR-203a by lncRNA PVT1 in multiple myeloma promotes cell proliferation. Arch Med Sci 14(6):1333–1339
Gu C et al (2021) CHEK1 and circCHEK1_246aa evoke chromosomal instability and induce bone lesion formation in multiple myeloma. Mol Cancer 20(1):84
Liu D, Wang Y, Li H, Peng S, Tan H, Huang Z. Circular RNA circ-CCT3 promotes bortezomib resistance in multiple myeloma via modulating miR-223-3p/BRD4 axis. Anticancer Drugs 33(1):e145–e154
Fang W et al (2021) CircRERE confers the resistance of multiple myeloma to bortezomib depending on the regulation of CD47 by exerting the sponge effect on miR-152–3p. J Bone Oncol 30:100381
Liu J et al (2020) CircRNA ITCH increases bortezomib sensitivity through regulating the miR-615–3p/PRKCD axis in multiple myeloma. Life Sci 262:118506
Bach D-H, Lee SK, Sood AK (2019) Circular RNAs in cancer. Mol ther. Nucleic acids 16:118–129
Lin H et al (2021) A machine learning-based model to predict survival after transarterial chemoembolization for BCLC stage B hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol 11:608260
Xiang Y, Xu X, Yang B, Wu Z, Jiang R, Xie Y. Circular RNA_0000190 and its target microRNA-767-5p are dysregulated, and they are related to risk stratification as well as prognosis in multiple myeloma patients. Ir J Med Sci 191(2):671–679
Liu X et al (2020) hsa_circRNA_101237: a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target for multiple myeloma. Cancer Manag Res 12:2109–2118
Sun R et al (2021) Exosomal circRNA as a novel potential therapeutic target for multiple myeloma-related myocardial damage. Cancer Cell Int 21(1):311
Zhang Y et al (2021) Exosomal circRNA as a novel potential therapeutic target for multiple myeloma-related peripheral neuropathy. Cell Signal 78:109872
Luo Y, Gui R (2020) Circulating exosomal CircMYC is associated with recurrence and bortezomib resistance in patients with multiple myeloma. Turk J Haematol 37(4):248–262
Feng Y et al (2019) CircRNA circ_0000190 inhibits the progression of multiple myeloma through modulating miR-767–5p/MAPK4 pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):54
Zhou F et al (2020) Comprehensive profiling of circular RNA expressions reveals potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in multiple myeloma. BMC Cancer 20(1):40
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China 82170198, 81870164, 81372543, and 81170500 to JD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Du, J. CircRNAs: novel therapeutic targets in multiple myeloma. Mol Biol Rep 49, 10667–10676 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07668-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07668-8