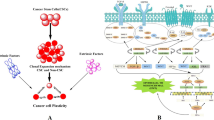
Abstract
Hippo signaling pathway is an evolutionarily conserved network that regulates organ size growth and tissue regeneration. Hippo signaling dysfunction results in uncontrolled cell proliferation and influences cell differentiation. Aberrant Hippo pathway signaling is implicated in cancer progression, by promoting cell proliferation, cancer stem cell properties, chemoresistance and metastatic capacity. Epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) is also well known to be implicated in carcinogenesis. Loss of cell polarity, disruption of cell–cell junctions and cytoskeletal remodeling are essential during EMT. At the same time, signals related to intercellular contact, cell-extracellular matrix contact, polarity and mechanotransduction are included in the list of regulatory inputs into Hippo pathway. Therefore, the emerging association between Hippo pathway and EMT in cancer is not surprising. Recent studies have begun to unravel the mechanisms of interaction between Hippo signaling pathway and EMT. In this review, we describe the existing evidence of cross talk between Hippo signaling pathway key molecules and the process of EMT, with emphasis on the role of Hippo—EMT interplay in cancer.

(created with BioRender.com)

(created with BioRender.com)

(created with BioRender.com)
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAPG:
-
Gelsolin-like actin-capping protein
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- CSC:
-
Scancer stem cells
- EMT:
-
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HIF1A:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
- LATS1/2:
-
Large tumor suppressor 1/2 kinases
- MOB1A/B:
-
MOB kinase activator 1A/B
- MSTs:
-
Mammalian sterile 20-like kinases
- NA:
-
NEDD8-activating enzyme
- OSCC:
-
Oral squamous cell carcinoma
- SAV1:
-
Salvador homolog 1
- TAZ:
-
Transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif
- TEAD:
-
TEA domain family
- WWC:
-
WW-and-C2-domain-containing proteins
- YAP:
-
Yes-associated protein
References
Zygulska AL, Krzemieniecki K, Pierzchalski P (2017) Hippo pathway—brief overview of its relevance in cancer. J Physiol Pharmacol 68(3):311–335
Wang Y, Xu X, Maglic D, Dill MT, Mojumdar K, Ng PK, Jeong KJ, Tsang YH, Moreno D, Bhavana VH, Peng X, Ge Z, Chen H, Li J, Chen Z, Zhang H, Han L, Du D, Creighton CJ, Mills GB (2018) Comprehensive molecular characterization of the Hippo signaling pathway in cancer. Cell Rep 25(5):1304-1317.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.001
Lian I, Kim J, Okazawa H, Zhao J, Zhao B, Yu J, Chinnaiyan A, Israel MA, Goldstein LS, Abujarour R, Ding S, Guan KL (2010) The role of YAP transcription coactivator in regulating stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Genes Dev 24(11):1106–1118. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1903310
Morice S, Danieau G, Rédini F, Brounais-Le-Royer B, Verrecchia F (2020) Hippo/YAP signaling pathway: a promising therapeutic target in bone paediatric cancers? Cancers (Basel) 12(3):645. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12030645
Kalluri R, Weinberg RA (2009) The basics of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. J Clin Investig 119(6):1420–1428. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI39104
Zanconato F, Cordenonsi M, Piccolo S (2016) YAP/TAZ at the roots of cancer. Cancer Cell 29(6):783–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.05.005
Overholtzer M, Zhang J, Smolen GA, Muir B, Li W, Sgroi DC, Deng CX, Brugge JS, Haber DA (2006) Transforming properties of YAP, a candidate oncogene on the chromosome 11q22 amplicon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(33):12405–12410. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605579103
Lei QY, Zhang H, Zhao B, Zha ZY, Bai F, Pei XH, Zhao S, Xiong Y, Guan KL (2008) TAZ promotes cell proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition and is inhibited by the hippo pathway. Mol Cell Biol 28(7):2426–2436. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01874-07
Chen N, Han X, Bai X, Yin B, Wang Y (2020) LASP1 induces colorectal cancer proliferation and invasiveness through Hippo signaling and nanog mediated EMT. Am J Transl Res 12(10):6490–6500
Ling HH, Kuo CC, Lin BX, Huang YH, Lin CW (2017) Elevation of YAP promotes the epithelial–mesenchymal transition and tumor aggressiveness in colorectal cancer. Exp Cell Res 350(1):218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.11.024
Feldker N, Ferrazzi F, Schuhwerk H, Widholz SA, Guenther K, Frisch I, Jakob K, Kleemann J, Riegel D, Bönisch U, Lukassen S, Eccles RL, Schmidl C, Stemmler MP, Brabletz T, Brabletz S (2020) Genome-wide cooperation of EMT transcription factor ZEB1 with YAP and AP-1 in breast cancer. EMBO J 39(17):e103209. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2019103209
