Abstract
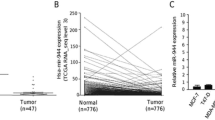
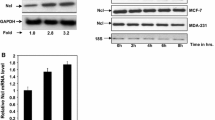
Matrix-metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2) is a foremost MMP, governing invasion of breast cancer cells during metastasis. miR-20a was reported to induce mesenchymal to epithelial transition in MDA-MB-231 cells and its endogenous expression varies directly with invasiveness of breast cancer cells. The inverse and direct correlation of invasiveness with miR-20a and Nucleolin respectively led us to study the post-transcriptional regulation of MMP2 by miR-20a and mRNA stabilizing protein, Nucleolin. Thus, understanding the mechanism of its regulation will enable modification of the invasion potential. MMP2 was found to be higher in MDA-MB-231 than MCF-7 cells both at RNA and protein levels. RNA–protein co-immunoprecipitation assay with Argonaute 2 revealed that MMP2 undergoes miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation. miR-20a decreased MMP2 expression as well as its enzymatic activity as found by zymogram assay. Reporter assay showed that miR-20a directly binds to its putative binding site in MMP2 3′-UTR as per in silico prediction. miR-20a additionally impeded MMP2 mRNA stability, and binding of stabilizing trans-factor Nucleolin to its 3′-UTR was confirmed by RNA–protein co-immunoprecipitation assay. Partial down-regulation of Nucleolin by Si-RNA resulted in the downregulation of MMP2 and Nucleolin over-expression rescued the inhibitory effect of miR-20a on MMP2 expression. Delineating the mechanism of post-transcriptional regulation of MMP2, two of its potent regulators, miR-20a and Nucleolin were identified. It was established for the first time that MMP2 is a direct target of miR-20a. The results also elucidated that Nucleolin binds to MMP2 3′ UTR and its abundance affects MMP2 expression.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the raw data and material used in the published article should be available.
Abbreviations
- MMP2:
-
Matrix-metalloproteinase 2
- miR:
-
MicroRNA
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- Ago2:
-
Argonaute2
- RISC:
-
RNAi induced silencing complex
- Nuc:
-
Nucleolin
- IP:
-
Immunoprecipitate
- TNBC:
-
Triple negative breast cancer
References
Fanjul-Fernández M, Folgueras AR, Cabrera S, López-Otín C (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases: evolution, gene regulation and functional analysis in mouse models. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 1803(1):3–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.07.004
Dong W, Li H, Zhang Y, Yang H, Guo M, Li L, Liu T (2011) Matrix metalloproteinase 2 promotes cell growth and invasion in colorectal cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 43(11):840–848
Webb AH, Gao BT, Goldsmith ZK, Irvine AS, Saleh N, Lee RP, Lendermon JB, Bheemreddy R, Zhang Q, Brennan RC, Johnson D, Steinle JJ, Wilson MW, Morales-Tirado VM (2017) Inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 decreases cellular migration, and angiogenesis in in vitro models of retinoblastoma. BMC Cancer 17(1):434–434. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-017-3418-y
Yu C-F, Chen F-H, Lu M-H, Hong J-H, Chiang C-S (2017) Dual roles of tumour cells-derived matrix metalloproteinase 2 on brain tumour growth and invasion. Br J Cancer 117(12):1828–1836. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2017.362
Kazes I, Il E, Sraer J-D, Hatmi M, Nguyen G (2000) Platelet release of trimolecular complex components MT1-MMP/TIMP2/MMP2: involvement in MMP2 activation and platelet aggregation. Blood 96(9):3064
Chen J-S, Huang X-h, Wang Q, Huang J-Q, Zhang L-j, Chen X-L, Lei J, Cheng Z-X (2013) Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway induces cell migration and invasion through focal adhesion kinase/AKT signaling-mediated activation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in liver cancer. Carcinogenesis 34(1):10–19
