Abstract
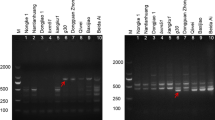
Wheat stem rust, caused by Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici (Pgt), is a fungus that causes the devastating fungalwheat stem rust disease in wheat production. Rapid identification of the physiological races of Pgt are very importance for the prevention of wheat stem rust. In this paper we developed a molecular method to identify the most prevalent race of Pgt, as a supplement for traditionally used host-specific methods. Amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) was employed as a means of analyzing DNA polymorphisms in six common physiological races of Pgt in China and Ug99. In total, 64 pairs of primers were used for AFLP screening of race-specific molecular markers. One primer pair-namely, E7/M7 (5′-GACTGCGTACCAATTCG G-3′/5′-GATGAGTCCTGAGTAACGG-3′)-yielded a unique band for the race 34MKG that was purified and cloned into the pGEM-T vector for sequencing. We then designed a new primer pairs (sequence—characterized amplified region marker) to amplify the 171-bp fragment and confirmed that the marker was highly specific for 34MKG. These results provide a new tool for monitoring different races of Pgt for improved control of wheat stem rust in China.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dolye JJ, Dolye JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from freshtissue. Focus 12:13–15
Janet R Wheat warning–new rust could spread like wildfire [EB/OL] Science News Online. [20052092247]. http://www.sciencenews.org/articles/food.asp
Singh RP, Hodson DP, Huerta-Espino J, Jin Y, Bhavani S, Njau P, Herrera-Foessel S, Singh PK, Singh S, Govindan V (2011) The emergence of Ug99 races of the stem rust fungus is a threat to world wheat production. Ann Rev Phytopathol 49:465–481
Chen XM, Line RF, Leung H (1993) Relationship between virulence variation and DNA polymorphism in Puccinia striiformis. Phytopathology 83:1489–1497
Chen XM, Line RF, Leung H (1995) Virulence and polymorphic DNA relationships of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. hordei to other rusts. Phytopathology 85:1335–1342
McCallum BD, Roelfs AP, Szabo LJ, Groth JV (1999) Comparison of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici from South America and Europe. Plant Pathol 48:574–581
Zambino PJ, Szabo LJ (1993) Phylogenetic relationships of selected cereal and grass rusts based on rDNA sequence analysis. Mycologia 85:401–414
Keiper FJ, Hayden MJ, Park RF, Wellings CR (2003) Molecular genetic variability of Australian isolates of five cereal rust pathogens. Mycolog Res 107:545–556
Kolmer JA, Liu JQ, Sies M (1995) irulence and molecular polymorphism in Puccinia recondita f. sp. tritici in Canada. Phytopathology 85:276–285
Kolmer JA, Liu JQ (2000) Virulence and molecular polymorphism in international collections of the wheat leaf rust fungus Puccinia triticina. Phytopathology 90:427–436
Liu TG, Wang X, Gao L, Liu B, Chen WQ (2014) A FIASCO–based approach for detection and diagnosis of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici in China. J Integr Agric 13:2438–2444
Szabo LJ (2007) Development of simple sequence repeat markers for the plant pathogenic rust fungus, Puccinia graminis. Mol Ecol Notes 7:92–94
Szabo LJ, Kolmer JA (2007) Development of simple sequence repeat markers for the plant pathogenic rust fungus Puccinia triticina. Mol Ecol Notes 7:708–710
Wang X, Liu TG, Xiang WS, Chen WQ (2011) Development of a SSR molecular marker for Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. Sci Agric Sin 44:4593–4599
Cao LH, Xu SC, Lin RM, Liu TG, Chen WQ (2008) Early molecular diagnosis and detection of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in China. Lett Appl Microbiol 46:501–506
Hao BJ, Wang BT, Li Q, Li GB, Wang F, Zhang B (2010) Aanalysis and SCAR marker establishment of Su11 group of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in China. Acta Phytopathol Sin 40:1–6
Wang BT, Hu XP, Li Q, Hao BJ, Zhang B, Li GB, Kang ZS (2010) Development of race–specific SCAR markers for detection of Chinese races CYR32 and CYR33 of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Plant Dis 94:221–228
Chen S, Cao YY, Li TY, Wu XX (2015) Simultaneous detection of three wheat pathogenic fungal species by multiplex PCR. Phytoparasitica 43:449–460
