Abstract
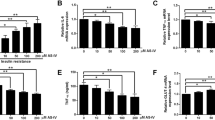
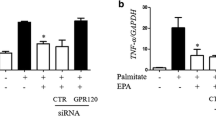
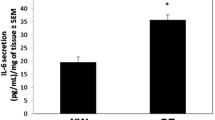
A role of Retinol Binding Protein-4 (RBP4) in insulin resistance is widely studied. However, there is paucity of information on its receptor viz., Stimulated by Retinoic Acid-6 (STRA6) with insulin resistance. To address this, we investigated the regulation of RBP4/STRA6 expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes exposed to glucolipotoxicity (GLT) and in visceral adipose tissue (VAT) from high fat diet (HFD) fed insulin-resistant rats. 3T3-L1 adipocytes were subjected to GLT and other experimental maneuvers with and without vildagliptin or metformin. Real-time PCR and western-blot experiments were performed to analyze RBP4, STRA6, PPARγ gene and protein expression. Adipored staining and glucose uptake assay were performed to evaluate lipid and glucose metabolism. Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and Insulin Tolerance Test (ITT) were performed to determine the extent of insulin resistance in HFD fed male Wistar rats. Total serum RBP4 was measured by quantitative sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit. Adipocytes under GLT exhibited significantly increased RBP4/STRA6 expressions and decreased insulin sensitivity/glucose uptake. Vildagliptin and metformin not only restored the above but also decreased the expression of IL-6, NFκB, SOCS-3 along with lipid accumulation. Furthermore, HFD fed rats exhibited significantly increased serum levels of RBP4 along with VAT expression of RBP4, STRA6, PPARγ, IL-6. These molecules were significantly altered by the vildagliptin/ metformin treatment. We conclude that RBP4/STRA6 pathway is primarily involved in mediating inflammation and insulin resistance in adipocytes and visceral adipose tissues under glucolipotoxicity and in insulin resistant rats.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is available and will be provided on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- RBP4:
-
Retinol Binding Protein-4
- STRA6:
-
Stimulated by retinoic Acid 6
- GLT:
-
Glucolipotoxicity
- VAT:
-
Visceral Adipose Tissue
- NPD:
-
Normal Pellet Diet
- HFD:
-
High Fat Diet
- JAK:
-
Janus Kinase
- STAT:
-
Signal Transducer and activator of Transcription
- PPARα/γ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/gamma
- IBMX:
-
Isobutyl methylxanthine
- cAMP:
-
Cyclic adenosine 3ʹ,5ʹ-cyclic monophosphate
References
Berry DC, Jin H, Majumdar A, Noy N (2011) Signaling by vitamin A and retinol-binding protein regulates gene expression to inhibit insulin responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:4340–4345. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1011115108
Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM et al (2005) Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature 436:356–362. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03711
Berry DC, Jacobs H, Marwarha G, Gely-Pernot A, O’Byrne SM, DeSantis D et al (2013) The STRA6 receptor is essential for retinol-binding protein induced insulin resistance but not for maintaining vitamin a homeostasis in tissues other than the eye. J Biol Chem 288:24528–24539. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.484014
Berry DC, Noy N (2012) Signaling by vitamin A and retinol-binding protein in regulation of insulin responses and lipid homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1821:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.07.002
Alapatt P, Guo F, Komanetsky SM, Wang S, Cai J, Sargsyan A, Rodríguez Díaz E, Bacon BT, Aryal P, Graham TE (2013) Liver retinol transporter and receptor for serum retinol-binding protein (RBP4). J Biol Chem 288:1250–1265. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.369132
Zemany L, Kraus BJ, Norseen J, Saito T, Peroni OD, Johnson RL et al (2014) Downregulation of STRA6 in adipocytes and adipose stromovascular fraction in obesity and effects of adipocyte-specific STRA6 knockdown in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 34:1170–1186. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.01106-13
Muenzner M, Tuvia N, Deutschmann C, Witte N, Tolkachov A, Valai A et al (2013) Retinol-binding protein 4 and its membrane receptor STRA6 control adipogenesis by regulating cellular retinoid homeostasis and retinoic acid receptor activity. Mol Cell Biol 33:4068–4082. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00221-13
Anjana RM, Pradeepa R, Deepa M, Datta M, Sudha V, Unnikrishnan R et al (2011) Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes (impaired fasting glucose and/or impaired glucose tolerance) in urban and rural India: Phase I results of the Indian council of medical research-INdia DIABetes (ICMR-INDIAB) study. Diabetologia 54:3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-011-2291-5
Mohan V, Amutha A, Ranjani H, Unnikrishnan R, Datta M, Anjana RM et al (2013) Associations of β-cell function and insulin resistance with youth-onset type 2 diabetes and prediabetes among Asian Indians. Diabetes Technol Ther 15:315–322. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2012.0259
Staimez LR, Weber MB, Ranjani H, Ali MK, Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, Phillips LS et al (2013) Evidence of reduced β-cell function in Asian Indians with mild dysglycemia. Diabetes Care 36:2772–2778. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc12-2290