Han Q, Kremerskothen J, Lin X, Zhang X, Rong X, Zhang D, Wang E (2018) WWC3 inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition of lung cancer by activating Hippo-YAP signaling. Onco Targets Ther 11:2581–2591. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S162387
Lee KY, Kuo TC, Chou CM, Hsu WJ, Lee WC, Dai JZ, Wu SM, Lin CW (2020) Upregulation of CD109 promotes the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness properties of lung adenocarcinomas via activation of the Hippo-YAP signaling. Cells 10(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010028
Liu M, Zhang Y, Yang J, Zhan H, Zhou Z, Jiang Y, Shi X, Fan X, Zhang J, Luo W, Fung KA, Xu C, Bronze MS, Houchen CW, Li M (2021) Zinc-dependent regulation of ZEB1 and YAP1 coactivation promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition plasticity and metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology S0016–5085(21):00025–00031. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.12.077
Moon JY, Ediriweera MK, Ryu JY, Kim HY, Cho SK (2021) Catechol enhances chemo- and radio-sensitivity by targeting AMPK/Hippo signaling in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep 45(3):1133–1141. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2021.7924
Segrelles C, Paramio JM, Lorz C (2018) The transcriptional co-activator YAP: a new player in head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol 86:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2018.08.020
Wang X, Zhao Y, Lu Q, Fei X, Lu C, Li C, Chen H (2020) MiR-34a-5p inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting LEF1 and inactivation of the Hippo-YAP1/TAZ signaling pathway. J Cancer 11(10):3072–3081. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.39861
Wen X, Wan J, He Q, Wang M, Li S, Jiang M, Qian Z, Liu B, Lu W, Wang K, Gao K, Wan X (2020) p190A inactivating mutations cause aberrant RhoA activation and promote malignant transformation via the Hippo-YAP pathway in endometrial cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):81. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-0170-6
Malgundkar SH, Burney I, Al Moundhri M, Al Kalbani M, Lakhtakia R, Okamoto A, Tamimi Y (2020) FAT4 silencing promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and invasion via regulation of YAP and β-catenin activity in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 20(1):374. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-06900-7
Yu S, Zhang Y, Li Q, Zhang Z, Zhao G, Xu J (2019) CLDN6 promotes tumor progression through the YAP1-snail1 axis in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis 10(12):949. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-2168-y
Zhao W, Dong QF, Li LW, Yan ZF, Huo JL, Chen XY, Yang X, Li PQ, Fei Z, Zhen HN (2021) Blockage of glioma cell survival by truncated TEAD-binding domain of YAP. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147(6):1713–1723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03577-8
Lu X, Yang C, Hu Y, Xu J, Shi C, Rao J, Yu W, Cheng F (2021) Upregulation of miR-1254 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via inactivation of the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway by decreasing PAX5. J Cancer 12(3):771–789. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.49680
Cordenonsi M, Zanconato F, Azzolin L, Forcato M, Rosato A, Frasson C, Inui M, Montagner M, Parenti AR, Poletti A, Daidone MG, Dupont S, Basso G, Bicciato S, Piccolo S (2011) The Hippo transducer TAZ confers cancer stem cell-related traits on breast cancer cells. Cell 147(4):759–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.048
Tiffon C, Giraud J, Molina-Castro SE, Peru S, Seeneevassen L, Sifré E, Staedel C, Bessède E, Dubus P, Mégraud F, Lehours P, Martin OCB, Varon C (2020) TAZ controls Helicobacter pylori-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like invasive and tumorigenic properties. Cells 9(6):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061462
Lin BY, Wen JL, Zheng C, Lin LZ, Chen CZ, Qu JM (2020) Eva-1 homolog a promotes papillary thyroid cancer progression and epithelial–mesenchymal transition via the Hippo signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med 24(22):13070–13080. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15909
Lin L, Wen J, Lin B, Chen H, Bhandari A, Qi Y, Zheng D, Wang O (2021) Phospholipase C Delta 3 inhibits apoptosis and promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of thyroid cancer cells via Hippo pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 53(4):481–491. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmab016
