Abstract
Background
Hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI) is a major factor affecting the prognosis of liver transplantation through a series of severe cell death and inflammatory responses. However, the potential role of miR-141-3p in hepatic IRI is currently unknown.
Methods
We collected the serum of liver transplantation patients to study the relationship between miR-141-3p and liver injury. A mouse hepatic IRI model was established to measure hepatic dysfunction and cell apoptosis. MiR-141-3p mimic and inhibitor were transfected into hepatocytes to explore the characteristics of hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R), a classical hepatic IRI in vitro model.
Results
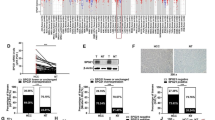
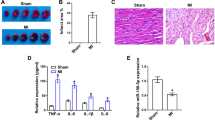
We found that miR-141-3p levels were negatively correlated with alanine aminotransferase (ALT)/aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in liver transplantation patients. The results demonstrated that miR-141-3p was decreased in mouse liver tissue after hepatic IRI in mice and in hepatocytes after H/R. Overexpression of miR-141-3p directly decreased Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) levels and attenuated cell apoptosis in vivo and in vitro, while inhibition of miR-141-3p facilitated apoptosis. Further experiments revealed that overexpression of miR-141-3p also attenuated oxidative stress-induced damage in hepatocytes under H/R conditions.
Conclusions
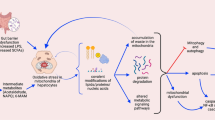
Our results indicate that miR-141-3p plays a major role in hepatic IRI through the Keap1 signaling pathway, and the present study suggests that miR-141-3p might have a protective effect on hepatic IRI to some extent.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhai Y, Petrowsky H, Hong JC, Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski JW (2013) Ischaemia-reperfusion injury in liver transplantation–from bench to bedside. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 10(2):79–89. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2012.225
Gb R, Panisello-Rosello A, Sanchez-Nuno S, Alva N, Rosello-Catafau J, Carbonell T (2021) Nrf2 and oxidative stress in liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. FEBS J. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.16336
Mao XL, Cai Y, Chen YH, Wang Y, Jiang XX, Ye LP, Li SW (2021) Novel targets and therapeutic strategies to protect against hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury. Front Med. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.757336
Shin JK, Kang JW, Lee SM (2016) Enhanced nitric oxide-mediated autophagy contributes to the hepatoprotective effects of ischemic preconditioning during ischemia and reperfusion. Nitric Oxide 58:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2016.05.007
Suyavaran A, Thirunavukkarasu C (2017) Preconditioning methods in the management of hepatic ischemia reperfusion- induced injury: Update on molecular and future perspectives. Hepatol Res 47(1):31–48. https://doi.org/10.1111/hepr.12706
Panda H, Wen H, Suzuki M, Yamamoto M (2022) Multifaceted roles of the KEAP1-NRF2 system in cancer and inflammatory disease milieu. Antioxidants. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11030538
Rojo de la Vega M, Chapman E, Zhang DD (2018) NRF2 and the hallmarks of cancer. Cancer Cell 34(1):21–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.03.022
Tebay LE, Robertson H, Durant ST, Vitale SR, Penning TM, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Hayes JD (2015) Mechanisms of activation of the transcription factor Nrf2 by redox stressors, nutrient cues, and energy status and the pathways through which it attenuates degenerative disease. Free Radic Biol Med 88(Pt B):108–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.021
Ryter SW (2022) Heme oxygenase-1: an anti-inflammatory effector in cardiovascular, lung, and related metabolic disorders. Antioxidants. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11030555
Cavallari I, Ciccarese F, Sharova E, Urso L, Raimondi V, Silic-Benussi M, D’Agostino DM, Ciminale V (2021) The miR-200 family of microRNAs: fine tuners of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and circulating cancer biomarkers. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13235874
Weiss JB, Eisenhardt SU, Stark GB, Bode C, Moser M, Grundmann S (2012) MicroRNAs in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Cardiovasc Dis 2(3):237–247
Fu Z, Wang L, Li S, Chen F, Au-Yeung KK, Shi C (2021) MicroRNA as an important target for anticancer drug development. Front Pharmacol 12:736323. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.736323
Jiang W, Kong L, Ni Q, Lu Y, Ding W, Liu G, Pu L, Tang W, Kong L (2014) miR-146a ameliorates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing IRAK1 and TRAF6. PLoS ONE 9(7):e101530. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101530
Huang Z, Mou T, Luo Y, Pu X, Pu J, Wan L, Gong J, Yang H, Liu Y, Li Z, Shen A, Wu Z (2020) Inhibition of miR-450b-5p ameliorates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury via targeting CRYAB. Cell Death Dis 11(6):455. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2648-0
Yousefi Z, Nourbakhsh M, Abdolvahabi Z, Ghorbanhosseini SS, Hesari Z, Yarahmadi S, Ezzati-Mobasser S, Seiri P, Borji M, Meshkani R, Malek M (2020) microRNA-141 is associated with hepatic steatosis by downregulating the sirtuin1/AMP-activated protein kinase pathway in hepatocytes. J Cell Physiol 235(2):880–890. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29002