Pandey GK, Balasubramanyam J, Balakumar M, Deepa M, Anjana RM, Abhijit S et al (2015) Altered circulating levels of retinol binding protein 4 and transthyretin in relation to insulin resistance, obesity, and glucose intolerance in Asian Indians. Endocr Pract 21:861–869. https://doi.org/10.4158/EP14558.OR
Sozio MS, Lu C, Zeng Y, Liangpunsakul S, Crabb DW (2011) Activated AMPK inhibits PPAR-α and PPAR-γ transcriptional activity in hepatoma cells. Am J Physiol 301:739–747. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00432.2010
Rosell M, Hondares E, Iwamoto S, Gonzalez FJ, Wabitsch M, Staels B et al (2012) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors-α and -γ and cAMP-mediated pathways, control retinol-binding protein-4 gene expression in brown adipose tissue. Endocrinology 153:1162–1173. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2011-1367
Scott MA, Nguyen VT, Levi B, James AW (2011) Current methods of adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 20:1793–1804. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2011.0040
Pandey GK, Vadivel S, Raghavan S, Mohan V, Balasubramanyam M, Gokulakrishnan K (2019) High molecular weight adiponectin reduces glucolipotoxicity-induced inflammation and improves lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity via APPL1-AMPK-GLUT4 regulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Atherosclerosis 288:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.07.011
Lenin R, Maria MS, Agrawal M, Balasubramanyam J, Mohan V, Balasubramanyam M (2012) Amelioration of glucolipotoxicity-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress by a chemical chaperone in human THP-1 monocytes. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:356487. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/356487
Ishii M, Shibata R, Kondo K, Kambara T, Shimizu Y, Tanigawa T et al (2014) Vildagliptin stimulates endothelial cell network formation and ischemia-induced revascularization via an endothelial nitric-oxide synthase-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 289:27235–27245. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.557835
Qin ZY, Zhang M, Dai YM, Wang YM, Zhu GZ, Zhao YP et al (2014) Metformin prevents LYRM1-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via a mitochondrial-dependent mechanism. Exp Biol Med 239:1567–1574. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370214537746
Rajaram N, Frees AE, Fontanella AN, Zhong J, Hansen K, Dewhirst MW et al (2013) Delivery rate affects uptake of a fluorescent glucose analog in murine metastatic breast cancer. PLoS ONE 8:e76524. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076524
Apaijai N, Chinda K, Palee S, Chattipakorn S, Chattipakorn N (2014) Combined vildagliptin and metformin exert better cardioprotection than monotherapy against ischemia-reperfusion injury in obese-insulin resistant rats. PLoS ONE 9:e102374. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0102374
Balakumar M, Raji L, Prabhu D, Sathishkumar C, Prabu P, Mohan V et al (2016) High-fructose diet is as detrimental as high-fat diet in the induction of insulin resistance and diabetes mediated by hepatic/pancreatic endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Mol Cell Biochem 423:93–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2828-5
Graham TE, Yang Q, Blüher M, Hammarstedt A, Ciaraldi TP, Henry RR et al (2006) Retinol-binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in lean, obese, and diabetic subjects. N Engl J Med 354:2552–2563. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-0616
Cheng J, Li Y, Wu G, Zheng J, Lu H, Shi X et al (2014) Ectopic expression of RBP4 impairs the insulin pathway and inguinal fat deposition in mice. J Physiol Biochem 70:479–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0326-3
Wang Y, Sun L, Lin X, Yuan JM, Koh WP, Pan A (2019) Retinol binding protein 4 and risk of type 2 diabetes in Singapore Chinese men and women: a nested case-control study. Nutr Metab 16:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12986-018-0329-0
Kwanbunjan K, Panprathip P, Phosat C, Chumpathat N, Wechjakwen N, Puduang S et al (2018) Association of retinol binding protein 4 and transthyretin with triglyceride levels and insulin resistance in rural thais with high type 2 diabetes risk. BMC Endocr Disord 18:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-018-0254-2
Fan J, Yin S, Lin D, Liu Y, Chen N, Bai X et al (2019) Association of serum retinol-binding protein 4 levels and the risk of incident type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes. Diabetes Care 42:1574–1581. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-0265
Farjo KM, Farjo RA, Halsey S, Moiseyev G, Ma J-X (2012) Retinol-binding protein 4 induces inflammation in human endothelial cells by an NADPH oxidase-and nuclear factor kappa b-dependent and retinol-independent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 32:5103–5115. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00820-12
Norseen J, Hosooka T, Hammarstedt A, Yore MM, Kant S, Aryal P et al (2012) Retinol-binding protein 4 inhibits insulin signaling in adipocytes by inducing proinflammatory cytokines in macrophages through a c-Jun N-terminal kinase- and toll-like receptor 4-dependent and retinol-independent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 32:2010–2019. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.06193-11