Li W, Dong S, Wei W, Wang G, Zhang A, Pu P, Jia Z (2016) The role of transcriptional coactivator TAZ in gliomas. Oncotarget 7(50):82686–82699. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12625
Janse van Rensburg HJ, Yang X (2016) The roles of the Hippo pathway in cancer metastasis. Cell Signal 28(11):1761–1772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.08.004
Molina-Castro SE, Tiffon C, Giraud J, Boeuf H, Sifre E, Giese A, Belleannée G, Lehours P, Bessède E, Mégraud F, Dubus P, Staedel C, Varon C (2020) The Hippo kinase LATS2 controls Helicobacter pylori-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition and intestinal metaplasia in gastric mucosa. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 9(2):257–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.10.007
Li N, Feng Y, Hu Y, He C, Xie C, Ouyang Y, Artim SC, Huang D, Zhu Y, Luo Z, Ge Z, Lu N (2018) Helicobacter pylori CagA promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition in gastric carcinogenesis via triggering oncogenic YAP pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):280. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0962-5
Debaugnies M, Sánchez-Danés A, Rorive S, Raphaël M, Liagre M, Parent MA, Brisebarre A, Salmon I, Blanpain C (2018) YAP and TAZ are essential for basal and squamous cell carcinoma initiation. EMBO Rep 19(7):e45809. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201845809
Shao DD, Xue W, Krall EB, Bhutkar A, Piccioni F, Wang X, Schinzel AC, Sood S, Rosenbluh J, Kim JW, Zwang Y, Roberts TM, Root DE, Jacks T, Hahn WC (2014) KRAS and YAP1 converge to regulate EMT and tumor survival. Cell 158(1):171–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.004
Lehmann W, Mossmann D, Kleemann J, Mock K, Meisinger C, Brummer T, Herr R, Brabletz S, Stemmler MP, Brabletz T (2016) ZEB1 turns into a transcriptional activator by interacting with YAP1 in aggressive cancer types. Nat Commun 7:10498. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10498
Wang L, Li B, Zhang L, Li Q, He Z, Zhang X, Huang X, Xu Z, Xia Y, Zhang Q, Li Q, Xu J, Sun G, Xu Z (2019) miR-664a-3p functions as an oncogene by targeting Hippo pathway in the development of gastric cancer. Cell Prolif 52(3):e12567. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12567
Ansari D, Ohlsson H, Althini C, Bauden M, Zhou Q, Hu D, Andersson R (2019) The Hippo signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res 39(7):3317–3321. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.13474
Xu J, Fang X, Long L, Wang S, Qian S, Lyu J (2021) HMGA2 promotes breast cancer metastasis by modulating Hippo-YAP signaling pathway. Cancer Biol Ther 22(1):5–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2020.1832429
Tang Y, Feinberg T, Keller ET, Li XY, Weiss SJ (2016) Snail/slug binding interactions with YAP/TAZ control skeletal stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Nat Cell Biol 18(9):917–929. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3394
Tang Y, Weiss SJ (2017) Snail/Slug-YAP/TAZ complexes cooperatively regulate mesenchymal stem cell function and bone formation. Cell Cycle 16(5):399–405. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2017.1280643
Mendonsa AM, Na TY, Gumbiner BM (2018) E-cadherin in contact inhibition and cancer. Oncogene 37(35):4769–4780. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0304-2
Ouyang H, Luong P, Frödin M, Hansen SH (2020) p190A RhoGAP induces CDH1 expression and cooperates with E-cadherin to activate LATS kinases and suppress tumor cell growth. Oncogene 39(33):5570–5587. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-1385-2
Kim NG, Koh E, Chen X, Gumbiner BM (2011) E-cadherin mediates contact inhibition of proliferation through Hippo signaling-pathway components. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(29):11930–11935. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1103345108
Matarrese P, Vona R, Ascione B, Paggi MG, Mileo AM (2021) Physical interaction between HPV16E7 and the actin-binding protein gelsolin regulates epithelial–mesenchymal transition via HIPPO-YAP axis. Cancers (Basel) 13(2):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13020353
Zhaojie L, Yuchen L, Miao C, Yacun C, Shayi W, Anbang H, Xinhui L, Meng Z, Peipei W, Hongbing M, Feng W, Zhiming C, Xinyuan G (2019) Gelsolin-like actin-capping protein has prognostic value and promotes tumorigenesis and epithelial–mesenchymal transition via the Hippo signaling pathway in human bladder cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol 11:1758835919841235. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758835919841235
Zhao W, Wang M, Cai M, Zhang C, Qiu Y, Wang X, Zhang T, Zhou H, Wang J, Zhao W, Shao R (2021) Transcriptional co-activators YAP/TAZ: potential therapeutic targets for metastatic breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 133:110956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110956