Adya R, Tan BK, Punn A, Chen J, Randeva HS (2008) Visfatin induces human endothelial VEGF and MMP-2/9 production via MAPK and PI3K/Akt signalling pathways: novel insights into visfatin-induced angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res 78(2):356–365
Kim Y, Lee Y-S, Choe J, Lee H, Kim Y-M, Jeoung D (2008) CD44-epidermal growth factor receptor interaction mediates hyaluronic acid-promoted cell motility by activating protein kinase c signaling involving Akt, Rac1, Phox, reactive oxygen species, focal adhesion kinase, and MMP-2. J Biol Chem 283(33):22513–22528
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5
Svoronos AA, Engelman DM, Slack FJ (2016) OncomiR or tumor suppressor? The duplicity of MicroRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res 76(13):3666–3670. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-16-0359
Li L, Li H (2013) Role of microRNA-mediated MMP regulation in the treatment and diagnosis of malignant tumors. Cancer Biol Ther 14(9):796–805. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.25936
Wang H, Zhu Y, Zhao M, Wu C, Zhang P, Tang L, Zhang H, Chen X, Yang Y, Liu G (2013) miRNA-29c suppresses lung cancer cell adhesion to extracellular matrix and metastasis by targeting integrin β1 and matrix metalloproteinase2 (MMP2). PLoS ONE 8(8):e70192
Wang Q, Tang H, Yin S, Dong C (2013) Downregulation of microRNA-138 enhances the proliferation, migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells through the upregulation of RhoC/p-ERK/MMP-2/MMP-9. Oncol Rep 29(5):2046–2052
Dai Y, Xia W, Song T, Su X, Li J, Li S, Chen Y, Wang W, Ding H, Liu X, Li H, Zhao Q, Shao N (2013) MicroRNA-200b is overexpressed in endometrial adenocarcinomas and enhances MMP2 activity by downregulating TIMP2 in human endometrial cancer cell line HEC-1A cells. Nucleic ACID Ther 23(1):29–34. https://doi.org/10.1089/nat.2012.0385
Lu L, Xue X, Lan J, Gao Y, Xiong Z, Zhang H, Jiang W, Song W, Zhi Q (2014) MicroRNA-29a upregulates MMP2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma to promote cancer invasion and anti-apoptosis. Biomed Pharmacother 68(1):13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2013.10.005
Mendell JT (2008) miRiad roles for the miR-17-92 cluster in development and disease. Cell 133(2):217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.001
Bray F, McCarron P, Parkin DM (2004) The changing global patterns of female breast cancer incidence and mortality. Breast Cancer Res 6(6):229–239. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr932
Yu Z, Wang C, Wang M, Li Z, Casimiro MC, Liu M, Wu K, Whittle J, Ju X, Hyslop T, McCue P, Pestell RG (2008) A cyclin D1/microRNA 17/20 regulatory feedback loop in control of breast cancer cell proliferation. J Cell Biol 182(3):509–517. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200801079
Kim K, Chadalapaka G, Lee SO, Yamada D, Sastre-Garau X, Defossez PA, Park YY, Lee JS, Safe S (2011) Identification of oncogenic microRNA-17-92/ZBTB4/specificity protein axis in breast cancer. Oncogene 31:1034. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.296
De S, Das S, Mukherjee S, Das S, Sengupta S (2017) Establishment of twist-1 and TGFBR2 as direct targets of microRNA-20a in mesenchymal to epithelial transition of breast cancer cell-line MDA-MB-231. Exp Cell Res 361(1):85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.10.005
Xu T, Jing C, Shi Y, Miao R, Peng L, Kong S, Ma Y, Li L (2015) microRNA-20a enhances the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells by modulating matrix metalloproteinases. Exp Ther Med 10(2):683–688. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2538
Zhao S, Yao D, Chen J, Ding N, Ren F (2015) MiR-20a promotes cervical cancer proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 10(3):e0120905
Van Tubergen EA, Banerjee R, Liu M, Broek RV, Light E, Kuo S, Feinberg SE, Willis AL, Wolf G, Carey T, Bradford C, Prince M, Worden FP, Kirkwood KL, Silva NJ (2013) Inactivation or loss of TTP promotes invasion in head and neck cancer via transcript stabilization and secretion of MMP9, MMP2, and IL-6. Clin Cancer Res 19(5):1169. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-12-2927