Capri M, Olivieri F, Lanzarini C, Remondini D, Borelli V, Lazzarini R, Graciotti L, Albertini MC, Bellavista E, Santoro A, Biondi F, Tagliafico E, Tenedini E, Morsiani C, Pizza G, Vasuri F, D’Errico A, Dazzi A, Pellegrini S, Magenta A, D’Agostino M, Capogrossi MC, Cescon M, Rippo MR, Procopio AD, Franceschi C, Grazi GL (2017) Identification of miR-31-5p, miR-141-3p, miR-200c-3p, and GLT1 as human liver aging markers sensitive to donor-recipient age-mismatch in transplants. Aging Cell 16(2):262–272. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12549
Shi L, Wu L, Chen Z, Yang J, Chen X, Yu F, Zheng F, Lin X (2015) MiR-141 activates Nrf2-dependent antioxidant pathway via down-regulating the expression of keap1 conferring the resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to 5-fluorouracil. Cell Physiol Biochem 35(6):2333–2348. https://doi.org/10.1159/000374036
Huang Z, Zheng D, Pu J, Dai J, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Wu Z (2019) MicroRNA-125b protects liver from ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting TRAF6 and NF-kappaB pathway. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 83(5):829–835. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2019.1569495
Yang W, Chen J, Meng Y, Chen Z, Yang J (2018) Novel targets for treating ischemia-reperfusion injury in the liver. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051302
Babaei K, Shams S, Keymoradzadeh A, Vahidi S, Hamami P, Khaksar R, Norollahi SE, Samadani AA (2020) An insight of microRNAs performance in carcinogenesis and tumorigenesis: an overview of cancer therapy. Life Sci 240:117077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117077
Yuan G, Yu Y, Ji L, Jie X, Yue L, Kang Y, Jianping G, Zuojin L (2016) Down-regulated receptor interacting protein 140 is involved in lipopolysaccharide-preconditioning-induced inactivation of kupffer cells and attenuation of hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury. PLoS ONE 11(10):e0164217. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0164217
Lee ST, Chu K, Jung KH, Yoon HJ, Jeon D, Kang KM, Park KH, Bae EK, Kim M, Lee SK, Roh JK (2010) MicroRNAs induced during ischemic preconditioning. Stroke 41(8):1646–1651. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.579649
Cheng LB, Li KR, Yi N, Li XM, Wang F, Xue B, Pan YS, Yao J, Jiang Q, Wu ZF (2017) miRNA-141 attenuates UV-induced oxidative stress via activating Keap1-Nrf2 signaling in human retinal pigment epithelium cells and retinal ganglion cells. Oncotarget. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14489
Yao B, Wan X, Zheng X, Zhong T, Hu J, Zhou Y, Qin A, Ma Y, Yin D (2020) Critical roles of microRNA-141-3p and CHD8 in hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Cell Biosci 10:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-020-00384-5
Ke B, Shen XD, Zhang Y, Ji H, Gao F, Yue S, Kamo N, Zhai Y, Yamamoto M, Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski JW (2013) KEAP1-NRF2 complex in ischemia-induced hepatocellular damage of mouse liver transplants. J Hepatol 59(6):1200–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2013.07.016
Jayasuriya R, Dhamodharan U, Ali D, Ganesan K, Xu B, Ramkumar KM (2021) Targeting Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway by bioactive natural agents: possible therapeutic strategy to combat liver disease. Phytomedicine 92:153755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153755
Rossi M, Thierry A, Delbauve S, Preyat N, Soares MP, Roumeguere T, Leo O, Flamand V, Le Moine A, Hougardy JM (2017) Specific expression of heme oxygenase-1 by myeloid cells modulates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Sci Rep 7(1):197. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00220-w
Yan XT, Cheng XL, He XH, Zheng WZ, Xiao-Fang Y, Hu C (2019) The HO-1-expressing bone mesenchymal stem cells protects intestine from ischemia and reperfusion injury. BMC Gastroenterol 19(1):124. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-019-1042-9
Liu RR, Li J, Gong JY, Kuang F, Liu JY, Zhang YS, Ma QL, Song CJ, Truax AD, Gao F, Yang K, Jin BQ, Chen LH (2015) MicroRNA-141 regulates the expression level of ICAM-1 on endothelium to decrease myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 309(8):H1303-1313. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00290.2015
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81873592, 81703063); the graduate tutor team construction project of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission Foundation, China (Grant No. dstd201801); and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (Grant No. cstc2018jscx-msybX0133).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81873592, 81703063); the graduate tutor team construction project of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission Foundation, China (Grant No. dstd201801); and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (Grant No. cstc2018jscx-msybX0133).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZW and TL participated in designing the experiments and editing the article. TL, XW and QC participated in the collection of samples. TL, QC, JD, ZH, YL, JP and HY participated in performing the studies. TL, ZH and TM wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Chen, Q., Dai, J. et al. MicroRNA-141-3p attenuates oxidative stress-induced hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury via Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Mol Biol Rep 49, 7575–7585 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07570-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07570-3