Zhu Q, Le Scolan E, Jahchan N, Ji X, Xu A, Luo K (2016) SnoN antagonizes the Hippo kinase complex to promote TAZ signaling during breast carcinogenesis. Dev Cell 37(5):399–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2016.05.002
Nozaki M, Yabuta N, Fukuzawa M, Mukai S, Okamoto A, Sasakura T, Fukushima K, Naito Y, Longmore GD, Nojima H (2019) LATS1/2 kinases trigger self-renewal of cancer stem cells in aggressive oral cancer. Oncotarget 10(10):1014–1030. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.26583
Li HL, Li QY, Jin MJ, Lu CF, Mu ZY, Xu WY, Song J, Zhang Y, Zhang SY (2021) A review: hippo signaling pathway promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by regulating target gene expression. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147(6):1569–1585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03604-8
Yin L, Li W, Xu A, Shi H, Wang K, Yang H, Wang R, Peng B (2020) SH3BGRL2 inhibits growth and metastasis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma via activating hippo/TEAD1-Twist1 pathway. EBioMedicine 51:102596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.12.005
Yu M, Chen Y, Li X, Yang R, Zhang L, Huangfu L, Zheng N, Zhao X, Lv L, Hong Y, Liang H, Shan H (2018) YAP1 contributes to NSCLC invasion and migration by promoting slug transcription via the transcription co-factor TEAD. Cell Death Dis 9(5):464. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0515-z
Cheng D, Jin L, Chen Y, Xi X, Guo Y (2020) YAP promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition by upregulating slug expression in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 13(4):701–710
Zhou H, Li G, Huang S, Feng Y, Zhou A (2019) SOX9 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition via the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway in gastric carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett 18(1):599–608. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10387
Li Z, Wang Y, Zhu Y, Yuan C, Wang D, Zhang W, Qi B, Qiu J, Song X, Ye J, Wu H, Jiang H, Liu L, Zhang Y, Song LN, Yang J, Cheng J (2015) The Hippo transducer TAZ promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell maintenance in oral cancer. Mol Oncol 9(6):1091–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2015.01.007
Wei H, Xu Z, Liu F, Wang F, Wang X, Sun X, Li J (2017) Hypoxia induces oncogene yes-associated protein 1 nuclear translocation to promote pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma invasion via epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Tumour Biol 39(5):1010428317691684. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317691684
Ben Q, An W, Sun Y, Qian A, Liu J, Zou D, Yuan Y (2020) A nicotine-induced positive feedback loop between HIF1A and YAP1 contributes to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39(1):181. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-020-01689-6
Tang X, Sun Y, Wan G, Sun J, Sun J, Pan C (2019) Knockdown of YAP inhibits growth in Hep-2 laryngeal cancer cells via epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. BMC Cancer 19(1):654. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5832-9
Zhan T, Zhu Q, Han Z, Tan J, Liu M, Liu W, Chen W, Chen X, Chen X, Deng J, Tian X, Huang X (2020) miR-455-3p functions as a tumor suppressor by restraining Wnt/β-catenin signaling via TAZ in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Manag Res 12:1483–1492. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S235794
Wang Y, Liu J, Ying X, Lin PC, Zhou BP (2016) Twist-mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition promotes breast tumor cell invasion via inhibition of Hippo pathway. Sci Rep 6:24606. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24606
Wang Y, Liao R, Chen X, Ying X, Chen G, Li M, Dong C (2020) Twist-mediated PAR1 induction is required for breast cancer progression and metastasis by inhibiting Hippo pathway. Cell Death Dis 11(7):520. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2725-4
Qiu B, Wei W, Zhu J, Fu G, Lu D (2018) EMT induced by loss of LKB1 promotes migration and invasion of liver cancer cells through ZEB1-induced YAP signaling. Oncol Lett 16(5):6465–6471. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9445
Lüönd F, Sugiyama N, Bill R, Bornes L, Hager C, Tang F, Santacroce N, Beisel C, Ivanek R, Bürglin T, Tiede S, van Rheenen J, Christofori G (2021) Distinct contributions of partial and full EMT to breast cancer malignancy. Dev Cell 56(23):3203-3221.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2021.11.006
Park J, Kim DH, Shah SR, Kim HN, Kshitiz KP, Quiñones-Hinojosa A, Levchenko A (2019) Switch-like enhancement of epithelial–mesenchymal transition by YAP through feedback regulation of WT1 and Rho-family GTPases. Nat Commun 10(1):2797. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10729-5