Pichiorri F, Palmieri D, De Luca L, Consiglio J, You J, Rocci A, Talabere T, Piovan C, Lagana A, Cascione L, Guan J, Gasparini P, Balatti V, Nuovo G, Coppola V, Hofmeister CC, Marcucci G, Byrd JC, Volinia S, Shapiro CL, Freitas MA, Croce CM (2013) In vivo NCL targeting affects breast cancer aggressiveness through miRNA regulation. J Exp Med 210(5):951–968. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20120950
Jordan M, Schallhorn A, Wurm FM (1996) Transfecting mammalian cells: optimization of critical parameters affecting calcium-phosphate precipitate formation. Nucleic Acids Res 24(4):596–601
Dasgupta P, Bandyopadhyay SS (2013) Role of di-allyl disulfide, a garlic component in NF-κB mediated transient G2-M phase arrest and apoptosis in human leukemic cell-lines. Nutr Cancer 65(4):611–622. https://doi.org/10.1080/01635581.2013.776090
Niranjanakumari S, Lasda E, Brazas R, Garcia-Blanco MA (2002) Reversible cross-linking combined with immunoprecipitation to study RNA–protein interactions in vivo. Methods 26(2):182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1046-2023(02)00021-X
Stamenkovic I (2000) Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol 10(6):415–433. https://doi.org/10.1006/scbi.2000.0379
Bridge KS, Shah KM, Li Y, Foxler DE, Wong SCK, Miller DC, Davidson KM, Foster JG, Rose R, Hodgkinson MR, Ribeiro PS, Aboobaker AA, Yashiro K, Wang X, Graves PR, Plevin MJ, Lagos D, Sharp TV (2017) Argonaute utilization for miRNA silencing is determined by phosphorylation-dependent recruitment of LIM-domain-containing proteins. Cell Rep 20(1):173–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.06.027
Diederichs S, Haber DA (2007) Dual role for argonautes in MicroRNA processing and posttranscriptional regulation of MicroRNA expression. Cell 131(6):1097–1108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.032
Lee P-T, Liao P-C, Chang W-C, Tseng JT (2007) Epidermal growth factor increases the interaction between nucleolin and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K/poly(C) binding protein 1 complex to regulate the gastrin mRNA Turnover. Mol Biol Cell 18(12):5004–5013. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e07-04-0384
Saha S, Chakraborty A, Bandyopadhyay SS (2015) Stabilization of oncostatin-M mRNA by binding of Nucleolin to a GC-Rich element in its 3′UTR. J Cell Biochem 117(4):988–999. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.25384
Kim JH, Jeon S, Shin BA (2017) MicroRNA-29 family suppresses the invasion of HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells by regulating matrix metalloproteinase 2 expression. Chonnam Med J 53(2):161–167. https://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2017.53.2.161
Hu Y, Li Y, Wu C, Zhou L, Han X, Wang Q, Xie X, Zhou Y, Du Z (2017) MicroRNA-140-5p inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by regulating VEGFA/MMP2 signaling in glioma. Tumor Biol 39(4):1010428317697558. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317697558
Hu J, Ni S, Cao Y, Zhang T, Wu T, Yin X, Lang Y, Lu H (2016) The angiogenic effect of microRNA-21 targeting TIMP3 through the regulation of MMP2 and MMP9. PLoS ONE 11(2):e0149537
Ghisolfi-Nieto L, Joseph G, Puvion-Dutilleul F, Amalric F, Bouvet P (1996) Nucleolin is a sequence-specific RNA-binding protein: characterization of targets on pre-ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol 260(1):34–53
Otake Y, Soundararajan S, Sengupta TK, Kio EA, Smith JC, Pineda-Roman M, Stuart RK, Spicer EK, Fernandes DJ (2007) Overexpression of nucleolin in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induces stabilization of bcl2 mRNA. Blood 109(7):3069–3075. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-08-043257