Chen S, Cao YY, Li TY (2015) Development of a specific SCAR marker to race 21C3CTH of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici in China. Int J Agric Biol 17:1200–1206
Chen S, Wu JZ, Huang WG, Wu GW, Li TY, Cao YY (2016) SSR markers screening of the races 21C3CPH and Ug99 of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. Mycosystema 12:1526–1534
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van der Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nuc Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Schmidt H, Ehrmann M, Vogela RF, Taniwakib MH, Niessena L (2003) Molecular typing of Aspergillus ohraceus and construction of species specific SCAR Primers based on AFLP. Syst Appl Microbiol 26:138–146
Paran I, Michelmore RW (1993) Development of reliable PCR–based markers linked to downy mildew resistance genes in lettuce. Theor Appl Genet 85:985–993
Zambino PJ, Kubelik AR, Szabo LJ (2000) Gene action and linkage of avirulence genes to DNA markers in the rust fungus Puccinia graminis. Phytopathology 90:819–826
Pu ZG (2004) Development of a molecular detection assay for the physiological race MFR of Puccinia triticina. Acta Phytopathol Sin 34:449–454
Cao YY, Cao YY, Si BB, Zhu GQ, Xu XF, Li WH, Chen S, Zhao J, Li TY (2019) Races and virulence of asexual and sexual populations of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici in China from 2009 to 2015. Eur J Plant Pathol 153:545–555
Yao P, Cao YY, Liu WZ, Wu YS (1997) Race population trend of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici in 1990–1994 in China. Acta Phytophyl Sin 24:297–302
Han JD, Cao YY, Sun ZG (2010) Race dynamics of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici in China and the virulence of CIMMYT wheat germplasm resistant to Ug99. J Triti Crops 30:163–166
Cao YY, Chen WQ (2010) Stepwise shift of differential hosts and racial designation of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. J Triti Crops 30:167–172
Roelfs AP, Martens JW (1988) An international system of nomenclature for Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. Phytopathology 78:526–533
Sun ZG, Cao YY, Han JD, Chen WS (2010) Comparison of diferent methods for extraction of DNA of wheat stem rust urediospores. Hubei Agric Sci 49:1281–1284
Aldrich J, Cullis CA (1993) RAPD analysis in flax: Optimization of yield and reproducibility using Klen Taq1DNA polymerase, chelexl 100, and gel purification of genomic DNA. Plant Mol Biol Rep 11:128–141
Qi XL, Li B, Song S, Chen X, Peng M (2011) A Kind of simple and efficient DNA recovery method from polyacrylamide gel. Chin Ari Sci Bull 27:214–217
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rdedition. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Stakman EC, Premeisel J (1917) A new strain of Puccinia graminis. Phytopathology 7:73
Jin Y, Szabo LJ, Rouse MN, Fetch T Jr, Pretorius Wanyera R, Njau P (2009) Detection of virulence to resistance gene Sr36 within the TTKS race lineage of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. Plant Dis 93:367–370
Tu C (1934) Physiologic forms of Puccinia graminis tritici in Kwangtung, Southern China. Phytopathology 24:423
Wu YS, Huang ZT (1987) Racial identification and dynamics analysis of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici for past 20 years in China. J Shenyang Agric Univ 18:105–138
Yao P, Cao YY, Wu YS (1993) Race identification of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici in China in 1990. J Plant Protect 20:65–70
Funding
This study was supported by the Heilongjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences Doctoral Research start-up fund, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31701738), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31471546) and Harbin science and technology bureau planning project (2016AE6AE001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Yang, X., Huang, Wg. et al. Development of a specific AFLP-based SCAR marker for Chinese Race 34MKG of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. Mol Biol Rep 47, 4303–4309 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05513-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05513-4