Selth LA, Das R, Townley SL, Coutinho I, Hanson AR, Centenera MM, Stylianou N, Sweeney K, Soekmadji C, Jovanovic L, Nelson CC, Zoubeidi A, Butler LM, Goodall GJ, Hollier BG, Gregory PA, Tilley WD (2017) A ZEB1-miR-375-YAP1 pathway regulates epithelial plasticity in prostate cancer. Oncogene 36(1):24–34. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.185
Fan K, Zebisch A, Horny K, Schrama D, Becker JC (2020) Highly expressed miR-375 is not an intracellular oncogene in merkel cell polyomavirus-associated merkel cell carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 12(3):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12030529
Zeng SHG, Xie JH, Zeng QY, Dai SHH, Wang Y, Wan XM, Liu JCH (2021) lncRNA PVT1 promotes metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through EZH2-mediated activation of Hippo/NOTCH1 signaling pathways. Cell J 23(1):21–31. https://doi.org/10.22074/cellj.2021.7010
Zhang H, Lang TY, Zou DL, Zhou L, Lou M, Liu JS, Li YZ, Ding DY, Li YC, Zhang N, Zheng XD, Zeng XH, Zhou Q, Li L (2019) miR-520b Promotes breast cancer stemness through Hippo/YAP signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther 12:11691–11700. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S236607
Gao Y, Yi J, Zhang K, Bai F, Feng B, Wang R, Chu X, Chen L, Song H (2017) Downregulation of MiR-31 stimulates expression of LATS2 via the hippo pathway and promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36(1):161. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0622-1
Han LL, Yin XR, Zhang SQ (2018) miR-103 promotes the metastasis and EMT of hepatocellular carcinoma by directly inhibiting LATS2. Int J Oncol 53(6):2433–2444. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4580
Tang L, Zhou L, Wu S, Shi X, Jiang G, Niu S, Ding D (2019) miR-125a-5p inhibits colorectal cancer cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition, invasion and migration by targeting TAZ. Onco Targets Ther 12:3481–3489. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S191247
Cao Y, Shen T, Zhang C, Zhang QH, Zhang ZQ (2019) MiR-125a-5p inhibits EMT of ovarian cancer cells by regulating TAZ/EGFR signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(19):8249–8256. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201910_19134
Shen S, Huang K, Wu Y, Ma Y, Wang J, Qin F, Ma J (2017) A miR-135b-TAZ positive feedback loop promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and tumorigenesis in osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett 407:32–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.08.005
Yang Y, Wang J (2020) Inhibition of MiR-10b restrains the migration and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of lung cells by targeting LATS2 via TAZ pathway. Med Sci Monit 26:e920275. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.920275
Zhang KJ, Hu Y, Luo N, Li X, Chen FY, Yuan JQ, Guo L (2020) miR-574-5p attenuates proliferation, migration and EMT in triple-negative breast cancer cells by targeting BCL11A and SOX2 to inhibit the SKIL/TAZ/CTGF axis. Int J Oncol 56(5):1240–1251. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2020.4995
Gan L, Yang Y, Li Q, Feng Y, Liu T, Guo W (2018) Epigenetic regulation of cancer progression by EZH2: from biological insights to therapeutic potential. Biomark Res 6:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40364-018-0122-2
Liu X, Li C, Zhang R, Xiao W, Niu X, Ye X, Li Z, Guo Y, Tan J, Li Y (2018) The EZH2- H3K27me3-DNMT1 complex orchestrates epigenetic silencing of the wwc1 gene, a Hippo/YAP pathway upstream effector, in breast cancer epithelial cells. Cell Signal 51:243–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.08.011
Hu Q, Li C, Wang S, Li Y, Wen B, Zhang Y, Liang K, Yao J, Ye Y, Hsiao H, Nguyen TK, Park PK, Egranov SD, Hawke DH, Marks JR, Han L, Hung MC, Zhang B, Lin C, Yang L (2019) LncRNAs-directed PTEN enzymatic switch governs epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Cell Res 29(4):286–304. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0134-3
Zhang H, Liu CY, Zha ZY, Zhao B, Yao J, Zhao S, Xiong Y, Lei QY, Guan KL (2009) TEAD transcription factors mediate the function of TAZ in cell growth and epithelial–mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 284(20):13355–13362. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M900843200
Yu T, Song J, Zhou H, Wu T, Liang Z, Du P, Liu CY, Wang G, Cui L, Liu Y (2021) Nuclear TEAD4 with SIX1 overexpression is an independent prognostic marker in the stage I-III colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res 13:1581–1589. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S260790