Abdelmohsen K, Tominaga K, Lee EK, Srikantan S, Kang M-J, Kim MM, Selimyan R, Martindale JL, Yang X, Carrier F, Zhan M, Becker KG, Gorospe M (2011) Enhanced translation by Nucleolin via G-rich elements in coding and non-coding regions of target mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 39(19):8513–8530. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr488
Fähling M, Steege A, Perlewitz A, Nafz B, Mrowka R, Persson PB, Thiele BJ (2005) Role of nucleolin in posttranscriptional control of MMP-9 expression. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 1731(1):32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbaexp.2005.08.005
Yang Y, Yang C, Zhang J (2015) C23 protein meditates bone morphogenetic protein-2-mediated EMT via up-regulation of Erk1/2 and Akt in gastric cancer. Med Oncol 32(3):76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0547-5
Hsu TI, Lin SC, Lu PS, Chang WC, Hung CY, Yeh YM, Su WC, Liao PC, Hung JJ (2014) MMP7-mediated cleavage of nucleolin at Asp255 induces MMP9 expression to promote tumor malignancy. Oncogene 34:826. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.22
Wolfson E, Solomon S, Schmukler E, Goldshmit Y, Pinkas-Kramarski R (2018) Nucleolin and ErbB2 inhibition reduces tumorigenicity of ErbB2-positive breast cancer. Cell Death Dis 9(2):47. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0067-7
Hovanessian AG, Puvion-Dutilleul F, Nisole S, Svab J, Perret E, Deng J-S, Krust B (2000) The cell-surface-expressed nucleolin is associated with the actin cytoskeleton. Exp Cell Res 261(2):312–328. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.2000.5071
Berger CM, Gaume X, Bouvet P (2015) The roles of nucleolin subcellular localization in cancer. Biochimie 113:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2015.03.023
Jia W, Yao Z, Zhao J, Guan Q, Gao L (2017) New perspectives of physiological and pathological functions of nucleolin (NCL). Life Sci 186:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.07.025
Zaidi SHE, Malter JS (1995) Nucleolin and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C proteins specifically interact with the 3′-untranslated region of amyloid protein precursor mRNA. J Biol Chem 270(29):17292–17298. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.29.17292
Chen C-Y, Gherzi R, Andersen JS, Gaietta G, Jürchott K, Royer H-D, Mann M, Karin M (2000) Nucleolin and YB-1 are required for JNK-mediated interleukin-2 mRNA stabilization during T-cell activation. Genes Dev 14(10):1236–1248. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.14.10.1236
Sengupta TK, Bandyopadhyay S, Fernandes DJ, Spicer EK (2004) Identification of nucleolin as an AU-rich element binding protein involved in bcl-2 mRNA stabilization. J Biol Chem 279(12):10855–10863. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M309111200
Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M (2012) RNA-binding protein nucleolin in disease. RNA Biol 9(6):799–808. https://doi.org/10.4161/rna.19718
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Prof. Tapas K. Sengupta (IISER, Kolkata, India) for pc-Nuc plasmid. We like to acknowledge the instrumental facilities funded by DST-FIST and UGC-CAS to the Department of Biophysics, Molecular Biology and Bioinformatics, University of Calcutta. This work was supported by fund from University Grants Commission, India [UGCF.5-1/2015/CAS-I (SAP-II)]. We acknowledge CSIR for providing the fellowship to S Das and S De.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S Das performed most of the experiments, statistical analysis and wrote the manuscript. S De performed some of the experiments. SS conceived the idea, wrote and corrected the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, S., De, S. & Sengupta, S. Post-transcriptional regulation of MMP2 mRNA by its interaction with miR-20a and Nucleolin in breast cancer cell lines. Mol Biol Rep 48, 2315–2324 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06261-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06261-9