Sell H, Eckel J (2012) Regulation of retinol binding protein 4 production in primary human adipocytes by adiponectin, troglitazone and TNF-alpha. Diabetologia 50:2221–2223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-007-0764-3
Chen CH, Hsieh TJ, Der LK, Lin HY, Lee MY, Hung WW et al (2012) Increased unbound retinol-binding protein 4 concentration induces apoptosis through receptor-mediated signaling. J Biol Chem 287:9694–9707. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.301721
Nair AK, Sugunan D, Kumar H, Anilkumar G (2010) Case-control analysis of SNPs in GLUT4, RBP4 and STRA6: association of SNPs in STRA6 with type 2 diabetes in a south indian population. PLoS ONE 5:e11444. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011444
Zhang L, Sun W, Duan X, Duan Y, Sun H (2019) Promoting differentiation and lipid metabolism are the primary effects for DINP exposure on 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Environ Pollut 255:113154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113154
Gumbilai V, Ebihara K, Aizawa-Abe M, Ebihara C, Zhao M, Yamamoto Y et al (2016) Fat mass reduction with adipocyte hypertrophy and insulin resistance in heterozygous PPARγ mutant rats. Diabetes 65:2954–2965. https://doi.org/10.2337/db15-1422
Moraes-Vieira PM, Yore MM, Dwyer PM, Syed I, Aryal P, Kahn BB (2014) RBP4 activates antigen-presenting cells, leading to adipose tissue inflammation and systemic insulin resistance. Cell Metab 19:512–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.01.018
Moraes-Vieira PM, Castoldi A, Aryal P, Wellenstein K, Peroni OD, Kahn BB (2016) Antigen presentation and T-cell activation are critical for RBP4-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 65:1317–1327. https://doi.org/10.2337/db15-1696
Bharath LP, Agrawal M, McCambridge G, Nicholas DA, Hasturk H, Liu J, Jiang K, Liu R, Guo Z, Deeney J, Apovian CM, Snyder-Cappione J, Hawk GS, Fleeman RM, Pihl RMF, Thompson K, Belkina AC, Cui L, Proctor EA, Kern PA, Nikolajczyk BS (2020) Metformin enhances autophagy and normalizes mitochondrial function to alleviate aging-associated inflammation. Cell Metab 32:44-55.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.015
Lazra Y, Falach A, Frenkel L, Rozenberg K, Sampson S, Rosenzweig T (2015) Autocrine/paracrine function of globular adiponectin: inhibition of lipid metabolism and inflammatory response in 3t3-l1 adipocytes. J Cell Biochem 116:754–766. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.25031
Kanuri BN, Kanshana JS, Rebello SC, Pathak P, Gupta AP, Gayen JR et al (2017) Altered glucose and lipid homeostasis in liver and adipose tissue pre-dispose inducible NOS knockout mice to insulin resistance. Sci Rep 7:41009. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41009
Yang R, Wang L, Xie J, Li X, Liu S, Qiu S et al (2018) Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus via reversing insulin resistance and regulating lipid homeostasis in vitro and in vivo using cajanonic acid A. Int J Mol Med 42:2329–2342. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3836
Lee JO, Lee SK, Kim JH, Kim N, You GY, Moon JW et al (2012) Metformin regulates glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) translocation through AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-mediated Cbl/CAP signaling in 3T3-L1 preadipocyte cells. J Biol Chem 287:44121–44129. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.361386
Akarte AS, Srinivasan BP, Gandhi S (2012) Vildagliptin selectively ameliorates GLP-1, GLUT4, SREBP-1c mRNA levels and stimulates β-cell proliferation resulting in improved glucose homeostasis in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Diabetes Complicat 26:266–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2012.03.013
Huang R, Yin S, Ye Y, Chen N, Luo S, Xia M et al (2020) Circulating retinol binding protein 4 is inversely associated with pancreatic β-cell function across the spectrum of glycemia. Diabetes Care 43:1258–1265. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-2432
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge research grant supports received from the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Govt. of India (Grant No. BT/PR4082/MED/30/684/2011) and the Madras Diabetes Research Foundation—Intramural Research Funding (MIRF). Gautam Kumar Pandey acknowledges the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), India for his financial assistance (Senior Research Fellowship). Dr. Kuppan Gokulakrishnan acknowledges the DBT/Wellcome Trust India Alliance for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KG conceptualized the work; KG and GKP designed & executed the study methods, analyzed data, interpreted the results and drafted the manuscript. GKP performed experiments and cell-culture related work. SC helped in confocal microscopy. SS and PD helped in performing animal study. KG, NM, MB, and VM edited the manuscript, critically reviewed and helped in drafting the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests. All authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gokulakrishnan, K., Pandey, G.K., Sathishkumar, C. et al. Augmentation of RBP4/STRA6 signaling leads to insulin resistance and inflammation and the plausible therapeutic role of vildagliptin and metformin. Mol Biol Rep 48, 4093–4106 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06420-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06420-y