Zhang W, Li J, Wu Y, Ge H, Song Y, Wang D, Yuan H, Jiang H, Wang Y, Cheng J (2018) TEAD4 overexpression promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition and associates with aggressiveness and adverse prognosis in head neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int 18:178. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-018-0675-z
Joo JS, Cho SY, Rou WS, Kim JS, Kang SH, Lee ES, Moon HS, Kim SH, Sung JK, Kwon IS, Eun HS, Lee BS (2020) TEAD2 as a novel prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 43(6):1785–1796. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2020.7578
Gao H, Teng C, Huang W, Peng J, Wang C (2015) SOX2 promotes the epithelial to mesenchymal transition of esophageal squamous cells by modulating slug expression through the activation of STAT3/HIF-α signaling. Int J Mol Sci 16(9):21643–21657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160921643
Huh HD, Kim DH, Jeong HS, Park HW (2019) Regulation of TEAD transcription factors in cancer biology. Cells 8(6):600. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060600
Höffken V, Hermann A, Pavenstädt H, Kremerskothen J (2021) WWC proteins: important regulators of Hippo signaling in cancer. Cancers (Basel) 13(2):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13020306
Mussell AL, Denson KE, Shen H, Chen Y, Yang N, Frangou C, Zhang J (2018) Loss of KIBRA function activates EGFR signaling by inducing AREG. Oncotarget 9(52):29975–29984. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.25724
Zhang Y, Yan S, Chen J, Gan C, Chen D, Li Y, Wen J, Kremerskothen J, Chen S, Zhang J, Cao Y (2017) WWC2 is an independent prognostic factor and prevents invasion via Hippo signalling in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med 21(12):3718–3729. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13281
Wang C, Yin W, Liu H (2020) MicroRNA-10a promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness maintenance of pancreatic cancer stem cells via upregulating the Hippo signaling pathway through WWC2 inhibition. J Cell Biochem 121(11):4505–4521. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29716
Yuan B, Yang J, Gu H, Ma C (2020) Down-regulation of LINC00460 represses metastasis of colorectal cancer via WWC2. Dig Dis Sci 65(2):442–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-05801-5
Nagashima S, Bao Y, Hata Y (2017) The Hippo pathway as drug targets in cancer therapy and regenerative medicine. Curr Drug Targets 18(4):447–454. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389450117666160112115641
Wu J, Zhao Z, Zhang H, Kong F, Jiang H, Huang K, Zheng H (2018) LATS1 inhibits metastasis and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 11(4):2053–2063
Clara JA, Monge C, Yang Y, Takebe N (2020) Targeting signalling pathways and the immune microenvironment of cancer stem cells—a clinical update. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 17(4):204–232. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-019-0293-2
Su L, Wang S, Yuan T, Xie X, Fu X, Ji P, Zhong L, Liu W (2020) Anti-oral squamous cell carcinoma effects of a potent TAZ inhibitor AR-42. J Cancer 11(2):364–373. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.32436
Li S, Zhang X, Zhang R, Liang Z, Liao W, Du Z, Gao C, Liu F, Fan Y, Hong H (2017) Hippo pathway contributes to cisplatin resistant-induced EMT in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cell Cycle 16(17):1601–1610. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2017.1356508
Ge L, Li DS, Chen F, Feng JD, Li B, Wang TJ (2017) TAZ overexpression is associated with epithelial–mesenchymal transition in cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer cells. Int J Oncol 51(1):307–315. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.3998
Zhao W, Li LW, Tian RF, Dong QF, Li PQ, Yan ZF, Yang X, Huo JL, Fei Z, Zhen HN (2019) Truncated TEAD-binding protein of TAZ inhibits glioma survival through the induction of apoptosis and repression of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biochem 120(10):17337–17344. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28997
Cao D, Zhu GY, Lu Y, Yang A, Chen D, Huang HJ, Peng SX, Chen LW, Li YW (2020) Luteolin suppresses epithelial–mesenchymal transition and migration of triple-negative breast cancer cells by inhibiting YAP/TAZ activity. Biomed Pharmacother 129:110462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110462
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akrida, I., Bravou, V. & Papadaki, H. The deadly cross-talk between Hippo pathway and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cancer. Mol Biol Rep 49, 10065–10076 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07590-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07590-z